Theta Year 7 Scheme of Work KS3 Maths Progress Theta 3
... use and interpret algebraic notation: coefficients written as fractions rather than as decimals use and interpret algebraic notation: brackets understand and use the concepts and vocabulary of expressions, equations, inequalities, terms and factors simplify and manipulate algebraic expressions to ma ...
... use and interpret algebraic notation: coefficients written as fractions rather than as decimals use and interpret algebraic notation: brackets understand and use the concepts and vocabulary of expressions, equations, inequalities, terms and factors simplify and manipulate algebraic expressions to ma ...
Geometry - Kingdom Schools
... Solve problems by applying properties of similar polygons. Proof certain triangles are similar using various methods. * Solve problems involving similar triangles. Use properties of similar triangles to find segment lengths ...
... Solve problems by applying properties of similar polygons. Proof certain triangles are similar using various methods. * Solve problems involving similar triangles. Use properties of similar triangles to find segment lengths ...
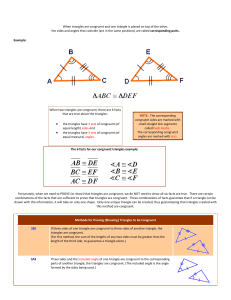
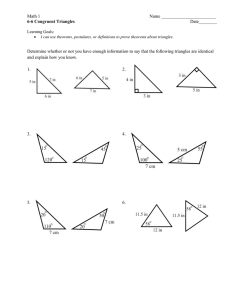
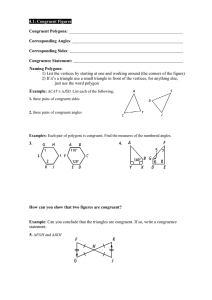
Name Date • Congruent triangles • If is congruent to , then the of the tw
... Corresponding Congruent Parts ...
... Corresponding Congruent Parts ...
Student Name
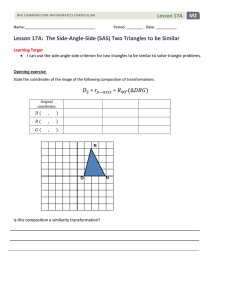
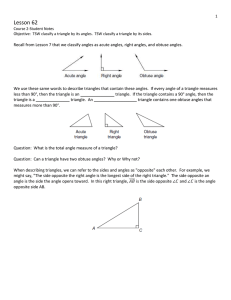
... fewer than 90 degrees. The resulting figure is represented by Figure 2, as shown below. ...
... fewer than 90 degrees. The resulting figure is represented by Figure 2, as shown below. ...
Apollonian network
In combinatorial mathematics, an Apollonian network is an undirected graph formed by a process of recursively subdividing a triangle into three smaller triangles. Apollonian networks may equivalently be defined as the planar 3-trees, the maximal planar chordal graphs, the uniquely 4-colorable planar graphs, and the graphs of stacked polytopes. They are named after Apollonius of Perga, who studied a related circle-packing construction.