DNA-dependent protein kinase in nonhomologous end joining: a
... in a manner that facilitates end joining. In contrast, the 2056 cluster (Fig. 3) has been reported to inhibit DNA end processing upon phosphorylation, suggesting that the 2609 and 2056 clusters work in an opposite direction (Cui et al., 2005). The latter finding has at present not been confirmed, an ...
... in a manner that facilitates end joining. In contrast, the 2056 cluster (Fig. 3) has been reported to inhibit DNA end processing upon phosphorylation, suggesting that the 2609 and 2056 clusters work in an opposite direction (Cui et al., 2005). The latter finding has at present not been confirmed, an ...
STRAND1 - Bulletin - Sigma
... G. Phosphorylation Using T4 Polynucleotide Kinase A convenient method for phosphorylating previously synthesized oligonucleotides is treatment with T4 polynucleotide kinase. Typically, 60-80% of a purified primer is phosphorylated under conditions described below. With unpurified primers, the extent ...
... G. Phosphorylation Using T4 Polynucleotide Kinase A convenient method for phosphorylating previously synthesized oligonucleotides is treatment with T4 polynucleotide kinase. Typically, 60-80% of a purified primer is phosphorylated under conditions described below. With unpurified primers, the extent ...
An active foamy virus integrase is required for virus replication
... Foamy viruses (FVs) make use of a replication strategy which is unique among retroviruses and shows analogies to hepadnaviruses. The presence of an integrase (IN) and obligate provirus integration distinguish retroviruses from hepadnaviruses. To clarify whether a functional IN is required for FV rep ...
... Foamy viruses (FVs) make use of a replication strategy which is unique among retroviruses and shows analogies to hepadnaviruses. The presence of an integrase (IN) and obligate provirus integration distinguish retroviruses from hepadnaviruses. To clarify whether a functional IN is required for FV rep ...
Forensics SH - Willmar Public Schools
... hypothesis, design and conduct an experiment to test the hypothesis, analyze the data, consider alternative explanations and draw conclusions supported by evidence from the investigation. Evaluate the explanations proposed by others by examining and comparing evidence, identifying faulty reasoning, ...
... hypothesis, design and conduct an experiment to test the hypothesis, analyze the data, consider alternative explanations and draw conclusions supported by evidence from the investigation. Evaluate the explanations proposed by others by examining and comparing evidence, identifying faulty reasoning, ...
Depth-stratified functional and taxonomic niche
... to increase cyanophage fitness (Bragg and Chisholm, 2008), and commonly constitutes a large fraction of total psbA genes in marine microbial metagenomes (Sharon et al., 2007). Beyond elevating cyanophage fitness, these viral psbA gene copies alter the evolutionary trajectory of globally distributed ...
... to increase cyanophage fitness (Bragg and Chisholm, 2008), and commonly constitutes a large fraction of total psbA genes in marine microbial metagenomes (Sharon et al., 2007). Beyond elevating cyanophage fitness, these viral psbA gene copies alter the evolutionary trajectory of globally distributed ...
Life: The Science of Biology, 10e
... Promoters bind and orient RNA polymerase so that the correct DNA strand is transcribed. All promoters have consensus sequences that allow them to be recognized by RNA polymerase. Different classes of consensus sequences are recognized by regulatory proteins called sigma factors. ...
... Promoters bind and orient RNA polymerase so that the correct DNA strand is transcribed. All promoters have consensus sequences that allow them to be recognized by RNA polymerase. Different classes of consensus sequences are recognized by regulatory proteins called sigma factors. ...
LacI_Biochem.ppt
... Binding of regulators to DNA is often at inverted repeats Binding sites have inverted repeats Regulator proteins bind as back-to-back dimer. This puts each binding domain in the right orientation with respect to the inverted repeat ...
... Binding of regulators to DNA is often at inverted repeats Binding sites have inverted repeats Regulator proteins bind as back-to-back dimer. This puts each binding domain in the right orientation with respect to the inverted repeat ...
Gene Section STAT5B (signal transducer and activator of transcription 5B)
... domain, and the carboxy-terminal transactivation domain. STATs remain latent in the cytoplasm until the binding of a cytokine or growth factor to its receptor, resulting in recruitment of the STAT to the ligand receptor complex (Levy and Darnell, 2002; Herrington et al., 1999; Heim et al., 1995). Th ...
... domain, and the carboxy-terminal transactivation domain. STATs remain latent in the cytoplasm until the binding of a cytokine or growth factor to its receptor, resulting in recruitment of the STAT to the ligand receptor complex (Levy and Darnell, 2002; Herrington et al., 1999; Heim et al., 1995). Th ...
A novel gene encoding a 54 kDa polypeptide is
... samples collected from oilfields. Three of them have been identified as Rhodococcus sp. IMT35, Pseudomonas sp. IMT37 and Pseudomonas sp. IMT40. SDS-PAGE analysis of the membrane of Rhodococcus sp. IMT35 revealed the presence of at least four polypeptides induced by propane. Polyclonal antibody raise ...
... samples collected from oilfields. Three of them have been identified as Rhodococcus sp. IMT35, Pseudomonas sp. IMT37 and Pseudomonas sp. IMT40. SDS-PAGE analysis of the membrane of Rhodococcus sp. IMT35 revealed the presence of at least four polypeptides induced by propane. Polyclonal antibody raise ...
A homologue of the breast cancer associated gene BARD1 is
... insertions could be identified. The insertion sites were determined in detail by PCR. Figure 4 provides a detailed characterisation of the T-DNA insertions of AtBARD1. The two atbard1 T-DNA insertions are located at the beginning of the gene. Both insertions carry left T-DNA borders at their ends, i ...
... insertions could be identified. The insertion sites were determined in detail by PCR. Figure 4 provides a detailed characterisation of the T-DNA insertions of AtBARD1. The two atbard1 T-DNA insertions are located at the beginning of the gene. Both insertions carry left T-DNA borders at their ends, i ...
Germ Line Transmission and Expression of a Corrected HPRT Gene
... In this clone, the exon 3-containing 1.3 kb EcoRl band has the same intensity as in the E14TG2a lane, indicating that exon 3 is not duplicated. In addition, the intensity of the 14.0 kb BamHl band is lower than in type 1 correctants, although the size of the band is not visibly different at this res ...
... In this clone, the exon 3-containing 1.3 kb EcoRl band has the same intensity as in the E14TG2a lane, indicating that exon 3 is not duplicated. In addition, the intensity of the 14.0 kb BamHl band is lower than in type 1 correctants, although the size of the band is not visibly different at this res ...
Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 Å
... Recombination, replication, mitotic condensation and transcription involve the chromatin substrate and are thus affected by its structure. The generally repressive nature of chromatin structure has long been appreciated in transcription regulation (10). Chromatin organization can facilitate the acti ...
... Recombination, replication, mitotic condensation and transcription involve the chromatin substrate and are thus affected by its structure. The generally repressive nature of chromatin structure has long been appreciated in transcription regulation (10). Chromatin organization can facilitate the acti ...
Functional Analysis of the Genes of Yeast Chromosome V by Genetic Footprinting.
... genomes of several microorganisms is a watershed for the new science of genomics. The next important challenge is to determine, in an efficient and reliable way, something about the function of each gene in these genomes. The 12,057-kb nonrepetitive portion of the S. cerevisiae genome—the first comp ...
... genomes of several microorganisms is a watershed for the new science of genomics. The next important challenge is to determine, in an efficient and reliable way, something about the function of each gene in these genomes. The 12,057-kb nonrepetitive portion of the S. cerevisiae genome—the first comp ...
DNA comparison ?`s
... 5. If the amino-acid sequences in gorillas and humans are similar, are the nucleotide sequences of their DNA also similar? EXPLAIN YOUR ANSWER ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 6. Accordin ...
... 5. If the amino-acid sequences in gorillas and humans are similar, are the nucleotide sequences of their DNA also similar? EXPLAIN YOUR ANSWER ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 6. Accordin ...
Nucleic Acids - UCR Chemistry - University of California, Riverside
... for A, and for T (or U) in nucleosides are also the most favorable tautomers of the free bases in aqueous solution, but G has two relatively favorable tautomers (Figure 23.21) [previous page]. Structure 1G is the form found in nucleic acids since G bonds to the anomeric carbon of ribose or deoxyribo ...
... for A, and for T (or U) in nucleosides are also the most favorable tautomers of the free bases in aqueous solution, but G has two relatively favorable tautomers (Figure 23.21) [previous page]. Structure 1G is the form found in nucleic acids since G bonds to the anomeric carbon of ribose or deoxyribo ...
13.3 Mutations
... – Now and then cells make mistakes in copying their own DNA, inserting the wrong base or even skipping a base as a strand is put together. – These variations are called mutations, from the Latin word mutare, meaning “to change.” – Mutations are heritable changes in genetic information. – All mutatio ...
... – Now and then cells make mistakes in copying their own DNA, inserting the wrong base or even skipping a base as a strand is put together. – These variations are called mutations, from the Latin word mutare, meaning “to change.” – Mutations are heritable changes in genetic information. – All mutatio ...
Huntingtin grabs a hammer: DNA repair in HD
... Huntingtin headlamps and the ATM foreman Truant’s team, helmed by postdoctoral researcher Tam Maiuri, used an innovative method to pursue their hypothesis, using molecules called “chromobodies.” These can attach to specific protein targets and emit fluorescent light, illuminating working proteins th ...
... Huntingtin headlamps and the ATM foreman Truant’s team, helmed by postdoctoral researcher Tam Maiuri, used an innovative method to pursue their hypothesis, using molecules called “chromobodies.” These can attach to specific protein targets and emit fluorescent light, illuminating working proteins th ...
13.3 Mutations
... – Now and then cells make mistakes in copying their own DNA, inserting the wrong base or even skipping a base as a strand is put together. – These variations are called mutations, from the Latin word mutare, meaning “to change.” – Mutations are heritable changes in genetic information. – All mutatio ...
... – Now and then cells make mistakes in copying their own DNA, inserting the wrong base or even skipping a base as a strand is put together. – These variations are called mutations, from the Latin word mutare, meaning “to change.” – Mutations are heritable changes in genetic information. – All mutatio ...
Exam Questions_150216_final
... The dnaB gene of E. coli encodes a helicase (DnaB) that unwinds DNA at the replication fork. Its properties have been studied using artificial substrates like those shown in Figure 1A. In such substrates, DnaB binds preferentially to the longest single-strand region (the largest target) available. Th ...
... The dnaB gene of E. coli encodes a helicase (DnaB) that unwinds DNA at the replication fork. Its properties have been studied using artificial substrates like those shown in Figure 1A. In such substrates, DnaB binds preferentially to the longest single-strand region (the largest target) available. Th ...
Unit 10.1.4 - Measuring Genetic Variation using Molecular Markers
... • Co-migration: same mobility, same protein? An assumption commonly made when comparing profiles is that proteins which share the same mobility and intensity in a gel are homologous proteins, that is, that they are products of the same gene(s). This is a questionable assumption, especially if only o ...
... • Co-migration: same mobility, same protein? An assumption commonly made when comparing profiles is that proteins which share the same mobility and intensity in a gel are homologous proteins, that is, that they are products of the same gene(s). This is a questionable assumption, especially if only o ...
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Multiple
... A) adding a single 5ʹ cap structure that resists degradation by nucleases B) causing specific double strand DNA breaks that result in blunt ends on both strands C) causing linear ends of the newly replicated DNA to circularize D) adding numerous short DNA sequences such as TTAGGG, which form a hairp ...
... A) adding a single 5ʹ cap structure that resists degradation by nucleases B) causing specific double strand DNA breaks that result in blunt ends on both strands C) causing linear ends of the newly replicated DNA to circularize D) adding numerous short DNA sequences such as TTAGGG, which form a hairp ...
Article - School of Chemistry and Biochemistry
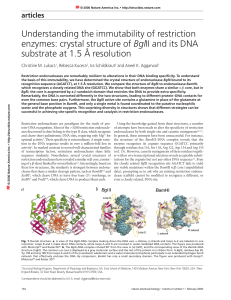
... phosphate groups and the main chain NH groups of residues 38 and 40. Interestingly, residues 38 and 40 are carried on a loop (loop A) that is missing in BamHI (Fig. 1b), which may explain the lack of analogous backbone changes in the BamHI DNA. Whether these transitions in the DNA backbone account f ...
... phosphate groups and the main chain NH groups of residues 38 and 40. Interestingly, residues 38 and 40 are carried on a loop (loop A) that is missing in BamHI (Fig. 1b), which may explain the lack of analogous backbone changes in the BamHI DNA. Whether these transitions in the DNA backbone account f ...