BASIC FEATURES OF BREEDING
... Sexual recombination in fish might occasionally happen in nature, but most were conducted artificially The principle of artificial sexual recombination is to impose the male and female gametes of different fishes to fuse together as a zygote by artificial methods that does not happen in natural ...
... Sexual recombination in fish might occasionally happen in nature, but most were conducted artificially The principle of artificial sexual recombination is to impose the male and female gametes of different fishes to fuse together as a zygote by artificial methods that does not happen in natural ...
Evolutionary Analysis 4/e
... Sometimes Plants (like humans) promote inbreeding (self-fertilization) Two different but closely related species: ...
... Sometimes Plants (like humans) promote inbreeding (self-fertilization) Two different but closely related species: ...
Genetics - Lectures For UG-5
... • In Drosophila, vestigial wings and ebony colour are due to two separate recessive genes. The dominant alleles are normal (long) wings and normal (gray) body colour. What type of offspring would you expect from a cross between a bomozygous vestigial ebony female and a normal double homozygous (lon ...
... • In Drosophila, vestigial wings and ebony colour are due to two separate recessive genes. The dominant alleles are normal (long) wings and normal (gray) body colour. What type of offspring would you expect from a cross between a bomozygous vestigial ebony female and a normal double homozygous (lon ...
11.1.1 Chromosomes Meiosis and Gamete Formation
... Fertilisation and Variability Further variability arises in a population if a greater number of alleles are present for each gene. If within the population there are individuals with red hair and green eyes, there is greater variability and an even greater opportunity for more gene combinations to ...
... Fertilisation and Variability Further variability arises in a population if a greater number of alleles are present for each gene. If within the population there are individuals with red hair and green eyes, there is greater variability and an even greater opportunity for more gene combinations to ...
Planet Earth and Its Environment A 5000
... Fertilisation and Variability Further variability arises in a population if a greater number of alleles are present for each gene. If within the population there are individuals with red hair and green eyes, there is greater variability and an even greater opportunity for more gene combinations to ...
... Fertilisation and Variability Further variability arises in a population if a greater number of alleles are present for each gene. If within the population there are individuals with red hair and green eyes, there is greater variability and an even greater opportunity for more gene combinations to ...
Fact Sheet 19 | ETHICAL ISSUES IN HUMAN GENETICS AND
... care). Similarly, individuals undergoing genetic testing have a responsibility to consider not only what it means for their own health, but also what the information may mean for their relatives, and their responsibilities towards those relatives. ...
... care). Similarly, individuals undergoing genetic testing have a responsibility to consider not only what it means for their own health, but also what the information may mean for their relatives, and their responsibilities towards those relatives. ...
Full Text - Harvard University
... Cheaters divide and conquer Three ‘killer genes’ in one species of fission yeast act selfishly and keep it reproductively isolated from a closely related species. ...
... Cheaters divide and conquer Three ‘killer genes’ in one species of fission yeast act selfishly and keep it reproductively isolated from a closely related species. ...
GENETICS REVIEW
... even 1 copy of the disordered gene, he suffers from the disorder. A female can carry 1 disordered gene on one X chromosome but still have a normal gene to mask it on the other X chromosome. A "carrier female" usually doesn't suffer from the disorder, she just carries it and can pass it on .... usual ...
... even 1 copy of the disordered gene, he suffers from the disorder. A female can carry 1 disordered gene on one X chromosome but still have a normal gene to mask it on the other X chromosome. A "carrier female" usually doesn't suffer from the disorder, she just carries it and can pass it on .... usual ...
LP - Columbia University
... common than B? Why is CF commoner in whites, Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) in blacks? Why do genes for drug resistance change, but gene for cytochrome c stays the same! Why is there more variation in introns than in exons? In other words, how did the particular state of affairs that now exists come to b ...
... common than B? Why is CF commoner in whites, Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) in blacks? Why do genes for drug resistance change, but gene for cytochrome c stays the same! Why is there more variation in introns than in exons? In other words, how did the particular state of affairs that now exists come to b ...
The faster-X effect: integrating theory and data
... Population genetics theory predicts that X (or Z) chromosomes could play disproportionate roles in speciation and evolutionary divergence, and recent genome-wide analyses have identified situations in which X or Z-linked divergence exceeds that on the autosomes (the so-called ‘faster-X effect’). Her ...
... Population genetics theory predicts that X (or Z) chromosomes could play disproportionate roles in speciation and evolutionary divergence, and recent genome-wide analyses have identified situations in which X or Z-linked divergence exceeds that on the autosomes (the so-called ‘faster-X effect’). Her ...
Genetics Topic Packet for the BLUE SENIORS
... 4.3.3 State that some genes have more than two alleles (multiple alleles). 4.3.4 Describe ABO blood groups as an example of codominance and multiple alleles. 4.3.5 Explain how the sex chromosomes control gender by referring to the inheritance of X and Y chromosomes in humans. 4.3.6 State tha ...
... 4.3.3 State that some genes have more than two alleles (multiple alleles). 4.3.4 Describe ABO blood groups as an example of codominance and multiple alleles. 4.3.5 Explain how the sex chromosomes control gender by referring to the inheritance of X and Y chromosomes in humans. 4.3.6 State tha ...
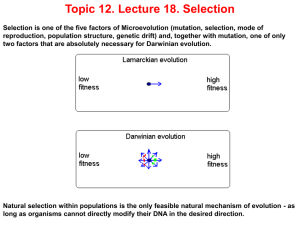
L18Selection
... lasting changes in the population only if it is, at least partially, due to variation among their genotypes. If we think in terms of populations, the impact of selection is obvious: the winner is the one who runs faster. Darwinian mechanism of evolution implies that withinpopulation variation is not ...
... lasting changes in the population only if it is, at least partially, due to variation among their genotypes. If we think in terms of populations, the impact of selection is obvious: the winner is the one who runs faster. Darwinian mechanism of evolution implies that withinpopulation variation is not ...
Polymorphisms of the bovine growth differentiation factor 9 gene
... mothers of dizygotic twins, and those variants are significantly related to increased ovulation rate (Palmer et al., 2006), which suggests that some variants may also be linked to a polyovulatory phenotype (Montgomery et al., 2004). Furthermore, Wang et al. (2010) have found that the GDF9 G546A muta ...
... mothers of dizygotic twins, and those variants are significantly related to increased ovulation rate (Palmer et al., 2006), which suggests that some variants may also be linked to a polyovulatory phenotype (Montgomery et al., 2004). Furthermore, Wang et al. (2010) have found that the GDF9 G546A muta ...
Genetic Inheritance Problems - Exercise 9
... monohybrid and dihybrid crosses. -Know how to do sex-linked crosses. -Be able to apply Incomplete Dominance and Codominance. ...
... monohybrid and dihybrid crosses. -Know how to do sex-linked crosses. -Be able to apply Incomplete Dominance and Codominance. ...
Genetics
... 3. If two alleles differ, then one, the dominant allele, is fully expressed in the organism’s appearance. •The other, the recessive allele, no noticeable effect on the ...
... 3. If two alleles differ, then one, the dominant allele, is fully expressed in the organism’s appearance. •The other, the recessive allele, no noticeable effect on the ...
Extensions of Mendelian Genetics
... The homozygous presence of a recessive allele may prevent or override the expression of other alleles at a second locus. In this case, the alleles at the first locus are epistatic to those at the second locus, and the alleles at the second locus are hypostatic to those at the first allele. (To help ...
... The homozygous presence of a recessive allele may prevent or override the expression of other alleles at a second locus. In this case, the alleles at the first locus are epistatic to those at the second locus, and the alleles at the second locus are hypostatic to those at the first allele. (To help ...
View Full Text-PDF
... inherited as dominant markers. This inheritance model does not allow differentiating heterozygous and homozygous dominant individuals without subsequent crossings. By observing a band on the gel, it is not possible to distinguish whether that segment was originated of one or two copies of the amplif ...
... inherited as dominant markers. This inheritance model does not allow differentiating heterozygous and homozygous dominant individuals without subsequent crossings. By observing a band on the gel, it is not possible to distinguish whether that segment was originated of one or two copies of the amplif ...
Ethical Issues in Genetic Testing: the Duty to Warn At
... healthcare providers have poor level of understanding about their test results – Comparable to group that was never tested – Far less than those tested by genetics professionals – High level of understanding – Low level of effective communication -> lack training in genetic counseling ...
... healthcare providers have poor level of understanding about their test results – Comparable to group that was never tested – Far less than those tested by genetics professionals – High level of understanding – Low level of effective communication -> lack training in genetic counseling ...
Class 5: Biology and behavior
... Affects only Black Americans. Two recessive alleles cause round blood cells to be sickle shaped. ...
... Affects only Black Americans. Two recessive alleles cause round blood cells to be sickle shaped. ...
Polymorphism (biology)

Polymorphism in biology is said to occur when two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species—in other words, the occurrence of more than one form or morph. In order to be classified as such, morphs must occupy the same habitat at the same time and belong to a panmictic population (one with random mating).Polymorphism as described here involves morphs of the phenotype. The term is also used somewhat differently by molecular biologists to describe certain point mutations in the genotype, such as SNPs (see also RFLPs). This usage is not discussed in this article.Polymorphism is common in nature; it is related to biodiversity, genetic variation and adaptation; it usually functions to retain variety of form in a population living in a varied environment. The most common example is sexual dimorphism, which occurs in many organisms. Other examples are mimetic forms of butterflies (see mimicry), and human hemoglobin and blood types.According to the theory of evolution, polymorphism results from evolutionary processes, as does any aspect of a species. It is heritable and is modified by natural selection. In polyphenism, an individual's genetic make-up allows for different morphs, and the switch mechanism that determines which morph is shown is environmental. In genetic polymorphism, the genetic make-up determines the morph. Ants exhibit both types in a single population.Polymorphism also refers to the occurrence of structurally and functionally more than two different types of individuals, called zooids within the same organism. It is a characteristic feature of Cnidarians.For example, in Obelia there are feeding individuals, the gastrozooids; the individuals capable of asexual reproduction only, the gonozooids, blastostyles and free-living or sexually reproducing individuals, the medusae.