GeneralOrganizationoftheNervousSystem(1)
... velocity, slowly adapting touch/pressure receptors; “fast” nociceptors. • Group IV 1mu or less in in diameter, not myelinated, <1 m/sec conduction; “slow” pain, temperature, itch, tickle, etc. ...
... velocity, slowly adapting touch/pressure receptors; “fast” nociceptors. • Group IV 1mu or less in in diameter, not myelinated, <1 m/sec conduction; “slow” pain, temperature, itch, tickle, etc. ...
Spinal and Cranial Nerves
... Cranial Nerves XI and XII Accessory (XI) • primarily motor • motor to muscles of soft palate, pharynx, larynx, neck, and back ...
... Cranial Nerves XI and XII Accessory (XI) • primarily motor • motor to muscles of soft palate, pharynx, larynx, neck, and back ...
Sensory neurons (감각 신경)
... motor impulses into unconscious coordination of movement. 좌표 와 운동의 의식이 조정 에 모터 충동 을 변조한다. • Hand-eye coordination. • Maintain posture and balance. 자세와 균형을 유 지. ...
... motor impulses into unconscious coordination of movement. 좌표 와 운동의 의식이 조정 에 모터 충동 을 변조한다. • Hand-eye coordination. • Maintain posture and balance. 자세와 균형을 유 지. ...
SBI4U - 9.3
... to communicate • Each hemisphere can be further subdivided into 4 lobes: frontal, temporal, occipital, and parietal ...
... to communicate • Each hemisphere can be further subdivided into 4 lobes: frontal, temporal, occipital, and parietal ...
Questions on the Nervous system
... - structural classification of nervous system - functional classification of nervous system - classification of the motor nervous system - the two principle types of nerve cells and function of each - common structure of neuron - the complex receptors - the simple receptors - structural classificati ...
... - structural classification of nervous system - functional classification of nervous system - classification of the motor nervous system - the two principle types of nerve cells and function of each - common structure of neuron - the complex receptors - the simple receptors - structural classificati ...
Schematic Drawing of the Lumbar Plexus
... Comparison of Somatic and Sympathetic Pathways in the Thorax ...
... Comparison of Somatic and Sympathetic Pathways in the Thorax ...
Anatomy or the trigeminal nerve. Key anatomical facts for MRI
... course towards its distribution territory, crossing several regions with a complex anatomy and establishing important relationships with several structures. The nerve fibers originate in the brainstem and are part of several grey matter nuclei occupying all the brainstem and even the first spinal ce ...
... course towards its distribution territory, crossing several regions with a complex anatomy and establishing important relationships with several structures. The nerve fibers originate in the brainstem and are part of several grey matter nuclei occupying all the brainstem and even the first spinal ce ...
Cerebrum - ISpatula
... pathway from the inner ear to the brain transverse tracts that interconnect right and left side of the cerebellum (middle ...
... pathway from the inner ear to the brain transverse tracts that interconnect right and left side of the cerebellum (middle ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM I
... • hypoglossal n. (12th) • 3 pairs are sensory: • olfactory n. (1st) • optic n. (2nd) • vestibulocochlear n. (8th) ...
... • hypoglossal n. (12th) • 3 pairs are sensory: • olfactory n. (1st) • optic n. (2nd) • vestibulocochlear n. (8th) ...
1 Chapter 12 Central Nervous System Spinal Cord
... • Dorsal horns – associated with afferent, sensory nerve impulses from receptors, C1-L5 neuron cell bodies bundled in dorsal root ganglion • Ventral horns – associated with efferent, motor nerve impulses to effectors, C1-L5 neuron cell bodies are in gray matter of ventral horn • Lateral horns – only ...
... • Dorsal horns – associated with afferent, sensory nerve impulses from receptors, C1-L5 neuron cell bodies bundled in dorsal root ganglion • Ventral horns – associated with efferent, motor nerve impulses to effectors, C1-L5 neuron cell bodies are in gray matter of ventral horn • Lateral horns – only ...
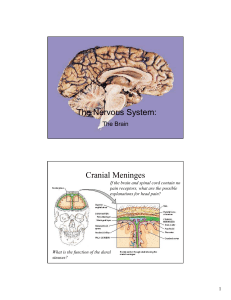
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
... b. linking conscious intellectual functions of cerebrum with unconscious & autonomic functions in brainstem c. long term memory storage & retrieval V. Cerebellum - functions include control of subconscious skeletal muscle movement necessary for balance, coordination & posture - separated from cerebr ...
... b. linking conscious intellectual functions of cerebrum with unconscious & autonomic functions in brainstem c. long term memory storage & retrieval V. Cerebellum - functions include control of subconscious skeletal muscle movement necessary for balance, coordination & posture - separated from cerebr ...
BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY Zsolt Liposits and Imre Kalló 2016
... One has gained sufficient knowledge, if understands and can explain the followings: 1) The thalamus is a complex nucleus; each of its nuclei are in reciprocal connection with the corresponding areas of the cerebral cortex. 2) There is a functional distinction among the thalamic nuclei; there are nuc ...
... One has gained sufficient knowledge, if understands and can explain the followings: 1) The thalamus is a complex nucleus; each of its nuclei are in reciprocal connection with the corresponding areas of the cerebral cortex. 2) There is a functional distinction among the thalamic nuclei; there are nuc ...
16. Anatomy of Brainstem
... pons. – 2 bulging cerebral peduncles on the ventral side. These contain: • Descending fibers that go to the cerebellum via the pons • Descending pyramidal tracts ...
... pons. – 2 bulging cerebral peduncles on the ventral side. These contain: • Descending fibers that go to the cerebellum via the pons • Descending pyramidal tracts ...
Cranial Nerve Nuclei
... Trigeminal nerve (afferent: touch, muscle spindle/joint, pain & temperature from head efferent: chewing muscles) ...
... Trigeminal nerve (afferent: touch, muscle spindle/joint, pain & temperature from head efferent: chewing muscles) ...
12_lecture_ppt Motor and Sensory Cortex Only
... – Axons leave CNS thru nerves, innervate skeletal muscles (motor units) – Cell bodies found in cranial nuclei or anterior horn of spinal cord gray matter ...
... – Axons leave CNS thru nerves, innervate skeletal muscles (motor units) – Cell bodies found in cranial nuclei or anterior horn of spinal cord gray matter ...
3-As.Tracts 2014 (final).
... • The third-order neurone has its cell body in the thalamus. • Its axon passes to the somatosensory cortex of the parietal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere. ...
... • The third-order neurone has its cell body in the thalamus. • Its axon passes to the somatosensory cortex of the parietal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere. ...
L4-As.Tracts 2014 (final).
... The first-order neurone or primary afferent neurone) enters the spinal cord through the dorsal root of a spinal nerve and its cell body lies in the dorsal root ganglion. ...
... The first-order neurone or primary afferent neurone) enters the spinal cord through the dorsal root of a spinal nerve and its cell body lies in the dorsal root ganglion. ...
Neuro Anatomy Lec.6 د.عبد الجبار الحبي طي The Pons Is the middle
... of the extra-ocular muscles , and also contains edinger-westphal nucleus as a parasympathetic part whose fibers goes to ciliary ganglion to supply constrictor pupillae muscle and ciliary body . ii- Nucleus of the trochlear nerve: - in the lower part of midbrain at the level of inf. Colliculus. iii- ...
... of the extra-ocular muscles , and also contains edinger-westphal nucleus as a parasympathetic part whose fibers goes to ciliary ganglion to supply constrictor pupillae muscle and ciliary body . ii- Nucleus of the trochlear nerve: - in the lower part of midbrain at the level of inf. Colliculus. iii- ...
3-As.Tracts 2015 (final).
... The first-order neurone or primary afferent neurone) enters the spinal cord through the dorsal root of a spinal nerve and its cell body lies in the dorsal root ganglion. ...
... The first-order neurone or primary afferent neurone) enters the spinal cord through the dorsal root of a spinal nerve and its cell body lies in the dorsal root ganglion. ...
3-As.Tracts 2016-17
... The first-order neurone or primary afferent neurone) enters the spinal cord through the dorsal root of a spinal nerve and its cell body lies in the dorsal root ganglion. ...
... The first-order neurone or primary afferent neurone) enters the spinal cord through the dorsal root of a spinal nerve and its cell body lies in the dorsal root ganglion. ...
Organization of NS and the neuron File
... Primary reflex centre Protected by vertebrae, meninges and cerebrospinal fluid Sensory nerves enter spinal cord via Dorsal root and motor nerves leave through ventral root ...
... Primary reflex centre Protected by vertebrae, meninges and cerebrospinal fluid Sensory nerves enter spinal cord via Dorsal root and motor nerves leave through ventral root ...
Trigeminal nerve

The trigeminal nerve (the fifth cranial nerve, or simply CN V) is a nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing. The largest of the cranial nerves, its name (""trigeminal"" = tri-, or three and -geminus, or twin; thrice-twinned) derives from the fact that each trigeminal nerve (one on each side of the pons) has three major branches: the ophthalmic nerve (V1), the maxillary nerve (V2), and the mandibular nerve (V3). The ophthalmic and maxillary nerves are purely sensory, and the mandibular nerve has sensory (or ""cutaneous"") and motor functions.Sensory information from the face and body is processed by parallel pathways in the central nervous system. The motor division of the trigeminal nerve derives from the basal plate of the embryonic pons, and the sensory division originates in the cranial neural crest.