4th Quarter test
... Which of the following is not a reason to classify organisms? a. To make it easier to identify unknown organisms b. To show relationships among organisms c. To organize information about different types of organisms d. To provide organisms with Latin names ...
... Which of the following is not a reason to classify organisms? a. To make it easier to identify unknown organisms b. To show relationships among organisms c. To organize information about different types of organisms d. To provide organisms with Latin names ...
Greedy Algorithms
... At each of the following t-2 iterations, finds a “best” l-mer in sequence i from the perspective of the already constructed (i-1) x l alignment matrix for the first (i-1) sequences In other words, it finds an l-mer in sequence i maximizing Score(s,i,DNA) ...
... At each of the following t-2 iterations, finds a “best” l-mer in sequence i from the perspective of the already constructed (i-1) x l alignment matrix for the first (i-1) sequences In other words, it finds an l-mer in sequence i maximizing Score(s,i,DNA) ...
4th Quarter test A
... #25 Pieces of DNA from one kind of organism that contains DNA from another kind of organism is called ______. a. b. c. d. ...
... #25 Pieces of DNA from one kind of organism that contains DNA from another kind of organism is called ______. a. b. c. d. ...
Organization of DNA replication origins in the fission yeast genome
... cerevisiae because they are easy to isolate in plasmids as autonomous replication sequences (ARSs). The presence of a consensus sequence 11 bp long has allowed the isolation of an origin recognition complex (ORC) that binds to it throughout the cell cycle (Bell and Stillman, 1992; Diffley et al., 19 ...
... cerevisiae because they are easy to isolate in plasmids as autonomous replication sequences (ARSs). The presence of a consensus sequence 11 bp long has allowed the isolation of an origin recognition complex (ORC) that binds to it throughout the cell cycle (Bell and Stillman, 1992; Diffley et al., 19 ...
ppt_I
... Human genome: Current status • 22,287 'gene loci‘ defined, consisting of 19,599 protein-coding genes in the human genome and 2,188 DNA additional segments ‘predicted’ to be protein-coding genes – 1183 genes ‘were born’ in the last 60-100 My – ~ 30 genes ‘died’ in a similar time period ...
... Human genome: Current status • 22,287 'gene loci‘ defined, consisting of 19,599 protein-coding genes in the human genome and 2,188 DNA additional segments ‘predicted’ to be protein-coding genes – 1183 genes ‘were born’ in the last 60-100 My – ~ 30 genes ‘died’ in a similar time period ...
The Close Relationship Between the A and B Genomes in Avena L
... satellited. Thus, this set of chromosomes was designated as B genome (Rajhathy and Morrison, 1959). Although four different genomes (A, B, C, and D) have been designated to Aena species, two of them are present in the diploid level (A and C), three at the tetraploid level (AB and AC), and three at ...
... satellited. Thus, this set of chromosomes was designated as B genome (Rajhathy and Morrison, 1959). Although four different genomes (A, B, C, and D) have been designated to Aena species, two of them are present in the diploid level (A and C), three at the tetraploid level (AB and AC), and three at ...
BLAST_and_Genome_Browser_tutorial
... Genome browser is a dynamic graphical display of several features identified from rice as well as from maize, sorghum, barley and wheat that were mapped on the rice genome. Some of these features are sequenced genetic markers, ESTs, cDNAs, CDSs, genes, insertion and repeat elements. The browser is a ...
... Genome browser is a dynamic graphical display of several features identified from rice as well as from maize, sorghum, barley and wheat that were mapped on the rice genome. Some of these features are sequenced genetic markers, ESTs, cDNAs, CDSs, genes, insertion and repeat elements. The browser is a ...
Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers
... • Demethylation at the 5’ end of the gene and the promoter region is necessary for transcription. • CpG islands surround the promoters of constitutively expressed genes where they are unmethylated. • They are also found at the promoters of some tissue-regulated genes. • There are ~29,000 CpG islands ...
... • Demethylation at the 5’ end of the gene and the promoter region is necessary for transcription. • CpG islands surround the promoters of constitutively expressed genes where they are unmethylated. • They are also found at the promoters of some tissue-regulated genes. • There are ~29,000 CpG islands ...
Development of a codominant PCR-based marker for the wheat Wx
... upstream of the Waxy gene is annotated as repetitive sequence, except for an 1828 bp region, which is annotated as coding for a hypothetical protein. However, it appears that this protein is not expressed, since BLAST searches did not identify cereal EST sequences with homology to this putative gene ...
... upstream of the Waxy gene is annotated as repetitive sequence, except for an 1828 bp region, which is annotated as coding for a hypothetical protein. However, it appears that this protein is not expressed, since BLAST searches did not identify cereal EST sequences with homology to this putative gene ...
Identification of the Minus-Dominance Gene Ortholog in
... of gamete RNA. Total RNA was isolated with the RNeasy Midi kit (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany; protocol for heart, muscle, and skin tissue) after the cells had been homogenized with ceramic beads and a wash brush (Nozaki et al. 1997, 2006). Full-length cDNA synthesis from the total RNA was carried out wit ...
... of gamete RNA. Total RNA was isolated with the RNeasy Midi kit (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany; protocol for heart, muscle, and skin tissue) after the cells had been homogenized with ceramic beads and a wash brush (Nozaki et al. 1997, 2006). Full-length cDNA synthesis from the total RNA was carried out wit ...
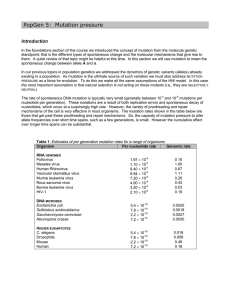
Genetic engineering compared to natural genetic variations
... splices DNA segments together at relatively short specific or consensus sequences, the underlying enzymes can very occasionally also use one of a large number of different secondary crossover sites. These latter, quite rare activities are a good source of evolutionally relevant fusions of different ...
... splices DNA segments together at relatively short specific or consensus sequences, the underlying enzymes can very occasionally also use one of a large number of different secondary crossover sites. These latter, quite rare activities are a good source of evolutionally relevant fusions of different ...
Species tree
... because the methodology results in a degree of disconnection between the underlying genetic data and the final tree produced. Bininda-Emonds et al. 2002 ...
... because the methodology results in a degree of disconnection between the underlying genetic data and the final tree produced. Bininda-Emonds et al. 2002 ...
Inheritance of Organelle DNA Sequences in a Citrus–Poncirus
... shown). Because paternal parents of openpollination progeny are unknown, a specific model for segregation of the P. trifoliata atpA configuration could not be tested. However, the segregation of both ...
... shown). Because paternal parents of openpollination progeny are unknown, a specific model for segregation of the P. trifoliata atpA configuration could not be tested. However, the segregation of both ...
COMPUTATIONAL BIOLOGY
... Database entries corresponding to bacterial genes are relatively easy to read and understand. Their genome is a single, circular DNA molecule in the order of a few million base pairs. Their gene density, i.e., the number of genes per base pairs in the genome, is approximately one gene per 1,000 base ...
... Database entries corresponding to bacterial genes are relatively easy to read and understand. Their genome is a single, circular DNA molecule in the order of a few million base pairs. Their gene density, i.e., the number of genes per base pairs in the genome, is approximately one gene per 1,000 base ...
1 A CAPS marker, FER-G8, for detection of Ty3 and Ty3a alleles
... begomovirus resistance genes. Zamir et al. (1994) used LA1969 as a source of Ty-1 gene in chromosome 6 (ca. 8 cM). LA1969 was also the source of resistance against Tomato yellow leaf curl virus (TYLCV) for new lines developed in Cuba (Piňón et al., 2005). Scott and his team (Agrama and Scott, 2006; ...
... begomovirus resistance genes. Zamir et al. (1994) used LA1969 as a source of Ty-1 gene in chromosome 6 (ca. 8 cM). LA1969 was also the source of resistance against Tomato yellow leaf curl virus (TYLCV) for new lines developed in Cuba (Piňón et al., 2005). Scott and his team (Agrama and Scott, 2006; ...
Deletion of Exon 4 in the N-Acetylgalactosamine-4 - J
... N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase (ARSB), one of the enzymes required for the degradation of dermatan sulfate (DS). Accumulation of DS in connective tissue causes growth failure, resulting in short stature. Here, we observed a 5-year-old girl who was the only one affected member of her family and wh ...
... N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase (ARSB), one of the enzymes required for the degradation of dermatan sulfate (DS). Accumulation of DS in connective tissue causes growth failure, resulting in short stature. Here, we observed a 5-year-old girl who was the only one affected member of her family and wh ...
- Wiley Online Library
... CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) was coined [2]. Several years later, in silico analysis showed that portions of these sequences mapped to viral and phage genomes, suggesting a role in host genome defense, and, by 2007, functional studies had validated this hypothes ...
... CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) was coined [2]. Several years later, in silico analysis showed that portions of these sequences mapped to viral and phage genomes, suggesting a role in host genome defense, and, by 2007, functional studies had validated this hypothes ...
Slide 1
... • add one or more extra nucleotides into the DNA – usually caused by transposable elements – or errors during replication of repeating elements (e.g. AT repeats) • in the non/coding region of a gene may alter: – splicing of the mRNA (splice site mutation) – or cause a shift in the reading frame (fra ...
... • add one or more extra nucleotides into the DNA – usually caused by transposable elements – or errors during replication of repeating elements (e.g. AT repeats) • in the non/coding region of a gene may alter: – splicing of the mRNA (splice site mutation) – or cause a shift in the reading frame (fra ...
Construction of a set of convenient saccharomyces cerevisiae
... follows: (1) 5 pg of plasmid pMRFW2 was digested with BamHI and SmaI; (2) the BamHISmaI fragment that contains ura3-52 was used to transform strain S288C; (3) after the final step in the transformation procedure (the incubation in PEG), the cells were pelleted, resuspended in 5 ml of YPD, and grown ...
... follows: (1) 5 pg of plasmid pMRFW2 was digested with BamHI and SmaI; (2) the BamHISmaI fragment that contains ura3-52 was used to transform strain S288C; (3) after the final step in the transformation procedure (the incubation in PEG), the cells were pelleted, resuspended in 5 ml of YPD, and grown ...
preparation - Discover the Microbes Within!
... controls and/or + control DNA samples. As in the previous lab, students should work in groups of two. In this activity we will not only seek to amplify the possible Wolbachia DNA but we will also be amplifying a portion of Eukaryotic DNA. This second amplification is, in effect, a procedural control ...
... controls and/or + control DNA samples. As in the previous lab, students should work in groups of two. In this activity we will not only seek to amplify the possible Wolbachia DNA but we will also be amplifying a portion of Eukaryotic DNA. This second amplification is, in effect, a procedural control ...
Document
... Plus strand, Minus strand, Sense Strand, Anti-sense strand. Transcription For a given gene, only one strand of the DNA serves as the template for transcription. An example is shown below. The bottom (blue) strand in this example is the template strand, which is also called the minus (-) strand,or t ...
... Plus strand, Minus strand, Sense Strand, Anti-sense strand. Transcription For a given gene, only one strand of the DNA serves as the template for transcription. An example is shown below. The bottom (blue) strand in this example is the template strand, which is also called the minus (-) strand,or t ...
Frontiers in Zoology
... Phylogenetic and phenetic analyses (Bayesian and Neighbor-joining) of these and many additional sequences (to be published elsewhere) mostly grouped sequences of those specimens from Ranomafana and Andasibe that a priori had been considered to be conspecific (exceptions were Mantidactylus boulengeri ...
... Phylogenetic and phenetic analyses (Bayesian and Neighbor-joining) of these and many additional sequences (to be published elsewhere) mostly grouped sequences of those specimens from Ranomafana and Andasibe that a priori had been considered to be conspecific (exceptions were Mantidactylus boulengeri ...
sequence DNA - DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska
... microelectronics industry have been key in developing the precise micro arrays of ssDNA ‘blots’ (Chee et al 1996). Recently, the processing has further improved the massively parallel processing of over 5000 spots (i.e. ssDNA probes) on a DNA chip using complete robotic automation (Yoon et al 2000). ...
... microelectronics industry have been key in developing the precise micro arrays of ssDNA ‘blots’ (Chee et al 1996). Recently, the processing has further improved the massively parallel processing of over 5000 spots (i.e. ssDNA probes) on a DNA chip using complete robotic automation (Yoon et al 2000). ...