Environmental Management of Deep
... Both vent and seep ecosystems are fueled primarily by microbial primary production through a process known as chemosynthesis. Instead of using energy from sunlight to fix inorganic carbon into organic carbon (photosynthesis), microbes in vent and seep ecosystems use chemical energy from the oxidatio ...
... Both vent and seep ecosystems are fueled primarily by microbial primary production through a process known as chemosynthesis. Instead of using energy from sunlight to fix inorganic carbon into organic carbon (photosynthesis), microbes in vent and seep ecosystems use chemical energy from the oxidatio ...
Deep life: Teeming masses of organisms thrive beneath the seafloor
... how water flushes through the ocean crust, offering clues to the best places to look for microbes. People tend to think of water sitting on top of the seafloor, says Fisher, but in fact water zips through undersea rocks — cycling the equivalent of the ocean’s entire volume through the crust every ha ...
... how water flushes through the ocean crust, offering clues to the best places to look for microbes. People tend to think of water sitting on top of the seafloor, says Fisher, but in fact water zips through undersea rocks — cycling the equivalent of the ocean’s entire volume through the crust every ha ...
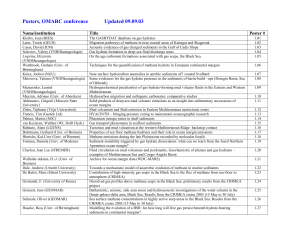
Registered talks and posters, OMARC conference
... Hydrocarbon migration and authigenic carbonates: comparative studies Solid products of deep-sea mud volcanic emissions as an insight into sedimentary successions of ocean margins Mud volcanism and fluid emission in Eastern Mediterranean neotectonic zones HYACINTH – bringing pressure coring to mainst ...
... Hydrocarbon migration and authigenic carbonates: comparative studies Solid products of deep-sea mud volcanic emissions as an insight into sedimentary successions of ocean margins Mud volcanism and fluid emission in Eastern Mediterranean neotectonic zones HYACINTH – bringing pressure coring to mainst ...
Mid ocean ridge worksheet
... Mid-Ocean Ridges 1. In what year did scientists discover mid-ocean ridges? 213 ________________________________ 2. Summarize how scientists were able to map out the ocean floor. 213 ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ...
... Mid-Ocean Ridges 1. In what year did scientists discover mid-ocean ridges? 213 ________________________________ 2. Summarize how scientists were able to map out the ocean floor. 213 ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ...
Teacher Resources - Fish Eye Project
... Ø What role do hydrothermal vents play in the ocean? Answer: Seafloor hydrothermal vent complexes can be compared to household ventilation systems, in that these systems transfer heat and chemicals from the ...
... Ø What role do hydrothermal vents play in the ocean? Answer: Seafloor hydrothermal vent complexes can be compared to household ventilation systems, in that these systems transfer heat and chemicals from the ...
as PDF
... in the region will continue with the examination of brine pools and cold methane seeps. Mussels living on these “underwater lakes” thrive in very low oxygen environments, existing on a symbiotic relationship with chemosynthetic bacteria and scientists are continuing to learn about how they are able ...
... in the region will continue with the examination of brine pools and cold methane seeps. Mussels living on these “underwater lakes” thrive in very low oxygen environments, existing on a symbiotic relationship with chemosynthetic bacteria and scientists are continuing to learn about how they are able ...
Hydrothermal Vents
... • smoke does not come out of the black smoker chimney • hydrothermal fluid is hot enough to melt metal (600-750°F) • dissolved metals come from deep beneath the ocean floor • when the fluid mixes with seawater, metals combine with sulfur to form tiny black particles; this gives the appearance of smo ...
... • smoke does not come out of the black smoker chimney • hydrothermal fluid is hot enough to melt metal (600-750°F) • dissolved metals come from deep beneath the ocean floor • when the fluid mixes with seawater, metals combine with sulfur to form tiny black particles; this gives the appearance of smo ...
lecture notes
... which is shallow and near a terrigenous source and the deep ocean basin, which is deep and far from a terrigenous source Seaward water becomes deeper and more distant from a terrigenous source o Shelf sedimentation is strongly controlled by tides, waves, and currents, but their influence decreases ...
... which is shallow and near a terrigenous source and the deep ocean basin, which is deep and far from a terrigenous source Seaward water becomes deeper and more distant from a terrigenous source o Shelf sedimentation is strongly controlled by tides, waves, and currents, but their influence decreases ...
Deep-sea genetic resources - Archimer
... metazoan communities that develop, share some cognate taxa with vent and seep communities. State-of-the-art technology for deep-sea biological studies in France. State-of-the-art technology is of primary importance to study deep-sea ecosystems (location, mapping, exploration and sampling). Important ...
... metazoan communities that develop, share some cognate taxa with vent and seep communities. State-of-the-art technology for deep-sea biological studies in France. State-of-the-art technology is of primary importance to study deep-sea ecosystems (location, mapping, exploration and sampling). Important ...
Dynamics and Evolution of European Margins
... Generally speaking, the European margin can be divided into two different tectonic settings: (1) Atlantic margins, consisting of rifted and shear margin segments where continental break up has ...
... Generally speaking, the European margin can be divided into two different tectonic settings: (1) Atlantic margins, consisting of rifted and shear margin segments where continental break up has ...
Geology Chapter 14
... Big Ideas Seventy-one percent of Earth's surface is covered by ocean water. There are four main ocean basins: the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, and Arctic. The bathymetry of the ocean seafloor is very varied, a result of many different geological processes. Space and Time The margins of continents (inc ...
... Big Ideas Seventy-one percent of Earth's surface is covered by ocean water. There are four main ocean basins: the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, and Arctic. The bathymetry of the ocean seafloor is very varied, a result of many different geological processes. Space and Time The margins of continents (inc ...
10750_2017_3120_MOESM1_ESM
... The Persian Gulf is a shallow, semi-enclosed marginal sea situated among the Arabian Peninsula in the west, the Taurus Mountains in the north, and the Zagros Mountains in the east and northeast. It is connected with the Gulf of Oman and the Indian Ocean through the Strait of Hormuz, and extends for ...
... The Persian Gulf is a shallow, semi-enclosed marginal sea situated among the Arabian Peninsula in the west, the Taurus Mountains in the north, and the Zagros Mountains in the east and northeast. It is connected with the Gulf of Oman and the Indian Ocean through the Strait of Hormuz, and extends for ...
RESOURCES BIOMASS & BIOFUELS OIL & GAS
... hydrates, as well as other clathrate-forming gases such as hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide. Such gases escape from sediments at depth, rise along faults, and form gas hydrates at or just below the seafloor, but on a worldwide basis, these are of minor volumetric importance compared to methane hy ...
... hydrates, as well as other clathrate-forming gases such as hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide. Such gases escape from sediments at depth, rise along faults, and form gas hydrates at or just below the seafloor, but on a worldwide basis, these are of minor volumetric importance compared to methane hy ...
Chemotrophic Microbial Mats and Their Potential
... edimentary structures such as stromatolites were argued to represent fossilized plant or algal material more than a century ago (Walcott, 1883; Matthew, 1890). These interpretations were controversial until modern cyanobacterial mats associated with recent stromatolites were shown to trap and bind s ...
... edimentary structures such as stromatolites were argued to represent fossilized plant or algal material more than a century ago (Walcott, 1883; Matthew, 1890). These interpretations were controversial until modern cyanobacterial mats associated with recent stromatolites were shown to trap and bind s ...
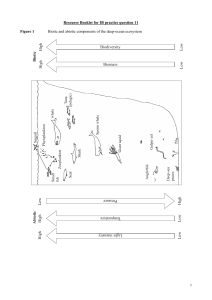
Resource Booklet for IB practice question 11
... Of great interest to marine scientists was the discovery of communities of animals living around deep vents on the ocean floor. From these vents pour large quantities of heated seawater which contain high quantities of hydrogen sulfides and dissolved minerals. These vents occur where tectonic plates ...
... Of great interest to marine scientists was the discovery of communities of animals living around deep vents on the ocean floor. From these vents pour large quantities of heated seawater which contain high quantities of hydrogen sulfides and dissolved minerals. These vents occur where tectonic plates ...
Consulta: creatorFacets:"Bollinger, Claire" Registros recuperados: 7
... We report rare earth element (REE) and neodymium (Nd) isotope data for the organic fraction of sediments collected from various depositional environments, i.e. rivers (n=25), estuaries (n=18), open-ocean settings (n=15), and cold seeps (n=12). Sedimentary Organic Matter (SOM) was extracted using a ...
... We report rare earth element (REE) and neodymium (Nd) isotope data for the organic fraction of sediments collected from various depositional environments, i.e. rivers (n=25), estuaries (n=18), open-ocean settings (n=15), and cold seeps (n=12). Sedimentary Organic Matter (SOM) was extracted using a ...
PDF
... between the Western and Central Transects (WC on Fig. 1) during Cruise V. Sam- Environment of the study area ples for analysis of meiofauna and macroThe Gulf of Mexico shares more deepfauna, as well as a suite of sediment sea species with the Atlantic, even to the characteristics and inclusions [e.g ...
... between the Western and Central Transects (WC on Fig. 1) during Cruise V. Sam- Environment of the study area ples for analysis of meiofauna and macroThe Gulf of Mexico shares more deepfauna, as well as a suite of sediment sea species with the Atlantic, even to the characteristics and inclusions [e.g ...
Byron Pedler Sherwood (PDF)
... turnover of marine dissolved organic matter--insights from a model system" The ocean contains one of the largest reservoirs of reduced carbon on Earth in the form of dissolved organic matter (DOM). The objective of this study was to investigate the physiological and ecological constraints on microbi ...
... turnover of marine dissolved organic matter--insights from a model system" The ocean contains one of the largest reservoirs of reduced carbon on Earth in the form of dissolved organic matter (DOM). The objective of this study was to investigate the physiological and ecological constraints on microbi ...
History of Deep Sea Biology - Monterey Bay Aquarium Research
... Azoic Theory disproved. Animals present throughout the deep sea to 5500 m one sample at 7000 m Japan Trench. ...
... Azoic Theory disproved. Animals present throughout the deep sea to 5500 m one sample at 7000 m Japan Trench. ...
Insert overline, title and author names here after formatting
... vehicle (ROV) Kaiko to explore and sample a dense, chemosyntheticReality caught up with fiction on 23 January 1960, when U.S. Navy based community dominated by a previously undescribed species of a Lieutenant Don Walsh and Swiss engineer and oceanographer Jacques Piccard descended in the bathyscaphe ...
... vehicle (ROV) Kaiko to explore and sample a dense, chemosyntheticReality caught up with fiction on 23 January 1960, when U.S. Navy based community dominated by a previously undescribed species of a Lieutenant Don Walsh and Swiss engineer and oceanographer Jacques Piccard descended in the bathyscaphe ...
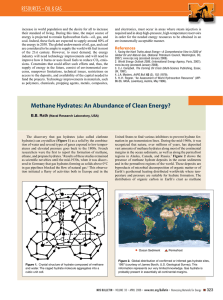
hydrothermal vents and chemosynthesis
... Hydrothermal vents were discovered in 1977 in the Pacific Ocean. Since then, they have been found in the Atlantic, Indian, and most recently, the Arctic Ocean. Most occur at an average depth of about 2,100 meters (7,000 ft) in areas of seafloor spreading along the Mid-Ocean Ridge system — the underw ...
... Hydrothermal vents were discovered in 1977 in the Pacific Ocean. Since then, they have been found in the Atlantic, Indian, and most recently, the Arctic Ocean. Most occur at an average depth of about 2,100 meters (7,000 ft) in areas of seafloor spreading along the Mid-Ocean Ridge system — the underw ...
MPIMM Research activities and assets
... Anaerobic bacterial degradation of hydrocarbons It is well-known that terminal degraders in the anaerobic "food chain", e.g. sulfatereducing and denitrifying bacteria, degrade fermentation products such as fatty acids from the primary breakdown of biopolymers. We have, however, only little knowledge ...
... Anaerobic bacterial degradation of hydrocarbons It is well-known that terminal degraders in the anaerobic "food chain", e.g. sulfatereducing and denitrifying bacteria, degrade fermentation products such as fatty acids from the primary breakdown of biopolymers. We have, however, only little knowledge ...
ARTHROPODS HOST INTRACELLULAR CHEMOSYNTHETIC
... plasticity of microbes prevents definitive phylogenetic assignment, the overall similarity of the shrimp endosymbionts with those previously reported in Lophotrochozoa (Dubilier et al., 2008) is striking and may indicate a shared bacterial lineage or convergence. We are currently examining the bacte ...
... plasticity of microbes prevents definitive phylogenetic assignment, the overall similarity of the shrimp endosymbionts with those previously reported in Lophotrochozoa (Dubilier et al., 2008) is striking and may indicate a shared bacterial lineage or convergence. We are currently examining the bacte ...
Cold seep

A cold seep (sometimes called a cold vent) is an area of the ocean floor where hydrogen sulfide, methane and other hydrocarbon-rich fluid seepage occurs, often in the form of a brine pool. ""Cold"" does not mean that the temperature of the seepage is lower than that of the surrounding sea water. On the contrary, its temperature is often slightly higher. Cold seeps constitute a biome supporting several endemic species.Cold seeps develop unique topography over time, where reactions between methane and seawater create carbonate rock formations and reefs. These reactions may also be dependent on bacterial activity. Ikaite, a hydrous calcium carbonate, can be associated with oxidizing methane at cold seeps.