The Extended Evolutionary Synthesis and the role of soft inheritance
... Evolutionary biology today has to incorporate soft inheritance, saltational changes due to systemic mutations, and various types of genetic exchange and cooperation. These all challenge the assumptions of the Modern Synthesis. We believe that rather than trying to continue to work within the framewo ...
... Evolutionary biology today has to incorporate soft inheritance, saltational changes due to systemic mutations, and various types of genetic exchange and cooperation. These all challenge the assumptions of the Modern Synthesis. We believe that rather than trying to continue to work within the framewo ...
15.3 The formation of polymers, membranes, and self
... – Humans and chimpanzees are more alike as fetuses than as adults ...
... – Humans and chimpanzees are more alike as fetuses than as adults ...
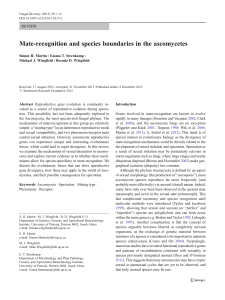
Mate-recognition and species boundaries in the ascomycetes
... al. 1999; O’Donnell et al. 2004). It was proposed by Coppin et al. (1997) that sexual reproduction in homothallic species may rely on alternate expression of genes for one or the other mating type in different cells. Another route to selffertility in filamentous species is via “pseudohomothallism”, ...
... al. 1999; O’Donnell et al. 2004). It was proposed by Coppin et al. (1997) that sexual reproduction in homothallic species may rely on alternate expression of genes for one or the other mating type in different cells. Another route to selffertility in filamentous species is via “pseudohomothallism”, ...
The interaction between developmental bias and natural
... The basic observation here is that although there are at least 3000 species of centipede (Lewis, 1981), and although their trunk segment numbers range from 15 to 191 (Minelli and Bortoletto, 1988; Arthur, 1999; Minelli et al, 2000), there is no centipede species that is characterized by an even numb ...
... The basic observation here is that although there are at least 3000 species of centipede (Lewis, 1981), and although their trunk segment numbers range from 15 to 191 (Minelli and Bortoletto, 1988; Arthur, 1999; Minelli et al, 2000), there is no centipede species that is characterized by an even numb ...
Prediction of Blastulation
... mitotic intermediates that are comprised of chromatin masses surrounded by nuclear envelope, which then fuse to form a single nucleus Chavez et al (2010) studied if the appearance of embryonic micronuclei had any effects on developmental potential ...
... mitotic intermediates that are comprised of chromatin masses surrounded by nuclear envelope, which then fuse to form a single nucleus Chavez et al (2010) studied if the appearance of embryonic micronuclei had any effects on developmental potential ...
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The... copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research
... evolution, or whether it manifested primarily within just the wealthy minority. Males have probably always competed for mates to some extent with their brothers, but no more intensely than with neighbouring unrelated males. It is reasonable to assume that most human families, on a global scale throu ...
... evolution, or whether it manifested primarily within just the wealthy minority. Males have probably always competed for mates to some extent with their brothers, but no more intensely than with neighbouring unrelated males. It is reasonable to assume that most human families, on a global scale throu ...
Adaptive basis of codon usage in the haploid moss
... lack of translational selection in mammals and some Drosophila species has been explained by their relatively small effective population sizes, meaning that genetic drift will dominate the evolutionary dynamics of mutations that only differ marginally in fitness (Shields et al, 1988; Sharp et al, 19 ...
... lack of translational selection in mammals and some Drosophila species has been explained by their relatively small effective population sizes, meaning that genetic drift will dominate the evolutionary dynamics of mutations that only differ marginally in fitness (Shields et al, 1988; Sharp et al, 19 ...
p - Bonnabel Home Page
... extinctions have occurred in which 50% or more of the Earth’s species went extinct ...
... extinctions have occurred in which 50% or more of the Earth’s species went extinct ...
Infection elevates diversity - Aneil Agrawal
... use of the fact that exchange of chromosomal material (crossover events) occurs 4–5 days before eggs are laid. In their bacterial-infection experiments, the authors found an increase in recombinant progeny even in the first 4 days after the mothers were infected. This rapid response points to transm ...
... use of the fact that exchange of chromosomal material (crossover events) occurs 4–5 days before eggs are laid. In their bacterial-infection experiments, the authors found an increase in recombinant progeny even in the first 4 days after the mothers were infected. This rapid response points to transm ...
Environment, Development, and Evolution
... done in ecological developmental biology, a new and more inclusive evolutionary theory is being forged. So far, eco-devo has contributed at least three components to this nascent evolutionary synthesis. These are the three concepts introduced in the first section of the textbook. The first concept i ...
... done in ecological developmental biology, a new and more inclusive evolutionary theory is being forged. So far, eco-devo has contributed at least three components to this nascent evolutionary synthesis. These are the three concepts introduced in the first section of the textbook. The first concept i ...
Document
... et al. 2005; Anderson et al. 2011; Wit et al. 2013). This is primarily due to limited evidence for the abundance of trade-offs in natural populations (Leroi et al. 2005). This could be either because mutations with detrimental effects are not tolerated and hence selected out of the evolving populati ...
... et al. 2005; Anderson et al. 2011; Wit et al. 2013). This is primarily due to limited evidence for the abundance of trade-offs in natural populations (Leroi et al. 2005). This could be either because mutations with detrimental effects are not tolerated and hence selected out of the evolving populati ...
HS-SCI-APB-Unit 5 -- Chapter 32- Introduction to
... relationships that emerged in the Cambrian period generated diversity through natural selection. Predators acquired novel adaptations, such as forms of locomotion that helped them catch prey, while prey species acquired new defenses, such as protective shells. Another hypothesis focuses on a rise in ...
... relationships that emerged in the Cambrian period generated diversity through natural selection. Predators acquired novel adaptations, such as forms of locomotion that helped them catch prey, while prey species acquired new defenses, such as protective shells. Another hypothesis focuses on a rise in ...
11.1 the work of gregor mendel answer key biology
... that is unsurpassed.Your customers will taste the . Mendel's Laws. Gregor Mendel described laws of inheritance many years before the discovery of DNA. Learn about his laws and the genius behind them. The CK-12 Biology Workbook complements the CK-12 Biology FlexBook® textbook and includes six workshe ...
... that is unsurpassed.Your customers will taste the . Mendel's Laws. Gregor Mendel described laws of inheritance many years before the discovery of DNA. Learn about his laws and the genius behind them. The CK-12 Biology Workbook complements the CK-12 Biology FlexBook® textbook and includes six workshe ...
Adaptive evolution: evaluating empirical support for
... insecticide resistance arose in isolated D. melanogaster populations several times in the past 50 years15. Many insecticides target a neuronal signalling enzyme encoded by the Acetylcholine esterase (Ace) locus, and four sites in Ace have mutated to cause insecticide resistance in different local ge ...
... insecticide resistance arose in isolated D. melanogaster populations several times in the past 50 years15. Many insecticides target a neuronal signalling enzyme encoded by the Acetylcholine esterase (Ace) locus, and four sites in Ace have mutated to cause insecticide resistance in different local ge ...
gymo and angio plants 2
... evolution of flowers to entice the insects and animals to spread their pollen Gymnosperms rely on wind as their main source of pollination, which leads to trees with very similar genotypes in a very concentrated area (think of dense pine forests) TIME FROM POLLINATION TO FERTILIZATION Angiosperm ...
... evolution of flowers to entice the insects and animals to spread their pollen Gymnosperms rely on wind as their main source of pollination, which leads to trees with very similar genotypes in a very concentrated area (think of dense pine forests) TIME FROM POLLINATION TO FERTILIZATION Angiosperm ...
An Overview of Animal Diversity
... are of interest in the study of evo-devo, the interface between evolution and development (see Chapters 21 and 25). Like all features of organisms, animal body plans have evolved over time. Some of the evolutionary changes appear to have occurred early in the history of animal life. For example, rec ...
... are of interest in the study of evo-devo, the interface between evolution and development (see Chapters 21 and 25). Like all features of organisms, animal body plans have evolved over time. Some of the evolutionary changes appear to have occurred early in the history of animal life. For example, rec ...
Full Text - The International Journal of Developmental Biology
... between historical (traditional) developmental biology and new approaches in molecular biology. In my Development Biology lecture course, as well in the introduction of this course, I discuss the following topics related to eye development: 1. The classical transplantation experiment of the eye-anla ...
... between historical (traditional) developmental biology and new approaches in molecular biology. In my Development Biology lecture course, as well in the introduction of this course, I discuss the following topics related to eye development: 1. The classical transplantation experiment of the eye-anla ...
patt3
... dimensions change at the same rate (no allometry). if a > 1, then y changes faster than x (positive allometry - leg length), and if a < 1, then there is negative allometry. Obviously, allometric differences become more pronounced as the organism increases in size... so large organisms and small ofte ...
... dimensions change at the same rate (no allometry). if a > 1, then y changes faster than x (positive allometry - leg length), and if a < 1, then there is negative allometry. Obviously, allometric differences become more pronounced as the organism increases in size... so large organisms and small ofte ...
Chapter 34A
... All chordates have some sort of tail posterior to the anus: • may be greatly reduced during embryonic development in some species (e.g., Homo sapiens) • contains skeletal and muscle elements that may play a role in propulsion (aquatic species) or balance & support (terrestrial species) Post-anal tai ...
... All chordates have some sort of tail posterior to the anus: • may be greatly reduced during embryonic development in some species (e.g., Homo sapiens) • contains skeletal and muscle elements that may play a role in propulsion (aquatic species) or balance & support (terrestrial species) Post-anal tai ...
Karl Ernst von Baer`s Laws of Embryology
... By: Barnes, M. Elizabeth Keywords: Laws of Embryology [2] von Baer's laws of embryology [3] In 1828, while working at the University of Königsberg in Königsberg, Germany, Karl Ernst von Baer [4] proposed four laws of animal development, which came to be called von Baer's laws [5] of embryology [6]. ...
... By: Barnes, M. Elizabeth Keywords: Laws of Embryology [2] von Baer's laws of embryology [3] In 1828, while working at the University of Königsberg in Königsberg, Germany, Karl Ernst von Baer [4] proposed four laws of animal development, which came to be called von Baer's laws [5] of embryology [6]. ...
long program - Pan
... meeting happen. For this, I am deeply grateful. Observing their remarkable dedication and determination over the last 2 years, and the result, is what makes this a truly historical event for our field in the Americas. I end by thanking our sponsors for their generous support of all the different eve ...
... meeting happen. For this, I am deeply grateful. Observing their remarkable dedication and determination over the last 2 years, and the result, is what makes this a truly historical event for our field in the Americas. I end by thanking our sponsors for their generous support of all the different eve ...