Gene Section RBM15 (RNA binding motif protein 15) in Oncology and Haematology
... Cytogenetics 60% of cases have the t(1;22) as a single anomaly; the remaining cases exhibit complex and hyperploid clones. Hybrid/Mutated gene 5' OTT - 3' MAL, comprisng most of OTT fused to most of MAL; the reciprocal 5' MAL - 3' OTT may or may not be present. Abnormal protein Includes most of OTT ...
... Cytogenetics 60% of cases have the t(1;22) as a single anomaly; the remaining cases exhibit complex and hyperploid clones. Hybrid/Mutated gene 5' OTT - 3' MAL, comprisng most of OTT fused to most of MAL; the reciprocal 5' MAL - 3' OTT may or may not be present. Abnormal protein Includes most of OTT ...
Genetics
... • A trait that is covered over, or dominated, by another form of that trait and seems to disappear • Hidden when the other copy of the gene contains the dominant allele. • A recessive allele shows up only when there is no dominant allele present • Shown with a lower-case letter ...
... • A trait that is covered over, or dominated, by another form of that trait and seems to disappear • Hidden when the other copy of the gene contains the dominant allele. • A recessive allele shows up only when there is no dominant allele present • Shown with a lower-case letter ...
Document
... To evaluate the effects of transcription factor mutants, a combined metabolic and regulatory model was used to evaluate whether the deletion of a transcription factor is lethal for growth on glycerol minimal medium. ...
... To evaluate the effects of transcription factor mutants, a combined metabolic and regulatory model was used to evaluate whether the deletion of a transcription factor is lethal for growth on glycerol minimal medium. ...
Document
... The success of the GO Consortium’s work has been to demonstrate the great utility of shared community ontologies in the genomics community. This success has inspired the development of similar ontologies for other domains and has promoted open collaborations among groups working on similar projects ...
... The success of the GO Consortium’s work has been to demonstrate the great utility of shared community ontologies in the genomics community. This success has inspired the development of similar ontologies for other domains and has promoted open collaborations among groups working on similar projects ...
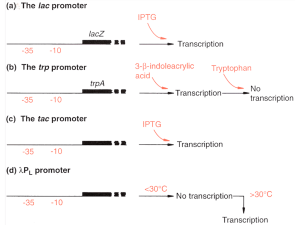
Transcription Control in Eukaryotes
... Eukaryotes Transcription control in eukaryotes is more complex than in prokaryotes, with more gene-gene interactions, presumably required to produce more different cell types in more complex organisms. We will consider some examples and models to illustrate some general principles. ...
... Eukaryotes Transcription control in eukaryotes is more complex than in prokaryotes, with more gene-gene interactions, presumably required to produce more different cell types in more complex organisms. We will consider some examples and models to illustrate some general principles. ...
Gene set tes-ng
... ROAST gene set test • The ques'on asked is “Do the genes in this gene set tend to be differen'ally expressed?” • It is NOT compared rela've to other genes • It is designed such that if > 25-50% of genes in the gene set are differen'ally expressed it will be significant • It uses sophis'cate ...
... ROAST gene set test • The ques'on asked is “Do the genes in this gene set tend to be differen'ally expressed?” • It is NOT compared rela've to other genes • It is designed such that if > 25-50% of genes in the gene set are differen'ally expressed it will be significant • It uses sophis'cate ...
TamarEldad
... Classical Biology – collect a set of features for each protein Systems Biology – study protein function in the context of a network ...
... Classical Biology – collect a set of features for each protein Systems Biology – study protein function in the context of a network ...
If you have BRCA in the family (Scotland)
... is a BRCA1/2 gene mutation carrier and there is a strong possibility that this gene mutation will have been passed on to me. According to SIGN Guideline 3.2.2: “BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation analysis should be considered in a family where there is a 10% or greater risk of mutations present” I am therefor ...
... is a BRCA1/2 gene mutation carrier and there is a strong possibility that this gene mutation will have been passed on to me. According to SIGN Guideline 3.2.2: “BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation analysis should be considered in a family where there is a 10% or greater risk of mutations present” I am therefor ...
Fish sampling - BioMed Central
... The fish were killed by a blow to the head. Tissue samples from six organs, i.e. gills, liver, head kidney, brain, white muscle and posterior intestine, were dissected out and immediately frozen in cryo tubes in liquefied nitrogen and stored at –80°C before further processing. After weight and lengt ...
... The fish were killed by a blow to the head. Tissue samples from six organs, i.e. gills, liver, head kidney, brain, white muscle and posterior intestine, were dissected out and immediately frozen in cryo tubes in liquefied nitrogen and stored at –80°C before further processing. After weight and lengt ...
Topic 6
... Protein A is a bacterial protein that binds tightly to IgG Streptavidin binds biotin strongly (Kd~10-15). MBP = maltose binding protein GST = glutathione-S-transferase ...
... Protein A is a bacterial protein that binds tightly to IgG Streptavidin binds biotin strongly (Kd~10-15). MBP = maltose binding protein GST = glutathione-S-transferase ...
Gene Section RNASET2 (ribonuclease T2) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... A processed pseudogene showing 85% identity with RNASET2 mRNA maps to chromosome 7p11.2. The expression pattern of this pseudogene is not known. ...
... A processed pseudogene showing 85% identity with RNASET2 mRNA maps to chromosome 7p11.2. The expression pattern of this pseudogene is not known. ...
Genetic Engineering ppt
... As plasmids are extremely small, we cannot tell by looking which ones have got the human gene in the right place. We need to use a ‘shotgun’ approach and incubate thousands of plasmids with hundreds of bacterial cells ...
... As plasmids are extremely small, we cannot tell by looking which ones have got the human gene in the right place. We need to use a ‘shotgun’ approach and incubate thousands of plasmids with hundreds of bacterial cells ...
Multimedia Information Gathering
... Processing techniques capture dynamic relations between sets of genes The results obtained from the microarray data are promising ...
... Processing techniques capture dynamic relations between sets of genes The results obtained from the microarray data are promising ...
bio 11 genetics sep 15
... When individuals at the upper and lower ends have the highest fitness Birds with big and small beaks are more fit ...
... When individuals at the upper and lower ends have the highest fitness Birds with big and small beaks are more fit ...
16.1 Genes and Variations
... • When individuals at the upper and lower ends have the highest fitness • Birds with big and small beaks are more fit ...
... • When individuals at the upper and lower ends have the highest fitness • Birds with big and small beaks are more fit ...
Text S1.
... parent genes in which all overlapping exons are excluded from both parent genes. Those mRNAs ...
... parent genes in which all overlapping exons are excluded from both parent genes. Those mRNAs ...
Quick Unit Summary A gene is a stretch of DNA that codes for a
... A gene is a stretch of DNA that codes for a specific characteristic or physical trait. Organisms always have 2 copies of each gene- the one they inherited from their biological mother and the one they inherited from their biological father. Genes have varying levels of expression, referred to as dom ...
... A gene is a stretch of DNA that codes for a specific characteristic or physical trait. Organisms always have 2 copies of each gene- the one they inherited from their biological mother and the one they inherited from their biological father. Genes have varying levels of expression, referred to as dom ...
BB30055: Genes and genomes
... signal transduction and immune function) However, only 3 cases where a combination of 3 domain types shared by human & yeast proteins. e.g carbomyl-phosphate synthase (involved in the first 3 steps of de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis) has 7 domain types, which occurs once in human and yeast but twice ...
... signal transduction and immune function) However, only 3 cases where a combination of 3 domain types shared by human & yeast proteins. e.g carbomyl-phosphate synthase (involved in the first 3 steps of de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis) has 7 domain types, which occurs once in human and yeast but twice ...
cDNA cloning, expression and chromosomal localization of the
... ATCCCC-3´) and amplified by PCR a fragment from human genomic DNA (Clontech). We cloned the fragment in pGEM-Teasy vector and sequenced it in both directions confirming the sequence of the EMBL entry AC005874. The analysis of the sequence cloned, strongly suggested that this genomic fragment might c ...
... ATCCCC-3´) and amplified by PCR a fragment from human genomic DNA (Clontech). We cloned the fragment in pGEM-Teasy vector and sequenced it in both directions confirming the sequence of the EMBL entry AC005874. The analysis of the sequence cloned, strongly suggested that this genomic fragment might c ...
Gene Section AML1 (acute myeloid leukemia 1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Mariano Rocchi, Resources for Molecular Cytogenetics. Laboratories willing to validate the probes are welcome: contact M Rocchi. ...
... Mariano Rocchi, Resources for Molecular Cytogenetics. Laboratories willing to validate the probes are welcome: contact M Rocchi. ...
Uses of Genomic Information in the Diagnosis of Disease
... http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/deaths.htm ...
... http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/deaths.htm ...