L3. Olfaction (Zoltán Nusser) Olfactory epithelium: Cilium and
... Oscillation: rhythmic changes in the LFP. It requires periodic and synchronous neuronal activity. The LFP oscillation on its own does not carry any information, but indicates that the activity of a population of nerve cells in a given brain region is periodic and synchronous Odors evoke stimulus-spe ...
... Oscillation: rhythmic changes in the LFP. It requires periodic and synchronous neuronal activity. The LFP oscillation on its own does not carry any information, but indicates that the activity of a population of nerve cells in a given brain region is periodic and synchronous Odors evoke stimulus-spe ...
Neural coding in the primary olfactory cortex
... The primary olfactory (piriform) cortex is a phylogenetically-ancient three-layered structure that is the first cortical destination of olfactory information. The comparatively simple architecture of the piriform cortex (PC) suggests that it may be a valuable model system for the study of cortical s ...
... The primary olfactory (piriform) cortex is a phylogenetically-ancient three-layered structure that is the first cortical destination of olfactory information. The comparatively simple architecture of the piriform cortex (PC) suggests that it may be a valuable model system for the study of cortical s ...
PRACTICE QUIZ
... The loss of taste sensation is called _________________________________________________________. ...
... The loss of taste sensation is called _________________________________________________________. ...
Slide ()
... The olfactory epithelium. A. The olfactory epithelium contains sensory neurons interspersed with supporting cells as well as a basal layer of stem cells. Cilia extend from the dendrite of each neuron into the mucus lining the nasal cavity. An axon extends from the basal end of each neuron to the olf ...
... The olfactory epithelium. A. The olfactory epithelium contains sensory neurons interspersed with supporting cells as well as a basal layer of stem cells. Cilia extend from the dendrite of each neuron into the mucus lining the nasal cavity. An axon extends from the basal end of each neuron to the olf ...
Chemical Senses
... Dickson, 2005) is that of a fly antennal lobe (AL), the equivalent of the vertebrate olfactory bulb. As you can see, the AL is composed of spheroidal structures, the glomeruli. While vertebrate olfactory bulbs may contain thousands of glomeruli, the fly AL contains only ~43 glomeruli. Furthermore, e ...
... Dickson, 2005) is that of a fly antennal lobe (AL), the equivalent of the vertebrate olfactory bulb. As you can see, the AL is composed of spheroidal structures, the glomeruli. While vertebrate olfactory bulbs may contain thousands of glomeruli, the fly AL contains only ~43 glomeruli. Furthermore, e ...
Slide 1
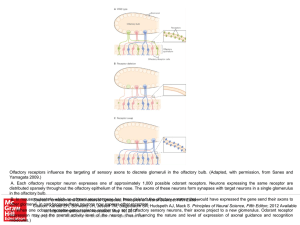
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
Slide ()
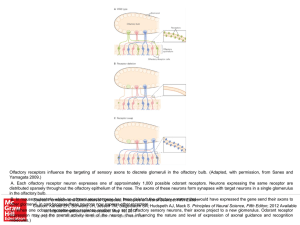
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...