Leukaemia Section del(11)(q23q23) MLL/ARHGEF12 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... domain: methyltransferase; methylates H3, including histones in the HOX area for allowing chromatin to be open to transcription. MLL is cleaved by taspase 1 into 2 proteins before entering the nucleus: a p300/320 Nterm protein called MLL-N, and a p180 C-term protein, called MLL-C. The FYRN and a FRY ...
... domain: methyltransferase; methylates H3, including histones in the HOX area for allowing chromatin to be open to transcription. MLL is cleaved by taspase 1 into 2 proteins before entering the nucleus: a p300/320 Nterm protein called MLL-N, and a p180 C-term protein, called MLL-C. The FYRN and a FRY ...
WORKSHEET UNIT V
... 27. Of the genetic expressions covered in lecture which one gives you a heterozygote that has an intermediate phenotype form between the pure breeding parent generation. 28. In the human chromosomes 1 through 22 are called ...
... 27. Of the genetic expressions covered in lecture which one gives you a heterozygote that has an intermediate phenotype form between the pure breeding parent generation. 28. In the human chromosomes 1 through 22 are called ...
Section 6: Information Flow
... We have spent the last several sections discussing molecular differences between the prokaryotes and eukaryotes that serve as targets for antibiotic binding. Here we refer back to initial discussions in Section 2 where we introduced the tree of life. Observable (phenotypic) differences between group ...
... We have spent the last several sections discussing molecular differences between the prokaryotes and eukaryotes that serve as targets for antibiotic binding. Here we refer back to initial discussions in Section 2 where we introduced the tree of life. Observable (phenotypic) differences between group ...
Dear Notetaker - Home Sign In Page
... Point mutations: missense (1 amino acid swapped for another, still have a protein made, just varied, like glutamic acid instead of valine) and nonsense (stop codon, UAG, is the result of the mutation, full protein not made) Result from a substitution of a single nucleotide base by a different ba ...
... Point mutations: missense (1 amino acid swapped for another, still have a protein made, just varied, like glutamic acid instead of valine) and nonsense (stop codon, UAG, is the result of the mutation, full protein not made) Result from a substitution of a single nucleotide base by a different ba ...
gene therapy: ethical and social issues
... attempts to develop a practical review process for research protocols. It was at this time that the distinction between somatic and germ-line genetic engineering was put forward as a way of distinguishing appropriate from inappropriate types of genetic interventions. Many felt that somatic cell gene ...
... attempts to develop a practical review process for research protocols. It was at this time that the distinction between somatic and germ-line genetic engineering was put forward as a way of distinguishing appropriate from inappropriate types of genetic interventions. Many felt that somatic cell gene ...
Module 2: T-COFFEE & Module 8: Horizontal Gene Transfer
... – Tree-based Consistency Objective Function for alignment Evaluation • Focuses on orthologous gene sequences • Used to generate multiple sequence alignments ...
... – Tree-based Consistency Objective Function for alignment Evaluation • Focuses on orthologous gene sequences • Used to generate multiple sequence alignments ...
Mendel & Heredity
... Codominance – two dominant alleles are expressed at the same time. Ex. Roan color in cattle (both red and white hairs are present) Heredity – passing of traits from parents to offspring Mutation – a change in a gene due to damage or being copied incorrectly Mutation – a change in an organism’s DNA ...
... Codominance – two dominant alleles are expressed at the same time. Ex. Roan color in cattle (both red and white hairs are present) Heredity – passing of traits from parents to offspring Mutation – a change in a gene due to damage or being copied incorrectly Mutation – a change in an organism’s DNA ...
Three-letter Symbols - Online Open Genetics
... Three alleles in a series for the w gene. The first is wild type; the second two are different mutant alleles. ...
... Three alleles in a series for the w gene. The first is wild type; the second two are different mutant alleles. ...
Presentation Slides - Genetics in Primary Care Institute
... • DNA is converted into RNA and then translated into protein • DNA bases are “read” in groups of three • Each codon (three bases) is specific for a single amino acid ...
... • DNA is converted into RNA and then translated into protein • DNA bases are “read” in groups of three • Each codon (three bases) is specific for a single amino acid ...
Ch. 11 Genetic Problems
... and child may indicate that a man alleged to be the father could not possibly have fathered the child. For the following mother and child combinations, indicated which blood groups of potential fathers would be exonerated (i.e. not the father). Blood Group of ...
... and child may indicate that a man alleged to be the father could not possibly have fathered the child. For the following mother and child combinations, indicated which blood groups of potential fathers would be exonerated (i.e. not the father). Blood Group of ...
Gene Section IKZF1 (Ikaros family zinc finger 1) in Oncology and Haematology
... Hosokawa Y, Maeda Y, Ichinohasama R, Miura I, Taniwaki M, Seto M. The Ikaros gene, a central regulator of lymphoid differentiation, fuses to the BCL6 gene as a result of t(3;7)(q27;p12) translocation in a patient with diffuse large Bcell lymphoma. Blood. 2000 Apr 15;95(8):2719-21 ...
... Hosokawa Y, Maeda Y, Ichinohasama R, Miura I, Taniwaki M, Seto M. The Ikaros gene, a central regulator of lymphoid differentiation, fuses to the BCL6 gene as a result of t(3;7)(q27;p12) translocation in a patient with diffuse large Bcell lymphoma. Blood. 2000 Apr 15;95(8):2719-21 ...
Detecting Gene Polymorphisms- PCR
... TAS2R38 gene- PTC Bitter Taste Receptor: Restriction Enzyme-Based Detection There are 5 tastes- sweet, sour, bitter, salty and umami. Each is detected by specific receptor proteins. The gene products from TAS1R2 and TAS1R3 detect sweetness as a heterodimer. Gene products from TAS1R1 and TAS1R3 detec ...
... TAS2R38 gene- PTC Bitter Taste Receptor: Restriction Enzyme-Based Detection There are 5 tastes- sweet, sour, bitter, salty and umami. Each is detected by specific receptor proteins. The gene products from TAS1R2 and TAS1R3 detect sweetness as a heterodimer. Gene products from TAS1R1 and TAS1R3 detec ...
2007-10_GO-resources_jblake
... icons represent the relationship of the term to its parent, either "is a" and "part of" the parent term. The GO term identifier and term name can be clicked to get a more detailed view of the term, including the definition and all genes and gene products annotated to the term. Following the term ID ...
... icons represent the relationship of the term to its parent, either "is a" and "part of" the parent term. The GO term identifier and term name can be clicked to get a more detailed view of the term, including the definition and all genes and gene products annotated to the term. Following the term ID ...
Test Information Sheet ASPA Gene Analysis in Canavan Disease
... developmental delay. Severe CD is associated with delayed motor skills and the inability for these children to sit, stand, walk or talk. Many severe patients also have optic atrophy. Over time, spasticity develops and sleep disturbance, seizures and feeding difficulties may be present. Spongy degene ...
... developmental delay. Severe CD is associated with delayed motor skills and the inability for these children to sit, stand, walk or talk. Many severe patients also have optic atrophy. Over time, spasticity develops and sleep disturbance, seizures and feeding difficulties may be present. Spongy degene ...
Dr. Sabika Firasat - University of Wah
... PCR products were pooled and analyzed on ABI 3100 or ABI 3730 genetic analyzer using gene scan software and haplotypes were constructed. ...
... PCR products were pooled and analyzed on ABI 3100 or ABI 3730 genetic analyzer using gene scan software and haplotypes were constructed. ...
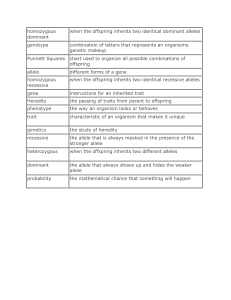
Punnett Square Practice
... Step 5: Fill in each box of the Punnett square by transferring the letter above and at the side of each box into the appropriate box. As a general rule, the capital letter goes first and a lowercase letter follows. ...
... Step 5: Fill in each box of the Punnett square by transferring the letter above and at the side of each box into the appropriate box. As a general rule, the capital letter goes first and a lowercase letter follows. ...
Xenorhabdus nematophila: Mutualist and Pathogen
... bioluminescent, produces anthraquinone The inclusion body formed by PixA is absent in the pixA mutant strain (B). pigments, and has an active catalase, all of which are absent in Xenorhabdus. atode interaction locus (nil) in Xenorhabdus that Their respective nematode hosts are distantly encodes thre ...
... bioluminescent, produces anthraquinone The inclusion body formed by PixA is absent in the pixA mutant strain (B). pigments, and has an active catalase, all of which are absent in Xenorhabdus. atode interaction locus (nil) in Xenorhabdus that Their respective nematode hosts are distantly encodes thre ...
Guidelines for BioLINK Gene List Evaluation
... short 'gene symbol' is the first entry in the list which may be followed by a longer 'gene name' and then finally alternate forms used to refer to the gene. These names are NOT unique and can be found in other gene lists. In some cases, the databases use specific formatting for indicating special ...
... short 'gene symbol' is the first entry in the list which may be followed by a longer 'gene name' and then finally alternate forms used to refer to the gene. These names are NOT unique and can be found in other gene lists. In some cases, the databases use specific formatting for indicating special ...
PPT
... An important topic in microarray data mining is to bind transcriptionally modulated genes to functional pathways or how transcriptional modulation can be associated with specific biological events such as genetic disease phenotype, cell differentiation etc. However, the amount of functional annotati ...
... An important topic in microarray data mining is to bind transcriptionally modulated genes to functional pathways or how transcriptional modulation can be associated with specific biological events such as genetic disease phenotype, cell differentiation etc. However, the amount of functional annotati ...
Alignments -> Database Searching
... A Ramachandran plot (also known as a Ramachandran map or a Ramachandran diagram), is a way to visualize dihedral angles φ against ψ of amino acid residues in protein structure. It shows the possible conformations of φ and ψ angles for a polypeptide. Mathematically, the Ramachandran plot is the ...
... A Ramachandran plot (also known as a Ramachandran map or a Ramachandran diagram), is a way to visualize dihedral angles φ against ψ of amino acid residues in protein structure. It shows the possible conformations of φ and ψ angles for a polypeptide. Mathematically, the Ramachandran plot is the ...
Pedigree Analysis
... (or carriers). An autosomal recessive condition may be transmitted through a long line of carriers before, by ill chance two carriers mate. Then there will be a ¼ chance that any child will be affected. The pedigree will therefore often only have one 'sibship' with affected members. ...
... (or carriers). An autosomal recessive condition may be transmitted through a long line of carriers before, by ill chance two carriers mate. Then there will be a ¼ chance that any child will be affected. The pedigree will therefore often only have one 'sibship' with affected members. ...
Cross-Validation Experiment
... near-human performance. We asked a group of curators to annotate a set of nearly 100,000 pairs of natural-text sentences and the corresponding automatically extracted statements. Using this large training corpus, we implemented a battery of automated classifiers and compared their performance with p ...
... near-human performance. We asked a group of curators to annotate a set of nearly 100,000 pairs of natural-text sentences and the corresponding automatically extracted statements. Using this large training corpus, we implemented a battery of automated classifiers and compared their performance with p ...
Conversion of Different TCGA Data Types to Boolean Values
... function in bioconductor. Then StepMiner [5], which fits patterns of one-step transitions by evaluating every possible placement of the transition (or step) and chooses the one that gives the best fit, was used to derive thresholds that divided the data into low and high states. A Boolean variable w ...
... function in bioconductor. Then StepMiner [5], which fits patterns of one-step transitions by evaluating every possible placement of the transition (or step) and chooses the one that gives the best fit, was used to derive thresholds that divided the data into low and high states. A Boolean variable w ...