RNA & Protein Synthesis
... RNA is the link between DNA & protein! • DNA is found in the nucleus of cells, but proteins are built in the cytoplasm. • DNA cannot leave the nucleus, so a copy of the gene is made in the form of a similar nucleic acid called RNA ...
... RNA is the link between DNA & protein! • DNA is found in the nucleus of cells, but proteins are built in the cytoplasm. • DNA cannot leave the nucleus, so a copy of the gene is made in the form of a similar nucleic acid called RNA ...
Special Topics gene expression
... I. Definition of gene expression II. Proteins- the end product of gene expression A. Polymers of monomers B. Joined by peptide bond C. Denaturing of proteins leads to loss of function i. Ways to denature protiens D. Genes code for proteins i. Genome vs. gene ii. Polymer of monomers (nucleic acid vs. ...
... I. Definition of gene expression II. Proteins- the end product of gene expression A. Polymers of monomers B. Joined by peptide bond C. Denaturing of proteins leads to loss of function i. Ways to denature protiens D. Genes code for proteins i. Genome vs. gene ii. Polymer of monomers (nucleic acid vs. ...
The Master Molecule
... Even in 93% of macaque DNA is the same as that of human beings. Ninety-nine percent of each person‘s DNA is identical to that of all other human beings. Today, the evolution of genes, programmed cell death (apoptosis), and the action of messenger RNA (mRNA) are three major targets of research. mRNA ...
... Even in 93% of macaque DNA is the same as that of human beings. Ninety-nine percent of each person‘s DNA is identical to that of all other human beings. Today, the evolution of genes, programmed cell death (apoptosis), and the action of messenger RNA (mRNA) are three major targets of research. mRNA ...
Chapter 15
... 4. Termination- at the end of genes are “stop” sequences causing transcription to stop, DNA/RNA hybrid to dissociate, RNA polymerase to release DNA and DNA to rewind. A GC hairpin is created to stop process. Modifications- 5 ̷ cap (protects against nucleases and phosphatases in ...
... 4. Termination- at the end of genes are “stop” sequences causing transcription to stop, DNA/RNA hybrid to dissociate, RNA polymerase to release DNA and DNA to rewind. A GC hairpin is created to stop process. Modifications- 5 ̷ cap (protects against nucleases and phosphatases in ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... to the ribosomes • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA), along with protein, makes up the ribosomes • Transfer RNA (tRNA) transfers amino acids to the ribosomes where proteins are synthesized ...
... to the ribosomes • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA), along with protein, makes up the ribosomes • Transfer RNA (tRNA) transfers amino acids to the ribosomes where proteins are synthesized ...
RNA_and_Protein_Synthesis
... Protein properties are determined by the order of the different amino acids joined together in polypeptide ...
... Protein properties are determined by the order of the different amino acids joined together in polypeptide ...
RNA Molecules: More than Mere Information Intermediaries
... Another gram-positive bacterium, Streptococcus pyogenes, also contains an RNAIII-like regulatory system, partly situated in the Fas operon. S. pyogenes also harbors a 459-nucleotide RNA, called pel for pleiotropic effect locus, that regulates expression of several virulence genes. As with RNAIII, pe ...
... Another gram-positive bacterium, Streptococcus pyogenes, also contains an RNAIII-like regulatory system, partly situated in the Fas operon. S. pyogenes also harbors a 459-nucleotide RNA, called pel for pleiotropic effect locus, that regulates expression of several virulence genes. As with RNAIII, pe ...
gene to protein 1
... Exons are cut out before mRNA leaves the nucleus. Nucleotides may be added at both ends of the RNA. Ribozymes may function in RNA splicing. RNA splicing can be catalyzed by spliceosomes. A primary transcript is often much longer than the final RNA molecule that leaves the nucleus. 7. Which of the fo ...
... Exons are cut out before mRNA leaves the nucleus. Nucleotides may be added at both ends of the RNA. Ribozymes may function in RNA splicing. RNA splicing can be catalyzed by spliceosomes. A primary transcript is often much longer than the final RNA molecule that leaves the nucleus. 7. Which of the fo ...
chapter 17 and 18 study guide
... near the promoter; in eukaryotes repressors can bind to the control elements within enhancers, to activators, or to other proteins in a way that blocks activators from binding to DNA Inducer? a specific small molecule that binds to a bacterial repressor protein and changes the repressor’s shape so t ...
... near the promoter; in eukaryotes repressors can bind to the control elements within enhancers, to activators, or to other proteins in a way that blocks activators from binding to DNA Inducer? a specific small molecule that binds to a bacterial repressor protein and changes the repressor’s shape so t ...
DNA Damage - Columbus Labs
... An RNA molecule (messenger RNA, or mRNA), containing in its base sequence the information that specifies a particular protein, acts as a template to direct the synthesis of the polypeptide. Each amino acid is brought to the template attached to an adapter molecule specific to that amino acid. These ...
... An RNA molecule (messenger RNA, or mRNA), containing in its base sequence the information that specifies a particular protein, acts as a template to direct the synthesis of the polypeptide. Each amino acid is brought to the template attached to an adapter molecule specific to that amino acid. These ...
Protein Synthesis and Mutations - Mrs. Gracie Gonzalez Biology Class
... Translation: (translating for an amino acid); occurs using ribosome floating in the cytoplasm of cells 5. With the help of the ribosome, mRNA is translated 6. tRNA transfers the complimentary anticodon with the amino acid attached to each codon on mRNA 7. Polypeptide chain is created where each ...
... Translation: (translating for an amino acid); occurs using ribosome floating in the cytoplasm of cells 5. With the help of the ribosome, mRNA is translated 6. tRNA transfers the complimentary anticodon with the amino acid attached to each codon on mRNA 7. Polypeptide chain is created where each ...
DNA, Transcription and Translation
... nucleus. They consist of DNA and therefore, carry the genes. They change shape at various stages of the cell’s life. • The DNA molecule is very long. In a human nucleus of 6μm, the DNA will be 1.8m long. • In eukaryotes the DNA is coiled around proteins called histones. When the DNA is coiled it is ...
... nucleus. They consist of DNA and therefore, carry the genes. They change shape at various stages of the cell’s life. • The DNA molecule is very long. In a human nucleus of 6μm, the DNA will be 1.8m long. • In eukaryotes the DNA is coiled around proteins called histones. When the DNA is coiled it is ...
Self-Replication
... • The overwhelming number of viruses are not harmful to their hosts and peacefully co-exist – We have more viral genes than human genes in us, if you take a whole body and process it for genes. • Viruses may have been a step in the sequence of evolution of cells, or a parallel line of evolution that ...
... • The overwhelming number of viruses are not harmful to their hosts and peacefully co-exist – We have more viral genes than human genes in us, if you take a whole body and process it for genes. • Viruses may have been a step in the sequence of evolution of cells, or a parallel line of evolution that ...
Glossary Algae: Unicellular or simple multicellular photosynthetic
... and rRNA. ribosomal RNA (rRNA): A class of RNA molecules found together with characteristic proteins, in ribosomes; transcribed from the DNA of the nucleolus. Ribosome: Complex ribonucleoprotein particle that in conjunction with messenger and transfer RNA and several other factors, constitute the si ...
... and rRNA. ribosomal RNA (rRNA): A class of RNA molecules found together with characteristic proteins, in ribosomes; transcribed from the DNA of the nucleolus. Ribosome: Complex ribonucleoprotein particle that in conjunction with messenger and transfer RNA and several other factors, constitute the si ...
Cytoplasmic RNA improves accuracy of mRNA
... nuclear fraction indicating cross contamination from the cytoplasmic fraction. B) Agarose gel electrophoresis indicating the cross contamination between the nuclear and the cytoplasmic fraction. Genomic DNA and ribosomal RNA traces are detectable in both fractions. Samples 1 and 2 show results with ...
... nuclear fraction indicating cross contamination from the cytoplasmic fraction. B) Agarose gel electrophoresis indicating the cross contamination between the nuclear and the cytoplasmic fraction. Genomic DNA and ribosomal RNA traces are detectable in both fractions. Samples 1 and 2 show results with ...
CHAPTER 17 - HCC Learning Web
... • Ribozymes are catalytic RNA molecules that function as enzymes and can splice RNA • The discovery of ribozymes rendered obsolete the belief that all biological catalysts were proteins ...
... • Ribozymes are catalytic RNA molecules that function as enzymes and can splice RNA • The discovery of ribozymes rendered obsolete the belief that all biological catalysts were proteins ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis - Port Washington School District
... • Uracil also would pair with adenine (U-A) ...
... • Uracil also would pair with adenine (U-A) ...
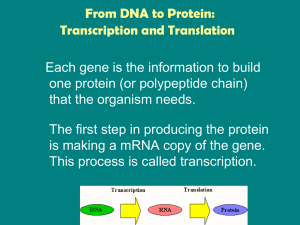
From DNA to Protein: Transcription and Translation
... Cells • Genes in eukaryotic organisms contain non-coding segments called introns. • The coding portions of the gene are called exons. • The noncoding introns need to be removed before the mRNA leaves the nucleus. ...
... Cells • Genes in eukaryotic organisms contain non-coding segments called introns. • The coding portions of the gene are called exons. • The noncoding introns need to be removed before the mRNA leaves the nucleus. ...
Gene expression powerpoint
... The Genetic Code 1.A triplet code comprised of three nucleotide bases in a sequence. ...
... The Genetic Code 1.A triplet code comprised of three nucleotide bases in a sequence. ...
Non-coding RNA for ZM401, a Pollen
... There were several reports of transcripts without a long open reading frame (ORF) in various eucaryotes (Brannan et al., 1990; Brockdorff et al., 1992; Brown et al. 1992; Askew et al., 1994; Crespi et al., 1994; Velleca et al., 1994; Watanabe and Yamamoto, 1994; Yoshida et al., 1994), and it has bee ...
... There were several reports of transcripts without a long open reading frame (ORF) in various eucaryotes (Brannan et al., 1990; Brockdorff et al., 1992; Brown et al. 1992; Askew et al., 1994; Crespi et al., 1994; Velleca et al., 1994; Watanabe and Yamamoto, 1994; Yoshida et al., 1994), and it has bee ...
How Proteins are Made - MDC Faculty Web Pages
... • Steps in Translation. – tRNA that matches the next codon ferries in the appropriate amino acid into the “A” site. The ribosome catalyzes the peptide bond between the first two amino acids at the “A” site; then the ribosome jumps along the mRNA to the next codon, moving the newly formed peptide to ...
... • Steps in Translation. – tRNA that matches the next codon ferries in the appropriate amino acid into the “A” site. The ribosome catalyzes the peptide bond between the first two amino acids at the “A” site; then the ribosome jumps along the mRNA to the next codon, moving the newly formed peptide to ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.