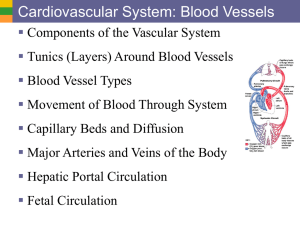
Major arteries of the body
... • The largest artery in the body • Arises from the left ventricle of the heart • Carries oxygenated blood to all parts of the body • Is divided into 4 parts: 1. Ascending aorta 2. Arch of aorta 3. Descending thoracic aorta 4. Descending abdominal aorta ...
... • The largest artery in the body • Arises from the left ventricle of the heart • Carries oxygenated blood to all parts of the body • Is divided into 4 parts: 1. Ascending aorta 2. Arch of aorta 3. Descending thoracic aorta 4. Descending abdominal aorta ...
Major arteries of the body
... Anatomic (True) End Artery: When NO anastomosis exists, e.g. artery of the retina. Functional End Artery: When an anastomosis exists but is incapable of providing a sufficient supply of blood, e.g. splenic artery, renal artery. ...
... Anatomic (True) End Artery: When NO anastomosis exists, e.g. artery of the retina. Functional End Artery: When an anastomosis exists but is incapable of providing a sufficient supply of blood, e.g. splenic artery, renal artery. ...
2-Copy of MAJOR ARTERIES OF BODY-PROF AHMED
... Anatomic (True) End Artery: When NO anastomosis exists, e.g. artery of the retina. Functional End Artery: When an anastomosis exists but is incapable of providing a sufficient supply of blood, e.g. splenic artery, renal artery. ...
... Anatomic (True) End Artery: When NO anastomosis exists, e.g. artery of the retina. Functional End Artery: When an anastomosis exists but is incapable of providing a sufficient supply of blood, e.g. splenic artery, renal artery. ...
Microsoft PowerPoint file
... and smaller vessels until finally they spread out into a bed of capillaries. Hundreds of miles of these microscopic vessels thread their way through the lungs and wrap around pockets of lung tissue called alveoli. The lungs contain about 750 million of these small air sacs, their combined surface ar ...
... and smaller vessels until finally they spread out into a bed of capillaries. Hundreds of miles of these microscopic vessels thread their way through the lungs and wrap around pockets of lung tissue called alveoli. The lungs contain about 750 million of these small air sacs, their combined surface ar ...
Histological Organization of Blood Vessels
... In areas such as the brain, heart, and stomach, a continuous, rich flow of blood is required In these areas, more than one artery supplies a specific area These arteries (collateral arteries) typically fuse forming an arterial anastomosis If one arteriole is blocked, the other one will suppl ...
... In areas such as the brain, heart, and stomach, a continuous, rich flow of blood is required In these areas, more than one artery supplies a specific area These arteries (collateral arteries) typically fuse forming an arterial anastomosis If one arteriole is blocked, the other one will suppl ...
Anatomy of the Thorax
... ○ The inferior border of the lung is sharp and separates the base from the costal surface. ○ The anterior and posterior borders separate the costal surface from the medial surface and are both smooth. 3 surfaces - costal, medial (mediastinal), inferior (diaphragmatic) ○ The costal surface lies immed ...
... ○ The inferior border of the lung is sharp and separates the base from the costal surface. ○ The anterior and posterior borders separate the costal surface from the medial surface and are both smooth. 3 surfaces - costal, medial (mediastinal), inferior (diaphragmatic) ○ The costal surface lies immed ...
electrical anatomy of the atrial chambers
... The internal profile of the left atrium is much simpler than that of the right, since the walls are almost exclusively smooth. The pectinate muscles are confined within the tubular appendage, which buds forwards from the anterior, superior and leftward corner of the chamber (Figure 10). The four pul ...
... The internal profile of the left atrium is much simpler than that of the right, since the walls are almost exclusively smooth. The pectinate muscles are confined within the tubular appendage, which buds forwards from the anterior, superior and leftward corner of the chamber (Figure 10). The four pul ...
Name
... Identify the small internal jugular veins next to the common carotid arteries. This is not present in some cats. Identify the large white vagus nerves that run along the common carotid arteries Remove the pericardium from the heart and identify the aorta and the pulmonary trunk. Follow the aorta and ...
... Identify the small internal jugular veins next to the common carotid arteries. This is not present in some cats. Identify the large white vagus nerves that run along the common carotid arteries Remove the pericardium from the heart and identify the aorta and the pulmonary trunk. Follow the aorta and ...
Collagen and Collagenous Tissues Collagen
... • Collagen is a ubiquitous structural protein with many types all having a triple helix structure that is cross- linked in a staggered array. • Some of the most common collagen types are fibrillar and the collagen can be organized in 1-D, 2-D or 3-D in different tissues to confer different ...
... • Collagen is a ubiquitous structural protein with many types all having a triple helix structure that is cross- linked in a staggered array. • Some of the most common collagen types are fibrillar and the collagen can be organized in 1-D, 2-D or 3-D in different tissues to confer different ...
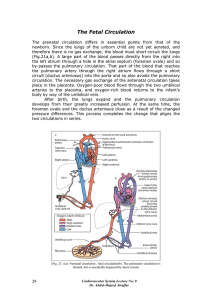
The Fetal Circulation The prenatal circulation differs in essential
... (ascending aorta), arches to the left as the aortic arch, and then runs downward on the left side in front of the vertebral column (descending aorta = thoracic aorta). After piercing the diaphragm through the aortic hiatus it runs as the abdominal aorta to the level of the 4th lumbar vertebra, where ...
... (ascending aorta), arches to the left as the aortic arch, and then runs downward on the left side in front of the vertebral column (descending aorta = thoracic aorta). After piercing the diaphragm through the aortic hiatus it runs as the abdominal aorta to the level of the 4th lumbar vertebra, where ...
Anomalous origin of left coronary artery in an adult
... advised catheter coronary angiogram and surgery, however, the patient refused and she is currently on medical management. ALCAPA is a rare congenital anomaly with an incidence of 1 in 300,000 live births and represents 0.5 per cent of all cases of congenital heart disease. Most of the cases (85%) ...
... advised catheter coronary angiogram and surgery, however, the patient refused and she is currently on medical management. ALCAPA is a rare congenital anomaly with an incidence of 1 in 300,000 live births and represents 0.5 per cent of all cases of congenital heart disease. Most of the cases (85%) ...
pertinent blood vessel routes
... superficial and deep palmar arches palmar metacarpal and palmar digital arteries DEEP VENOUS RETURN FROM THE RIGHT UPPER EXTREMITY palmar digital and palmar metacarpal veins superficial or deep palmar venous arches radial or ulnar veins brachial vein axillary vein subclavian vein right ...
... superficial and deep palmar arches palmar metacarpal and palmar digital arteries DEEP VENOUS RETURN FROM THE RIGHT UPPER EXTREMITY palmar digital and palmar metacarpal veins superficial or deep palmar venous arches radial or ulnar veins brachial vein axillary vein subclavian vein right ...
pertinent blood vessel routes
... superficial and deep palmar arches palmar metacarpal and palmar digital arteries DEEP VENOUS RETURN FROM THE RIGHT UPPER EXTREMITY palmar digital and palmar metacarpal veins superficial or deep palmar venous arches radial or ulnar veins brachial vein axillary vein subclavian vein right ...
... superficial and deep palmar arches palmar metacarpal and palmar digital arteries DEEP VENOUS RETURN FROM THE RIGHT UPPER EXTREMITY palmar digital and palmar metacarpal veins superficial or deep palmar venous arches radial or ulnar veins brachial vein axillary vein subclavian vein right ...
1. The lining of the inner walls of the heart`s chambers is termed the
... 28. Postganglionic sympathetic neurons release the neurotransmitter ______________. A) B) C) D) ...
... 28. Postganglionic sympathetic neurons release the neurotransmitter ______________. A) B) C) D) ...
Lecture 17: Vascular System Review 3 paired veins drain into the
... Forms a bypass through liver Enables most blood from placenta to pass directly to heart without passing through liver capillary networks Cardinal veins constitute main venous drainage system of embryo o Anterior cardinal veins Drain cranial part of embryo o Posterior cardinal veings Drain ca ...
... Forms a bypass through liver Enables most blood from placenta to pass directly to heart without passing through liver capillary networks Cardinal veins constitute main venous drainage system of embryo o Anterior cardinal veins Drain cranial part of embryo o Posterior cardinal veings Drain ca ...
Chapter 18 - Las Positas College
... Forms right border of heart Receives blood from systemic circuit Pectinate muscles ...
... Forms right border of heart Receives blood from systemic circuit Pectinate muscles ...
Chapter 21 Blood Vessels
... to cross-sectional area – blood flow is slower in the arterial branches • flow in aorta is 40 cm/sec while flow in capillaries is .1 cm/sec • slow rate in capillaries allows for exchange ...
... to cross-sectional area – blood flow is slower in the arterial branches • flow in aorta is 40 cm/sec while flow in capillaries is .1 cm/sec • slow rate in capillaries allows for exchange ...
Chapter 21: Immune System
... • Closed system of tubes that carries blood • Arteries carry blood from heart to tissues – elastic arteries – muscular arteries – arterioles ...
... • Closed system of tubes that carries blood • Arteries carry blood from heart to tissues – elastic arteries – muscular arteries – arterioles ...
Recommendations - Canadian Cardiovascular Society
... 1.In the setting of heart failure, angina and single territory coronary artery disease, PCI may be the treatment of first choice. However, PCI has not been shown to improve outcomes for patients with chronic stable heart failure, irrespective of ...
... 1.In the setting of heart failure, angina and single territory coronary artery disease, PCI may be the treatment of first choice. However, PCI has not been shown to improve outcomes for patients with chronic stable heart failure, irrespective of ...
ID_113_Topographical anatomy and oper_English_sem_
... Right intercostal artery Arch of the aorta Subclavian artery Anterior thoracic artery Which of the following statements describes nerve supply of the lungs correctly? Sympathetic fibers in the pulmonary plexus are preganglionic fibers Vagal fibers in the pulmonary plexus are postganglionic fibers Vi ...
... Right intercostal artery Arch of the aorta Subclavian artery Anterior thoracic artery Which of the following statements describes nerve supply of the lungs correctly? Sympathetic fibers in the pulmonary plexus are preganglionic fibers Vagal fibers in the pulmonary plexus are postganglionic fibers Vi ...
Location of the Heart
... Propagation on ventricular wall From the inner side of the ventricular wall, the many activation sites cause the formation of a wavefront which propagates through the ventricular mass toward the outer wall. This process results from cell-to-cell activation. After each ventricular muscle region has ...
... Propagation on ventricular wall From the inner side of the ventricular wall, the many activation sites cause the formation of a wavefront which propagates through the ventricular mass toward the outer wall. This process results from cell-to-cell activation. After each ventricular muscle region has ...
Thorax: CT, axial sections
... 25 Transaxial CT Images of the Thorax These images have been windowed to accentuate the water density structures of the heart and great vessels. As a result the lungs appear black, with little detail in them. Only the larger pulmonary vessels appear, as white spots around the hilar areas. On campus ...
... 25 Transaxial CT Images of the Thorax These images have been windowed to accentuate the water density structures of the heart and great vessels. As a result the lungs appear black, with little detail in them. Only the larger pulmonary vessels appear, as white spots around the hilar areas. On campus ...
Heart

The heart is a muscular organ in humans and other animals, which pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. Blood provides the body with oxygen and nutrients, and also assists in the removal of metabolic wastes. The heart is located in the middle compartment of the mediastinum in the chest.In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria; and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish in contrast have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall of the heart is made up of three layers: epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium.The heart pumps blood through both circulatory systems. Blood low in oxygen from the systemic circulation enters the right atrium from the superior and inferior vena cavae and passes to the right ventricle. From here it is pumped into the pulmonary circulation, through the lungs where it receives oxygen and gives off carbon dioxide. Oxygenated blood then returns to the left atrium, passes through the left ventricle and is pumped out through the aorta to the systemic circulation−where the oxygen is used and metabolized to carbon dioxide. In addition the blood carries nutrients from the liver and gastrointestinal tract to various organs of the body, while transporting waste to the liver and kidneys. Normally with each heartbeat the right ventricle pumps the same amount of blood into the lungs as the left ventricle pumps to the body. Veins transport blood to the heart and carry deoxygenated blood - except for the pulmonary and portal veins. Arteries transport blood away from the heart, and apart from the pulmonary artery hold oxygenated blood. Their increased distance from the heart cause veins to have lower pressures than arteries. The heart contracts at a resting rate close to 72 beats per minute. Exercise temporarily increases the rate, but lowers resting heart rate in the long term, and is good for heart health.Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are the most common cause of death globally as of 2008, accounting for 30% of deaths. Of these more than three quarters follow coronary artery disease and stroke. Risk factors include: smoking, being overweight, little exercise, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and poorly controlled diabetes, among others. Diagnosis of CVD is often done by listening to the heart-sounds with a stethoscope, ECG or by ultrasound. Specialists who focus on diseases of the heart are called cardiologists, although many specialties of medicine may be involved in treatment.