Flow of information
... A small ribosome subunit loaded with an initiator tRNA (one that can start the process) recognises an mRNA strand as it leaves the nucleus and travels to the cytoplasm. The ribosome subunit bonds to the methylated cap on the mRNA and moves along it ‘scanning’ for a n AUG start - once found, a large ...
... A small ribosome subunit loaded with an initiator tRNA (one that can start the process) recognises an mRNA strand as it leaves the nucleus and travels to the cytoplasm. The ribosome subunit bonds to the methylated cap on the mRNA and moves along it ‘scanning’ for a n AUG start - once found, a large ...
pptx - WVU School of Medicine
... DNA sequences “upstream” of transcription initiation site. • different σ factors recognize different promoters (σ70 = most genes; σ32 = heat shock proteins; σ28 = flagella & chemotaxis genes). • 2 DNA sequences (-35 & -10) found in most prokaryotic promoters – “upstream” of transcription start site ...
... DNA sequences “upstream” of transcription initiation site. • different σ factors recognize different promoters (σ70 = most genes; σ32 = heat shock proteins; σ28 = flagella & chemotaxis genes). • 2 DNA sequences (-35 & -10) found in most prokaryotic promoters – “upstream” of transcription start site ...
DNA –Protein synthesis
... •mRNA: Messenger RNA: carries information •tRNA: Transfer RNA: carries a.a. •One unique tRNA for each a.a. •rRNA: most prevalent type, in ribosome ...
... •mRNA: Messenger RNA: carries information •tRNA: Transfer RNA: carries a.a. •One unique tRNA for each a.a. •rRNA: most prevalent type, in ribosome ...
15.2 Regulation of Transcription & Translation
... If that was the case, cells in your pancreas would produce adrenaline, and cells in testicles would begin to release oestrogen! ...
... If that was the case, cells in your pancreas would produce adrenaline, and cells in testicles would begin to release oestrogen! ...
Protein Synthesis
... time the notes change to a new topic have them switch the color of pen they are using. This makes it simple for them to quickly find information during reviews. Finally, take the last two to three minutes of the lecture portion to have students use their highlighters to bold the most important infor ...
... time the notes change to a new topic have them switch the color of pen they are using. This makes it simple for them to quickly find information during reviews. Finally, take the last two to three minutes of the lecture portion to have students use their highlighters to bold the most important infor ...
Bell work Objectives: DNA replication DNA Replication
... http://stemcells.nih.gov/StaticResources/info/scireport/images/figurea6.jpg ...
... http://stemcells.nih.gov/StaticResources/info/scireport/images/figurea6.jpg ...
DNA Replication, Transcription, Translation Notes (Central Dogma)
... b) Evolutionary baggage? Selfish genes? c) We do know that having multiple exons in a gene allows eukaryotes to make multiple functional proteins from one gene ("alternative splicing") ...
... b) Evolutionary baggage? Selfish genes? c) We do know that having multiple exons in a gene allows eukaryotes to make multiple functional proteins from one gene ("alternative splicing") ...
幻灯片 1 - TUST
... The first stage of protein synthesis is amino acid activation, a process in which amino acids are attached to transfer RNA molecules. These RNA molecules are normally between 73 and 93 nucleotides in length and possess several characteristic structural features. The structure of tRNA becomes clearer ...
... The first stage of protein synthesis is amino acid activation, a process in which amino acids are attached to transfer RNA molecules. These RNA molecules are normally between 73 and 93 nucleotides in length and possess several characteristic structural features. The structure of tRNA becomes clearer ...
rss_genetics_lesson
... • 3 types: • messenger RNA: mRNA carries the DNA nucleotide sequence for a protein from the nucleus to the ribosome • transfer RNA: tRNA transports amino acids (building blocks of proteins) to the ribosome • ribosomal RNA: rRNA makes up the structure of the ribosome ...
... • 3 types: • messenger RNA: mRNA carries the DNA nucleotide sequence for a protein from the nucleus to the ribosome • transfer RNA: tRNA transports amino acids (building blocks of proteins) to the ribosome • ribosomal RNA: rRNA makes up the structure of the ribosome ...
unit-4-genetics-transmission-storage
... Translation (translation of mRNA into a combination of amino acids – polypeptide chain): The mRNA meets with a corresponding ribosome and awaits a tRNA (transfer RNA – which transfers amino acids) to bond with/complement its code (example: if the mRNA is CAG, the tRNA would be GUC). The code, or cod ...
... Translation (translation of mRNA into a combination of amino acids – polypeptide chain): The mRNA meets with a corresponding ribosome and awaits a tRNA (transfer RNA – which transfers amino acids) to bond with/complement its code (example: if the mRNA is CAG, the tRNA would be GUC). The code, or cod ...
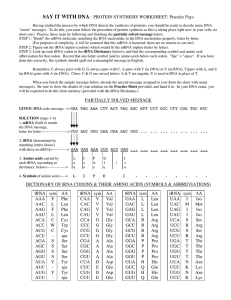
SAY IT WITH DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS WORKSHEET: Practice
... Having studied the process by which DNA directs the synthesis of proteins, you should be ready to decode some DNA "secret" messages. To do this, you must follow the procedure of protein synthesis as this is taking place right now in your cells; no short cuts! Practice these steps by following and fi ...
... Having studied the process by which DNA directs the synthesis of proteins, you should be ready to decode some DNA "secret" messages. To do this, you must follow the procedure of protein synthesis as this is taking place right now in your cells; no short cuts! Practice these steps by following and fi ...
Gene Section YPEL5 (yippee-like 5 (Drosophila)) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Hosono K, Noda S, Shimizu A, Nakanishi N, Ohtsubo M, Shimizu N, Minoshima S.. YPEL5 protein of the YPEL gene family is involved in the cell cycle progression by interacting with two distinct proteins RanBPM and RanBP10. Genomics. 2010 Aug;96(2):102-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2010.05.003. Epub 2010 May ...
... Hosono K, Noda S, Shimizu A, Nakanishi N, Ohtsubo M, Shimizu N, Minoshima S.. YPEL5 protein of the YPEL gene family is involved in the cell cycle progression by interacting with two distinct proteins RanBPM and RanBP10. Genomics. 2010 Aug;96(2):102-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2010.05.003. Epub 2010 May ...
ERT 101 Biochemistry
... respectively, in the other. DNA replication is a simple concept - a cell separates the two original strands and uses each as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. Biologists say that DNA replication is semiconservative because each daughter DNA molecule is composed of one origi ...
... respectively, in the other. DNA replication is a simple concept - a cell separates the two original strands and uses each as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. Biologists say that DNA replication is semiconservative because each daughter DNA molecule is composed of one origi ...
2368AOS1-genefunctiongenesinaction2
... Some genes are only active during the embryonic period whilst others such as Huntington’s disease are only expressed in the phenotype only when the individual is well into adulthood. Some genes are only active in certain tissues (eg. Genes that produce insulin are only active in the pancreas). ...
... Some genes are only active during the embryonic period whilst others such as Huntington’s disease are only expressed in the phenotype only when the individual is well into adulthood. Some genes are only active in certain tissues (eg. Genes that produce insulin are only active in the pancreas). ...
Dicer-Like
... What is Dicer’s role in RNAi? • Activated by exogenous double-stranded (ds) RNA • miRNA (micro RNA) -small, non-coding regions of double-stranded (ds) RNA 21-22 nucleotides ...
... What is Dicer’s role in RNAi? • Activated by exogenous double-stranded (ds) RNA • miRNA (micro RNA) -small, non-coding regions of double-stranded (ds) RNA 21-22 nucleotides ...
PowerPoint- Protein Shape
... Mutations (changes in the genetic code) that can lead to changes in the amino acid sequence and ultimately to the overall shape of the protein. Why? ...
... Mutations (changes in the genetic code) that can lead to changes in the amino acid sequence and ultimately to the overall shape of the protein. Why? ...
RNA & Protein Synthesis
... • People who are lactose intolerant have a mutation in the gene that codes for lactase. • Since they don’t produce lactase, they can’t digest lactose. ...
... • People who are lactose intolerant have a mutation in the gene that codes for lactase. • Since they don’t produce lactase, they can’t digest lactose. ...
Instructional Objectives—DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Objective 10: Identify the role of ribosomes in protein synthesis. What is the job of the ribosome? Objective 11: Describe the role of DNA, mRNA, tRNA and ribosomes in protein synthesis. Describe the importance of each of the following molecules during protein synthesis? DNAmRNAtRNARibosomesObject ...
... Objective 10: Identify the role of ribosomes in protein synthesis. What is the job of the ribosome? Objective 11: Describe the role of DNA, mRNA, tRNA and ribosomes in protein synthesis. Describe the importance of each of the following molecules during protein synthesis? DNAmRNAtRNARibosomesObject ...
Biology and computers - Cal State LA
... how Clustal W gives you a clue as to which part(s) of the Cytochrome C protein you would hypothesize are most important to its function (which is/are the same in all 3 organisms). Start your paragraph as a hypothesis as to which parts are most important, and write your discussion as a defense of you ...
... how Clustal W gives you a clue as to which part(s) of the Cytochrome C protein you would hypothesize are most important to its function (which is/are the same in all 3 organisms). Start your paragraph as a hypothesis as to which parts are most important, and write your discussion as a defense of you ...
RNA chapter 13.1 - Red Hook Central Schools
... code from the nucleus to the ribosomes • Ribosomal RNA: (rRNA) compose the two subunits that make up a ribosome • Transfer RNA: (tRNA) carries amino acids to the ribosome to be assembled into proteins ...
... code from the nucleus to the ribosomes • Ribosomal RNA: (rRNA) compose the two subunits that make up a ribosome • Transfer RNA: (tRNA) carries amino acids to the ribosome to be assembled into proteins ...
Transcription AND Translation
... • Before RNA leaves the nucleus, the introns are removed and the exons join together to form one strand: a “continuous coding sequence,” which makes up the mRNA molecule. (page 182) • This process is known as RNA splicing. The mRNA is now ready for translation. ...
... • Before RNA leaves the nucleus, the introns are removed and the exons join together to form one strand: a “continuous coding sequence,” which makes up the mRNA molecule. (page 182) • This process is known as RNA splicing. The mRNA is now ready for translation. ...
Fundamentals of Cell Biology
... Figure 08.10: Exposure of the polyadenylation sequence by endonuclease and exonuclease cleavage triggers addition of the poly(A) tail by pol(A) polymerase. ...
... Figure 08.10: Exposure of the polyadenylation sequence by endonuclease and exonuclease cleavage triggers addition of the poly(A) tail by pol(A) polymerase. ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.