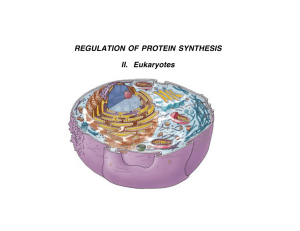
Regulating Protein Synthesis
... generally under positive control (proteins promote, rather than inhibit, RNA polymerase binding to DNA template). ...
... generally under positive control (proteins promote, rather than inhibit, RNA polymerase binding to DNA template). ...
1. Important Features
... (anticodon) with the triplet code (codon) of the mRNA. e.Enzyme "hooks" the amino acid to the last one in the chain forming a peptide bond. f. Protein chain continues to grow as each tRNA brings in its amino acid and adds it to the chain. - This is translation!! ...
... (anticodon) with the triplet code (codon) of the mRNA. e.Enzyme "hooks" the amino acid to the last one in the chain forming a peptide bond. f. Protein chain continues to grow as each tRNA brings in its amino acid and adds it to the chain. - This is translation!! ...
Protein Synthesis Test Review
... 7. What is a frameshift mutation? _The whole sequence is altered due to an insertion or deletion resulting in large scale changes to the genetic code.____________________ 8. Will the protein be the same if a mutation occurs? Why or why not? ___ If there are any gene alterations the protein will be d ...
... 7. What is a frameshift mutation? _The whole sequence is altered due to an insertion or deletion resulting in large scale changes to the genetic code.____________________ 8. Will the protein be the same if a mutation occurs? Why or why not? ___ If there are any gene alterations the protein will be d ...
Protein Synthesis Notes Review
... 2. To make proteins, what does the DNA have to be decoded into? 3. What are the three parts that make up a RNA nucleotide? 4. What are the three differences between DNA and RNA? 5. If a DNA chain had the following sequence, CCGTAATAGCAT, what RNA nucleotides would attach to this sequence? 6. What is ...
... 2. To make proteins, what does the DNA have to be decoded into? 3. What are the three parts that make up a RNA nucleotide? 4. What are the three differences between DNA and RNA? 5. If a DNA chain had the following sequence, CCGTAATAGCAT, what RNA nucleotides would attach to this sequence? 6. What is ...
Chapter 10B: Gene Expression
... Genes are segments of DNA that code for a particular protein (or RNA molecule) • the human genome contains ~3 billion base pairs (bps) and ~25,000 genes • almost all genes encode proteins • when we talk about “genes” we will focus on those that express proteins ( the “end products” for a small perce ...
... Genes are segments of DNA that code for a particular protein (or RNA molecule) • the human genome contains ~3 billion base pairs (bps) and ~25,000 genes • almost all genes encode proteins • when we talk about “genes” we will focus on those that express proteins ( the “end products” for a small perce ...
10.3 Protein Synthesis
... The Genetic Code • The language of mRNA is called the Genetic Code (A, G, U, C) (contains only 4 letters) • It is the matching of the RNA sequence to the correct amino acid to make proteins. • It is based on codons, which are 3 bases together on an mRNA chain. • Each codon codes for a specific am ...
... The Genetic Code • The language of mRNA is called the Genetic Code (A, G, U, C) (contains only 4 letters) • It is the matching of the RNA sequence to the correct amino acid to make proteins. • It is based on codons, which are 3 bases together on an mRNA chain. • Each codon codes for a specific am ...
mRNA - Decatur ISD
... Which gene is read on the DNA? • Promoter region – binding site before beginning of gene – Generally referred to as a TATA box because it is a repeating sequence of T and A – binding site for RNA polymerase & transcription factors ...
... Which gene is read on the DNA? • Promoter region – binding site before beginning of gene – Generally referred to as a TATA box because it is a repeating sequence of T and A – binding site for RNA polymerase & transcription factors ...
Protein Synthesis Notes Review
... What brings amino acids to the ribosome? How many different amino acids can a tRNA carry? What are the three unpaired bases at the bottom of a tRNA called? What type of bond forms between amino acids? What do the codons on mRNA specify? What are the three main steps of protein synthesis? Put the fol ...
... What brings amino acids to the ribosome? How many different amino acids can a tRNA carry? What are the three unpaired bases at the bottom of a tRNA called? What type of bond forms between amino acids? What do the codons on mRNA specify? What are the three main steps of protein synthesis? Put the fol ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis - Kent City School District
... Macromolecule made of nucleotides from DNA Used to build proteins 3 types total ...
... Macromolecule made of nucleotides from DNA Used to build proteins 3 types total ...
Modeling Protein synthesis lab
... DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in polypeptides, and thus the srructure of proteins. In a process called transcripaon which takes place in the nucleus of the cell, messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNlt's nucleotide sequences in the form of a complementary RNA molecule. Then the m ...
... DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in polypeptides, and thus the srructure of proteins. In a process called transcripaon which takes place in the nucleus of the cell, messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNlt's nucleotide sequences in the form of a complementary RNA molecule. Then the m ...
Protein Synthesis Notes - Hamilton Local Schools
... o The mRNA tells the ribosome what the sequence of amino acids is for that protein. ...
... o The mRNA tells the ribosome what the sequence of amino acids is for that protein. ...
Poster
... RNA polymerase II is essential to life in cells. Found in the nucleus of a cell, this molecule is a multi‐subunit protein. RNA Pol II makes messenger RNA (mRNA) copies of genes. This process is called transcription and is the first step in protein synthesis. Genes are made of DNA and contain t ...
... RNA polymerase II is essential to life in cells. Found in the nucleus of a cell, this molecule is a multi‐subunit protein. RNA Pol II makes messenger RNA (mRNA) copies of genes. This process is called transcription and is the first step in protein synthesis. Genes are made of DNA and contain t ...
Water
... as the mRNA is moved through the ribosome one codon at a time. (When completed, the polypeptide is released from the ribosome.) ...
... as the mRNA is moved through the ribosome one codon at a time. (When completed, the polypeptide is released from the ribosome.) ...
Anaerobic Respiration - Deans Community High School
... The completed molecule of mRNA leaves the nucleus through a pore in the nuclear membrane and enters the ____________. Each triplet of bases on mRNA is called a __________. tRNA A second type of RNA is found in the cell’s cytoplasm. This is called ____________ _____ (______). Each molecule of tRNA ha ...
... The completed molecule of mRNA leaves the nucleus through a pore in the nuclear membrane and enters the ____________. Each triplet of bases on mRNA is called a __________. tRNA A second type of RNA is found in the cell’s cytoplasm. This is called ____________ _____ (______). Each molecule of tRNA ha ...
01 - Denton ISD
... Translation converts an mRNA message into a polypeptide, or protein. VOCABULARY ...
... Translation converts an mRNA message into a polypeptide, or protein. VOCABULARY ...
Chapter 14
... • New formed mRNA is an unfinished molecule, not yet ready for use • mRNA transcripts are modified before leaving the nucleus – The 5’ end is capped with a special nucleotide that may serve as a “start” signal for translation – Noncoding portions (introns) are snipped out, and actual coding regions ...
... • New formed mRNA is an unfinished molecule, not yet ready for use • mRNA transcripts are modified before leaving the nucleus – The 5’ end is capped with a special nucleotide that may serve as a “start” signal for translation – Noncoding portions (introns) are snipped out, and actual coding regions ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS WORKSHEET
... 1. DNA CCT CTT TAC ACA CGG AGG GTA CGC TAT TCT ATG ATT ACA CGG TTG CGA mRNA _______________________________________________________________________________ protein _______________________________________________________________________________ 2. DNA AGA ACA TAA TAC CTC TTA ACA CTC TAA GCA CTC ...
... 1. DNA CCT CTT TAC ACA CGG AGG GTA CGC TAT TCT ATG ATT ACA CGG TTG CGA mRNA _______________________________________________________________________________ protein _______________________________________________________________________________ 2. DNA AGA ACA TAA TAC CTC TTA ACA CTC TAA GCA CTC ...
RNA & Protein Synthesis
... like much of the DNA. Also, just like the DNA, it has to be edited to make it sensible. ...
... like much of the DNA. Also, just like the DNA, it has to be edited to make it sensible. ...
Protein Synthesis
... • The ribosome consists of two smaller parts – the 60S and the 40S subunits. (The number refers to the size and the S is for the “sedimentation rate” of the molecule when placed in a centrifuge.) • The ribosome recognizes the 5' cap of the mRNA transcript and begins the process of translation at thi ...
... • The ribosome consists of two smaller parts – the 60S and the 40S subunits. (The number refers to the size and the S is for the “sedimentation rate” of the molecule when placed in a centrifuge.) • The ribosome recognizes the 5' cap of the mRNA transcript and begins the process of translation at thi ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS QUESTIONS
... 2. The template strand of a gene contains the sequence 3’ TTCAGTCGT 5’. Draw the nontemplate sequence and the mRNA sequence, indicating 5’ and 3’ ends of each. Compare the two sequences. 3. Imagine that the nontemplate sequence in question 2 was traqnscribed instead of the template sequence. Draw th ...
... 2. The template strand of a gene contains the sequence 3’ TTCAGTCGT 5’. Draw the nontemplate sequence and the mRNA sequence, indicating 5’ and 3’ ends of each. Compare the two sequences. 3. Imagine that the nontemplate sequence in question 2 was traqnscribed instead of the template sequence. Draw th ...
WLHS / AP Bio / Monson
... REVIEW QUESTIONS: (some may done on a separate sheet of paper and attached) 1) Explain (or use a sketch/diagram) how Hershey & Chase used radioactively labeled viruses to show that DNA, not protein, is the genetic material. 2) Briefly explain the function of each protein / enzyme listed below: A) He ...
... REVIEW QUESTIONS: (some may done on a separate sheet of paper and attached) 1) Explain (or use a sketch/diagram) how Hershey & Chase used radioactively labeled viruses to show that DNA, not protein, is the genetic material. 2) Briefly explain the function of each protein / enzyme listed below: A) He ...
Genetic Coding in Ce..
... DNA Replication cont. 3. The cell has spare DNA Units. 4. The correct DNA unit attaches itself to the appropriate rungs on each of the 2 half-ladders as the DNA molecule splits. A spare AT, a spare TA, a spare GC, & a spare CG. 5. After the DNA finishes “unzipping” and the spare DNA units join ...
... DNA Replication cont. 3. The cell has spare DNA Units. 4. The correct DNA unit attaches itself to the appropriate rungs on each of the 2 half-ladders as the DNA molecule splits. A spare AT, a spare TA, a spare GC, & a spare CG. 5. After the DNA finishes “unzipping” and the spare DNA units join ...
DNA Transcription Translation The Central Dogma Trait RNA
... The same genetic information is in all 100 trillion cells of any one person. Different cells use the same blueprint in different ways. ...
... The same genetic information is in all 100 trillion cells of any one person. Different cells use the same blueprint in different ways. ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.