No Slide Title - UK College of Agriculture
... Extensive studies indicate that biotech-derived foods are as safe or safer than conventional foods. Also although regulatory oversight is evolving, it is more extensive for biotech foods than any others. In balance biotech crops are considered to be beneficial to the environment. Their ...
... Extensive studies indicate that biotech-derived foods are as safe or safer than conventional foods. Also although regulatory oversight is evolving, it is more extensive for biotech foods than any others. In balance biotech crops are considered to be beneficial to the environment. Their ...
GMO-wady i zalety
... Which foods contain GMOs? More than 40 types of plants have been genetically modified worldwide. A much smaller number are commercially grown. The most common genetically modified plants are corn, canola, soybean and cotton. Others include papayas, chrysanthemums, poplars, spruce. GMOs have also be ...
... Which foods contain GMOs? More than 40 types of plants have been genetically modified worldwide. A much smaller number are commercially grown. The most common genetically modified plants are corn, canola, soybean and cotton. Others include papayas, chrysanthemums, poplars, spruce. GMOs have also be ...
Pros Cons Man has been doing selective breeding since agriculture
... the adverse consequences could take years to show up. Genetic pollution is fundamentally different since once the genes are inserted they cannot be recalled. The total herbicides and insecticides used with tolerant crops kill all weeds and insects thus reducing biodiversity in the field. ...
... the adverse consequences could take years to show up. Genetic pollution is fundamentally different since once the genes are inserted they cannot be recalled. The total herbicides and insecticides used with tolerant crops kill all weeds and insects thus reducing biodiversity in the field. ...
Genetic Engineering
... By changing which proteins are produced, genetic engineers can affect the overall traits of the organism. Genetic modification can be completed by a number of different methods: • Inserting new genetic material randomly or in targeted locations • Direct replacement of genes (recombination) • Rem ...
... By changing which proteins are produced, genetic engineers can affect the overall traits of the organism. Genetic modification can be completed by a number of different methods: • Inserting new genetic material randomly or in targeted locations • Direct replacement of genes (recombination) • Rem ...
Plant Breeding as an integral part of Sustainable Agriculture
... main criterion (for GE) is that an organism’s genetic material must have been altered using modern biotechnology to give rise to a novel composition, i.e. a sequence of nucleotides that did not arise by mating, “does not occur naturally” rather than “could occur naturally” ...
... main criterion (for GE) is that an organism’s genetic material must have been altered using modern biotechnology to give rise to a novel composition, i.e. a sequence of nucleotides that did not arise by mating, “does not occur naturally” rather than “could occur naturally” ...
Molecular genetics of gene expression
... bacterial gene for resistance to a specific herbicide. The herbicide has been manufactured by the company for many years. Using a strategy similar to that used to find glyphosate resistance, where might you start to look for a bacterium resistant to that herbicide? ...
... bacterial gene for resistance to a specific herbicide. The herbicide has been manufactured by the company for many years. Using a strategy similar to that used to find glyphosate resistance, where might you start to look for a bacterium resistant to that herbicide? ...
(GMO) Resource Sheet
... Traditional Breeding Traditional breeding is done by allowing two parent plants with the desired traits to crosspollinate – either naturally or hand pollinated in a controlled environment. The seeds generated contain those desirable traits, such as yield, disease resistance, flower color, fruit size ...
... Traditional Breeding Traditional breeding is done by allowing two parent plants with the desired traits to crosspollinate – either naturally or hand pollinated in a controlled environment. The seeds generated contain those desirable traits, such as yield, disease resistance, flower color, fruit size ...
Genetically Modified Organisms
... Traditional Breeding Traditional breeding is done by allowing two parent plants with the desired traits to crosspollinate – either naturally or hand pollinated in a controlled environment. The seeds generated contain those desirable traits, such as yield, disease resistance, flower color, fruit size ...
... Traditional Breeding Traditional breeding is done by allowing two parent plants with the desired traits to crosspollinate – either naturally or hand pollinated in a controlled environment. The seeds generated contain those desirable traits, such as yield, disease resistance, flower color, fruit size ...
Name
... c. Farmers who grow GM crops have much higher yields than farmers growing unmodified crops. d. The populations of bees on farms growing insect-resistant crops are half as large as bee populations on other farms. _____ 15. Which statement below might be used by someone who is arguing against the use ...
... c. Farmers who grow GM crops have much higher yields than farmers growing unmodified crops. d. The populations of bees on farms growing insect-resistant crops are half as large as bee populations on other farms. _____ 15. Which statement below might be used by someone who is arguing against the use ...
Genetic Engineering
... By changing which proteins are produced, genetic engineers can affect the overall traits of the organism. Genetic modification can be completed by a number of different methods: • Inserting new genetic material randomly or in targeted locations • Direct replacement of genes (recombination) • Rem ...
... By changing which proteins are produced, genetic engineers can affect the overall traits of the organism. Genetic modification can be completed by a number of different methods: • Inserting new genetic material randomly or in targeted locations • Direct replacement of genes (recombination) • Rem ...
genetically modified plants
... iron-storage gene from wild soybeans and vitamin E has been enhanced by the use of genes from rice and rock cress. 2008 ...
... iron-storage gene from wild soybeans and vitamin E has been enhanced by the use of genes from rice and rock cress. 2008 ...
Genetic Improvement of Crop Plants
... Like all new technologies there are concerns with the commercial application of biotechnology. These concerns can be divided into three areas [although in many cases the concern crosses more than one area]: ...
... Like all new technologies there are concerns with the commercial application of biotechnology. These concerns can be divided into three areas [although in many cases the concern crosses more than one area]: ...
Chapter 10
... Species can be programmed to make products previously only made by another species Much easier & cheaper to mass produce bacteria cells (than other species) Mass quantities of a useful product e.g insulin can be produced ...
... Species can be programmed to make products previously only made by another species Much easier & cheaper to mass produce bacteria cells (than other species) Mass quantities of a useful product e.g insulin can be produced ...
Goals of Genetic Enginnering - ASAB-NUST
... by increasing yield and reducing reliance upon chemical pesticides and herbicides. • Yet there are many challenges ahead for governments, especially in the areas of safety testing, regulation, international policy and food labeling. ...
... by increasing yield and reducing reliance upon chemical pesticides and herbicides. • Yet there are many challenges ahead for governments, especially in the areas of safety testing, regulation, international policy and food labeling. ...
FOOD UNIT2016
... • Originally a term equivalent to transgenic organism •Also called GMFs or “Frankenfoods” ...
... • Originally a term equivalent to transgenic organism •Also called GMFs or “Frankenfoods” ...
gm_crops_powerpoint
... What is a Genetically Modified (GM) Food? Foods that contain an added gene sequence Foods that have a deleted gene sequence Animal products from animals fed GM feed Products produced by GM organisms ...
... What is a Genetically Modified (GM) Food? Foods that contain an added gene sequence Foods that have a deleted gene sequence Animal products from animals fed GM feed Products produced by GM organisms ...
CAPT EMBEDDED TASK Bioengineered Foods
... genetically altered food based on scientific evidence. You used various sources to support your stance, carefully considering the credibility of those sources. ...
... genetically altered food based on scientific evidence. You used various sources to support your stance, carefully considering the credibility of those sources. ...
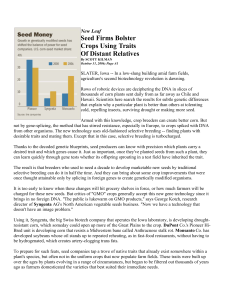
Seed Firms Bolster Crops Using Traits Of Distant Relatives
... from the risk of being decimated by a single killer disease. The technology shift spells change in the way crop-biotech companies wage their battles. Monsanto has grabbed customers from Pioneer by getting to market first with more genetically modified seeds. That and acquisitions have driven Monsant ...
... from the risk of being decimated by a single killer disease. The technology shift spells change in the way crop-biotech companies wage their battles. Monsanto has grabbed customers from Pioneer by getting to market first with more genetically modified seeds. That and acquisitions have driven Monsant ...
Genetically Modified Organisms and Food All modern agricultural
... modification, and introduction of DNA into a target organism; when the target organism is a crop plant or domesticated animal used for food, the purpose is usually to impart to the target organism a desired trait that is unknown or very difficult to obtain by traditional methods (those in use befo ...
... modification, and introduction of DNA into a target organism; when the target organism is a crop plant or domesticated animal used for food, the purpose is usually to impart to the target organism a desired trait that is unknown or very difficult to obtain by traditional methods (those in use befo ...
Genetic Engineering - University of Rhode Island
... transform the living cells. Ligases, which are enzymes that form a new chemical bond to join two molecules, and restriction enzymes, which can cut double-stranded DNA, can be very useful in the gene splicing process as well. The ability to modify DNA has great potential benefits. It could give human ...
... transform the living cells. Ligases, which are enzymes that form a new chemical bond to join two molecules, and restriction enzymes, which can cut double-stranded DNA, can be very useful in the gene splicing process as well. The ability to modify DNA has great potential benefits. It could give human ...
Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs)
... • Causes disease in plants. • Has the ability to transfer a portion of it DNA into plant cells • Once inside a plant cell, its DNA will be incorporated into the DNA of one of the plant’s chromosomes. ...
... • Causes disease in plants. • Has the ability to transfer a portion of it DNA into plant cells • Once inside a plant cell, its DNA will be incorporated into the DNA of one of the plant’s chromosomes. ...
Basic Biotechnology
... Help bacteria reproduce faster Bacteria will clean up after an industrial accident Bacteria will increase rate of nutrient cycling through ecosystem Microbes used to produce food products Control production of harmful bacteria in foods Control microbes in water ...
... Help bacteria reproduce faster Bacteria will clean up after an industrial accident Bacteria will increase rate of nutrient cycling through ecosystem Microbes used to produce food products Control production of harmful bacteria in foods Control microbes in water ...