L1 N L2 - Smarthome
... Leviton’s Catalog Nos.51120-1 (120/240V,single -phase version) and the 51120-3 (120/208V,3-phase version) Branch Panel Mounted TVSS devices have been designed to protect homes and small commercial establishments from high voltage transients.The standard J-Box metal enclosure with prepunched standard ...
... Leviton’s Catalog Nos.51120-1 (120/240V,single -phase version) and the 51120-3 (120/208V,3-phase version) Branch Panel Mounted TVSS devices have been designed to protect homes and small commercial establishments from high voltage transients.The standard J-Box metal enclosure with prepunched standard ...
3 Electronic Switches
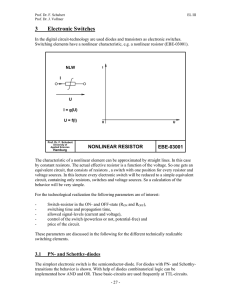
... GND). In the OFF-state the switch is blocked. This blocking behaviour will not be reached inertia-less. So this will limit the maximum frequency of the system. Using two phases or push-pull switches is possible fast switching to all states. Two complementary driven switches (one is in the ON-state, ...
... GND). In the OFF-state the switch is blocked. This blocking behaviour will not be reached inertia-less. So this will limit the maximum frequency of the system. Using two phases or push-pull switches is possible fast switching to all states. Two complementary driven switches (one is in the ON-state, ...
Parallel DC circuits This worksheet and all related files are
... Algebraically manipulate this equation to solve for one of the parallel resistances (R 1 ) in terms of the other two parallel resistances (R2 and R3 ) and the total resistance (R). In other words, write a formula that solves for R1 in terms of all the other variables. file 03067 Question 21 Suppose ...
... Algebraically manipulate this equation to solve for one of the parallel resistances (R 1 ) in terms of the other two parallel resistances (R2 and R3 ) and the total resistance (R). In other words, write a formula that solves for R1 in terms of all the other variables. file 03067 Question 21 Suppose ...
Current Measurements using Shunt
... “Shunt” is the resistor used for the measurements of circuit currents in electric circuits. Actually, shunt was previously taken as the resistor connecting up to the ammeters in parallel to expand the measuring range of electric indicating instruments (indicating meters). *See Diagram1 However, rece ...
... “Shunt” is the resistor used for the measurements of circuit currents in electric circuits. Actually, shunt was previously taken as the resistor connecting up to the ammeters in parallel to expand the measuring range of electric indicating instruments (indicating meters). *See Diagram1 However, rece ...
CASFPGA3 - Indico
... regulator, and measure the voltage drop with a differential amplifier. Below an example from a LLRF board designed by Larry Doolittle (LBNL). ...
... regulator, and measure the voltage drop with a differential amplifier. Below an example from a LLRF board designed by Larry Doolittle (LBNL). ...
Mixing Signals
... A mixer circuit is an important part of many audio systems. For example DJ’s use a mixer to ‘voice over’ records. Recording studios use mixers to balance the sound from different voices and instruments. Summing Amplifier The basic building block of a mixer is an inverting amplifier, configured as a ...
... A mixer circuit is an important part of many audio systems. For example DJ’s use a mixer to ‘voice over’ records. Recording studios use mixers to balance the sound from different voices and instruments. Summing Amplifier The basic building block of a mixer is an inverting amplifier, configured as a ...
Integrated circuit

An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small plate (""chip"") of semiconductor material, normally silicon. This can be made much smaller than a discrete circuit made from independent electronic components. ICs can be made very compact, having up to several billion transistors and other electronic components in an area the size of a fingernail. The width of each conducting line in a circuit can be made smaller and smaller as the technology advances; in 2008 it dropped below 100 nanometers, and has now been reduced to tens of nanometers.ICs were made possible by experimental discoveries showing that semiconductor devices could perform the functions of vacuum tubes and by mid-20th-century technology advancements in semiconductor device fabrication. The integration of large numbers of tiny transistors into a small chip was an enormous improvement over the manual assembly of circuits using discrete electronic components. The integrated circuit's mass production capability, reliability and building-block approach to circuit design ensured the rapid adoption of standardized integrated circuits in place of designs using discrete transistors.ICs have two main advantages over discrete circuits: cost and performance. Cost is low because the chips, with all their components, are printed as a unit by photolithography rather than being constructed one transistor at a time. Furthermore, packaged ICs use much less material than discrete circuits. Performance is high because the IC's components switch quickly and consume little power (compared to their discrete counterparts) as a result of the small size and close proximity of the components. As of 2012, typical chip areas range from a few square millimeters to around 450 mm2, with up to 9 million transistors per mm2.Integrated circuits are used in virtually all electronic equipment today and have revolutionized the world of electronics. Computers, mobile phones, and other digital home appliances are now inextricable parts of the structure of modern societies, made possible by the low cost of integrated circuits.