Ancient Greece
... Herodotus, a Greek scholar, tells the full story of the Persian Wars. He is considered to be the first historian. Persians blocked the entrance to the Hellespont, keeping Athens from trading in the Black Sea. The Persians controlled former Greek city-states in Asia Minor. This was a clash between ...
... Herodotus, a Greek scholar, tells the full story of the Persian Wars. He is considered to be the first historian. Persians blocked the entrance to the Hellespont, keeping Athens from trading in the Black Sea. The Persians controlled former Greek city-states in Asia Minor. This was a clash between ...
Greece #3
... Herodotus, a Greek scholar, tells the full story of the Persian Wars. He is considered to be the first historian. Persians blocked the entrance to the Hellespont, keeping Athens from trading in the Black Sea. The Persians controlled former Greek city-states in Asia Minor. This was a clash between ...
... Herodotus, a Greek scholar, tells the full story of the Persian Wars. He is considered to be the first historian. Persians blocked the entrance to the Hellespont, keeping Athens from trading in the Black Sea. The Persians controlled former Greek city-states in Asia Minor. This was a clash between ...
Persian Wars
... …battle was a total loss for the Greeks, but helped win the war …Persians are forced to retreat after the majority of their navy is defeated by the Athenians & other Greek allies Thermopylae ...
... …battle was a total loss for the Greeks, but helped win the war …Persians are forced to retreat after the majority of their navy is defeated by the Athenians & other Greek allies Thermopylae ...
Ancient Greece 4-3 Persia Attacks the Greeks
... 4) Battle of Plataea (479 B.C.) = Persians vs. Greeks Greeks win with largest Greek army ever Battle was turning point for the Greeks, pushing the Persians back into Asia Minor. By working together, the Greek city-states saved their homeland History of the Persian War – book by Herodotus ...
... 4) Battle of Plataea (479 B.C.) = Persians vs. Greeks Greeks win with largest Greek army ever Battle was turning point for the Greeks, pushing the Persians back into Asia Minor. By working together, the Greek city-states saved their homeland History of the Persian War – book by Herodotus ...
Greco-Persian War Essay, Research Paper In September of 490 BC
... Attica. The Athenians have just repulsed the first Persian invasion of Greece. The Greek army was vested to ten different generals each controlling one day of battle. The generals were evenly divided on whether to wait for the Persians to attack or to attack them. A civil official, Callimachus, who ...
... Attica. The Athenians have just repulsed the first Persian invasion of Greece. The Greek army was vested to ten different generals each controlling one day of battle. The generals were evenly divided on whether to wait for the Persians to attack or to attack them. A civil official, Callimachus, who ...
Marathon: The first battle of the Persian
... Earth and water: symbol of surrender in the ancient Achaemenid empire. ...
... Earth and water: symbol of surrender in the ancient Achaemenid empire. ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR GREEK QUIZ II Answer the following questions
... tor who wanted to take over Athens. 10 years after Marathon. 5. _____ The Greeks were called Hoplites because of the shape of their helmets. 21. _____ The Spartans wouldn’t fight because it was a religious holiday. 6. _____ The Greeks fought in a formation called a 22. _____ The Spartans had t ...
... tor who wanted to take over Athens. 10 years after Marathon. 5. _____ The Greeks were called Hoplites because of the shape of their helmets. 21. _____ The Spartans wouldn’t fight because it was a religious holiday. 6. _____ The Greeks fought in a formation called a 22. _____ The Spartans had t ...
Cambridge Ancient History, 2nd edition, Vol. IV
... R.S. Conway’s chapters on the same areas in the first edition. Economical chapters by David Ridgway, Edward Togo Salmon, J.H.W. Penney and David Asheri show the complexity o f the issues. Again, the timespan runs back well before 525, though the lower limit is the early fifth century. The heart o f ...
... R.S. Conway’s chapters on the same areas in the first edition. Economical chapters by David Ridgway, Edward Togo Salmon, J.H.W. Penney and David Asheri show the complexity o f the issues. Again, the timespan runs back well before 525, though the lower limit is the early fifth century. The heart o f ...
CH 4: Ancient Greece
... King Leonidas of Sparta leads Greek army Stalls the Persian army at a mountain pass Battle lasts three days Greeks betrayed by local who tells the Persians how to get around the mountains and attack the Greeks from behind ...
... King Leonidas of Sparta leads Greek army Stalls the Persian army at a mountain pass Battle lasts three days Greeks betrayed by local who tells the Persians how to get around the mountains and attack the Greeks from behind ...
Ch 5 Power Point
... Long after Greeks ceased to exert any direct political control on those areas, their culture remained a powerful influence. ...
... Long after Greeks ceased to exert any direct political control on those areas, their culture remained a powerful influence. ...
Greek cities of Anatolia – 5 year revolt against Persian rule (499 BCE)
... infantry, catapults = very new technology King Phillip’s son: Alexander the Great – invaded Persia (336 BCE) and won all the way to modern-day Pakistan. -kept administration apparatus of Persian Empire. Used Persian officials and Greeks and Macedonians. Successor to Persian King. Hellenistic Synthes ...
... infantry, catapults = very new technology King Phillip’s son: Alexander the Great – invaded Persia (336 BCE) and won all the way to modern-day Pakistan. -kept administration apparatus of Persian Empire. Used Persian officials and Greeks and Macedonians. Successor to Persian King. Hellenistic Synthes ...
notes
... i. Huge army, drawn from all over empire, brought together 1. Accuracy of troop numbers: Herodutus (contemporary): up to _____ million! 2. Modern estimates, based on supply limitations: __________________ ii. Herodutus claimed Persians had a fleet of over ___________ ships (probably more accurate) i ...
... i. Huge army, drawn from all over empire, brought together 1. Accuracy of troop numbers: Herodutus (contemporary): up to _____ million! 2. Modern estimates, based on supply limitations: __________________ ii. Herodutus claimed Persians had a fleet of over ___________ ships (probably more accurate) i ...
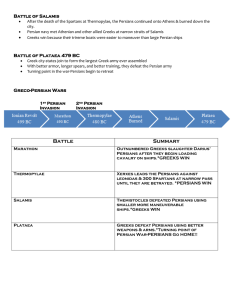
Battle of Salamis After the death of the Spartans at Thermopylae, the
... Greeks win because their trireme boats were easier to maneuver than large Persian ships ...
... Greeks win because their trireme boats were easier to maneuver than large Persian ships ...
The Persian Wars
... Persia conquers the Greeks along the Ionian coast and force them to pay tribute (taxes) to the Persian Empire ...
... Persia conquers the Greeks along the Ionian coast and force them to pay tribute (taxes) to the Persian Empire ...
The Persian Empire
... Created an army that grew into the Persian Empire Under Cyrus’ rule, the empire stretched to be about the size of the continental United States. Cyrus held his kingdom together by ruling fairly. Allowed his peoples to keep their own languages, religions, and laws. ...
... Created an army that grew into the Persian Empire Under Cyrus’ rule, the empire stretched to be about the size of the continental United States. Cyrus held his kingdom together by ruling fairly. Allowed his peoples to keep their own languages, religions, and laws. ...
this is a test
... Classical Greece – emerge 750 BCE and flourished for about 400 years Small competing city-states due to mountainous terrain (seas allowed for trade) ...
... Classical Greece – emerge 750 BCE and flourished for about 400 years Small competing city-states due to mountainous terrain (seas allowed for trade) ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR GREEK QUIZ II Answer the following questions
... tor who wanted to take over Athens. 10 years after Marathon. 5. _____ The Greeks were called Hoplites because 21. _____ The Spartans wouldn’t fight because of the shape of their helmets. it was a religious holiday. 6. _____ The Greeks fought in a formation called a 22. _____ The Spartans had t ...
... tor who wanted to take over Athens. 10 years after Marathon. 5. _____ The Greeks were called Hoplites because 21. _____ The Spartans wouldn’t fight because of the shape of their helmets. it was a religious holiday. 6. _____ The Greeks fought in a formation called a 22. _____ The Spartans had t ...
Greek Warfare - Little Miami Schools
... strength of lions or of bulls shall hold him, Strength against strength; for he has the power of Zeus, And will not be checked till one of these two he has consumed.” ...
... strength of lions or of bulls shall hold him, Strength against strength; for he has the power of Zeus, And will not be checked till one of these two he has consumed.” ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide
... Hellenistic Age- Historians’ term for the era, usually dated 323–30 B.C.E., in which Greek culture spread across western Asia and northeastern Africa after the conquests of Alexander the Great. The period ended with the fall of the last major Hellenistic kingdom to Rome, but Greek cultural influence ...
... Hellenistic Age- Historians’ term for the era, usually dated 323–30 B.C.E., in which Greek culture spread across western Asia and northeastern Africa after the conquests of Alexander the Great. The period ended with the fall of the last major Hellenistic kingdom to Rome, but Greek cultural influence ...
Classical Greece The High Point of Greek civilization is the time
... failed. The ruler of the Persian Empire at the time was Darius. He planned to seek revenge against the Greeks, specifically Athens. In 490 BC the Persians landed an army at the city of Marathon, only 26 miles from Athens. The Athenians and their allies were clearly outnumbered but continued to attac ...
... failed. The ruler of the Persian Empire at the time was Darius. He planned to seek revenge against the Greeks, specifically Athens. In 490 BC the Persians landed an army at the city of Marathon, only 26 miles from Athens. The Athenians and their allies were clearly outnumbered but continued to attac ...
Greek - Persian War Notes
... Chapter 28 – Greek and Persian Wars Issues: 1. There is no unit on Persian History in 6th grade – unfortunate. 2. Unify the Greek People for a time as one military force: When you attack a divided region, it unifies under common threat. Overview: 1. Battles of importance – Thermopoly (movie 300), Ma ...
... Chapter 28 – Greek and Persian Wars Issues: 1. There is no unit on Persian History in 6th grade – unfortunate. 2. Unify the Greek People for a time as one military force: When you attack a divided region, it unifies under common threat. Overview: 1. Battles of importance – Thermopoly (movie 300), Ma ...
AE80 Alexander the Great and the Alexander Tradition
... as far as the river Jaxartes. 522-486 BC Darius I, the first "Great King", usurps throne. Age of consolidation, with ruthless suppression of local uprisings that threatened the unity of the Achaemenid empire. [See representation on the Behistun Inscription, 521-519 BC]. 499 BC Revolt against Persian ...
... as far as the river Jaxartes. 522-486 BC Darius I, the first "Great King", usurps throne. Age of consolidation, with ruthless suppression of local uprisings that threatened the unity of the Achaemenid empire. [See representation on the Behistun Inscription, 521-519 BC]. 499 BC Revolt against Persian ...
Pontus (region)

Pontus (/ˈpɒntəs/; Greek: Πόντος, ""sea"") is a historical Greek designation for a region on the southern coast of the Black Sea, located in modern-day eastern Black Sea Region of Turkey. The name was applied to the coastal region and its mountainous hinterland (rising to the Pontic Alps in the east) in antiquity by the Greeks who colonized the area, and derived from the Greek name of the Black Sea: Πόντος Εύξεινος Pontos Euxeinos (""Hospitable Sea""), or simply Pontos. Having originally no specific name, the region east of the river Halys was spoken of as the country εν Πόντοι en Pontôi, ""on the [Euxeinos] Pontos"", and hence acquired the name of Pontus, which is first found in Xenophon's Anabasis. The extent of the region varied through the ages, but generally it extended from the borders of Colchis (modern Georgia) until well into Paphlagonia in the west, with varying amounts of hinterland. Several states and provinces bearing the name of Pontus or variants thereof were established in the region in Hellenistic, Roman and Byzantine periods, culminating in the late Byzantine Empire of Trebizond. Pontus is sometimes considered as the home of the Amazons, with the name Amasia not only used for a city (Amasya) but for all of Pontus in Greek mythology.