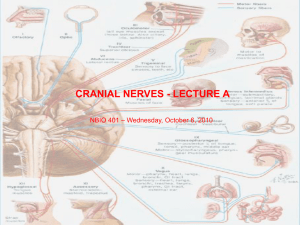
neurology part1_lab10_10_5_2011
... (A) Vestibular ganglia is sensory ganglia contain cell bodies of vestibular nerve & it’s in the periphery contain group of cell bodies but vestibular nuclei it’s centrally located in the central nervous system specifically in the brain stem. Axons of the vestibular nerve synapse in the vestibular nu ...
... (A) Vestibular ganglia is sensory ganglia contain cell bodies of vestibular nerve & it’s in the periphery contain group of cell bodies but vestibular nuclei it’s centrally located in the central nervous system specifically in the brain stem. Axons of the vestibular nerve synapse in the vestibular nu ...
Chapter 13 Central Nervous System
... VIII. Medulla Oblongata continuous with spinal cord A. Structure 1. gray matter a. nucleus gracilis - relay sensory information to thalamus b. nucleus cuneatus - as above c. olivary nuclei - relay to cerebellum from all other regions d. nuclei of cranial nerves numbers VIII, IX, X, XI, and XII e. re ...
... VIII. Medulla Oblongata continuous with spinal cord A. Structure 1. gray matter a. nucleus gracilis - relay sensory information to thalamus b. nucleus cuneatus - as above c. olivary nuclei - relay to cerebellum from all other regions d. nuclei of cranial nerves numbers VIII, IX, X, XI, and XII e. re ...
NEURO ANATOMY
... At the upper part of sulcus limitance there is a pigmented area known as substantia ferrigenea. Lateral to the sulcus limitance there is vestibular area contains some vestibular nuclei. ...
... At the upper part of sulcus limitance there is a pigmented area known as substantia ferrigenea. Lateral to the sulcus limitance there is vestibular area contains some vestibular nuclei. ...
Slide ()
... The central autonomic network. Nearly all of the cell groups illustrated here are interconnected with one another, forming the central autonomic network. A. Main afferent pathways. Visceral information (solid lines) is distributed to the brain from the nucleus of the solitary tract and from ascendin ...
... The central autonomic network. Nearly all of the cell groups illustrated here are interconnected with one another, forming the central autonomic network. A. Main afferent pathways. Visceral information (solid lines) is distributed to the brain from the nucleus of the solitary tract and from ascendin ...
Slide ()
... Development of the cranial nuclei. A–D. Schematic section through the hind brain at three developmental time points (A–C) and maturity (D). The space within the sections is the fourth ventricle. During development the fourth ventricle, initially flattened dorsoventrally just like the spinal cord, ex ...
... Development of the cranial nuclei. A–D. Schematic section through the hind brain at three developmental time points (A–C) and maturity (D). The space within the sections is the fourth ventricle. During development the fourth ventricle, initially flattened dorsoventrally just like the spinal cord, ex ...
Nervous System
... List the subdivisions of the nervous system Define the terms: grey matter, white matter, nucleus, ganglion, tract and nerve. List the parts of the brain. Identify the external and internal features of spinal cord. Enumerate the cranial nerves Describe the parts and distribution of the spinal nerve. ...
... List the subdivisions of the nervous system Define the terms: grey matter, white matter, nucleus, ganglion, tract and nerve. List the parts of the brain. Identify the external and internal features of spinal cord. Enumerate the cranial nerves Describe the parts and distribution of the spinal nerve. ...
11_1_Dienc_CzehlárB
... One of its main functions is the relaying of sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex. With the exception of the olfactory system, every sensory system includes a thalamic nucleus. In the visual system, the thalamus receives input from the retina, which is relayed to the brain via the optic ...
... One of its main functions is the relaying of sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex. With the exception of the olfactory system, every sensory system includes a thalamic nucleus. In the visual system, the thalamus receives input from the retina, which is relayed to the brain via the optic ...
Chp.6 Nervous System
... Consists of the brain, spinal cord, spinal nerves & cranial nerves It controls consciousness and all mental activities, voluntary functions of the five senses Seeing, hearing, feeling, smelling & tasting ...
... Consists of the brain, spinal cord, spinal nerves & cranial nerves It controls consciousness and all mental activities, voluntary functions of the five senses Seeing, hearing, feeling, smelling & tasting ...
Brain Anatomy - Seattle Central College
... • Balance; maintains muscle tone; coordinates fine muscle movement • Comparator: integrates proposed movements with current body position to produce smooth, exact movement • Involved in learning new balance-intensive activities – Riding a bike, yoga, climbing ...
... • Balance; maintains muscle tone; coordinates fine muscle movement • Comparator: integrates proposed movements with current body position to produce smooth, exact movement • Involved in learning new balance-intensive activities – Riding a bike, yoga, climbing ...
15 Anatomy of the Metencephalon and Mesencephalon
... Linking conscious cerebral cortical functions w/ unconscious functions of the brainstem Facilitating memory storage and retrieval ...
... Linking conscious cerebral cortical functions w/ unconscious functions of the brainstem Facilitating memory storage and retrieval ...
Ascending Spinal Tracts
... the thalamus, where it terminates. • The third-order neurone has its cell body in the thalamus. • Its axon passes to the somatosensory cortex of the parietal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere. ...
... the thalamus, where it terminates. • The third-order neurone has its cell body in the thalamus. • Its axon passes to the somatosensory cortex of the parietal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere. ...
13 Anatomy of the Metencephalon and Mesencephalon
... Functional grouping rather than anatomical Functions include: ...
... Functional grouping rather than anatomical Functions include: ...
The diencephalon
... lateral wall of third ventricle. There is hardly any activity in the body that is not influenced by the hypothalamus. ...
... lateral wall of third ventricle. There is hardly any activity in the body that is not influenced by the hypothalamus. ...
9.01 - Neuroscience & Behavior, Fall 2003 Massachusetts Institute of Technology
... 1) The Organ of Corti in the inner ear – the cochlea – contains the _________________ membrane, which vibrates in response to sound. This stimulates the ____________ cells, both the inner ones and the outer ones. 2) In the ventral cochlear nucleus, the fibers of the 8th nerve terminate in topographi ...
... 1) The Organ of Corti in the inner ear – the cochlea – contains the _________________ membrane, which vibrates in response to sound. This stimulates the ____________ cells, both the inner ones and the outer ones. 2) In the ventral cochlear nucleus, the fibers of the 8th nerve terminate in topographi ...
TSM7 - Somatosensory Pathways
... ipsilaterally through either the gracile or cuneate fasciculus o The gracile fasciculus conveys sensory information from the lower limbs and trunk o The cuneate fasciculus conveys sensory information from the upper limbs, trunk and neck At the medulla the primary afferents terminate at the gracile o ...
... ipsilaterally through either the gracile or cuneate fasciculus o The gracile fasciculus conveys sensory information from the lower limbs and trunk o The cuneate fasciculus conveys sensory information from the upper limbs, trunk and neck At the medulla the primary afferents terminate at the gracile o ...
Brain/Sc Notes
... Lobes: Frontal (motor areas), parietal, temporal, occipital, insula Outermost portion-cerebral cortex Nerve fibers cross over—motor area on right controls left skeletal muscles Hemisphere dominance—one side of cerebrum controls certain functions—Left hemi dom. In 90% of people. 2. Cerebellum ...
... Lobes: Frontal (motor areas), parietal, temporal, occipital, insula Outermost portion-cerebral cortex Nerve fibers cross over—motor area on right controls left skeletal muscles Hemisphere dominance—one side of cerebrum controls certain functions—Left hemi dom. In 90% of people. 2. Cerebellum ...
Sp.CBSTH functions
... Cranial nerve nuclei: The hypoglossal nerve Glossopharyngeal and Vagus nerves. ...
... Cranial nerve nuclei: The hypoglossal nerve Glossopharyngeal and Vagus nerves. ...
Directed study File
... 5. Which area of the body has the highest concentration of mechanoreceptors? Why might this be? 6. How does stimulation of a receptor transduce into a generator potential? 7. How is information about intensity and duration of a stimulus conveyed to the CNS? 8. With reference to sensation, what is me ...
... 5. Which area of the body has the highest concentration of mechanoreceptors? Why might this be? 6. How does stimulation of a receptor transduce into a generator potential? 7. How is information about intensity and duration of a stimulus conveyed to the CNS? 8. With reference to sensation, what is me ...
Trigeminal nerve

The trigeminal nerve (the fifth cranial nerve, or simply CN V) is a nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing. The largest of the cranial nerves, its name (""trigeminal"" = tri-, or three and -geminus, or twin; thrice-twinned) derives from the fact that each trigeminal nerve (one on each side of the pons) has three major branches: the ophthalmic nerve (V1), the maxillary nerve (V2), and the mandibular nerve (V3). The ophthalmic and maxillary nerves are purely sensory, and the mandibular nerve has sensory (or ""cutaneous"") and motor functions.Sensory information from the face and body is processed by parallel pathways in the central nervous system. The motor division of the trigeminal nerve derives from the basal plate of the embryonic pons, and the sensory division originates in the cranial neural crest.