Saving Darwin`s muse: evolutionary genetics for the recovery of the
... coalescent-based model. No methods currently exist that can incorporate historic and current samples in a model with divergent populations. Here, based on the model of Beaumont (2003), we developed a new approach that can, in principle, accommodate any number of populations and branching topologies ...
... coalescent-based model. No methods currently exist that can incorporate historic and current samples in a model with divergent populations. Here, based on the model of Beaumont (2003), we developed a new approach that can, in principle, accommodate any number of populations and branching topologies ...
chapter introduction - McGraw
... couple of these historical milestones include these from 1998-2000: 1998: Helped secure passage of the Birth Defects Prevention Act. This act established a national system for monitoring birth defects. In the same year, research that had been sponsored by MOD resulted in a surgery to treat spina bif ...
... couple of these historical milestones include these from 1998-2000: 1998: Helped secure passage of the Birth Defects Prevention Act. This act established a national system for monitoring birth defects. In the same year, research that had been sponsored by MOD resulted in a surgery to treat spina bif ...
Hb_lab_Activities_Guide - AIM-UP!
... Have a mechanistic, testable hypothesis for how an amino acid replacement may affect hemoglobin function. Know how the key amino acid replacements change across geography Know how key amino acid replacements correlate with important geographic variables. The functional differences HBA alleles ...
... Have a mechanistic, testable hypothesis for how an amino acid replacement may affect hemoglobin function. Know how the key amino acid replacements change across geography Know how key amino acid replacements correlate with important geographic variables. The functional differences HBA alleles ...
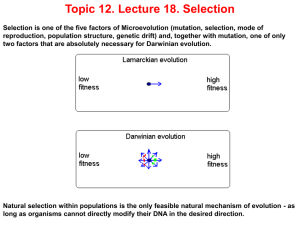
L18Selection
... individuals). Any other mode of selection needs to impose a larger genetic load in order to achieve the same result. ...
... individuals). Any other mode of selection needs to impose a larger genetic load in order to achieve the same result. ...
Proceedings of the Pittsburgh Workshop in History - Philsci
... the urn has an equal probability of being pulled. In the biological case, imagine a population of 1,000 individuals, only 100 of which will get to mate and reproduce. If each of the 1,000 individuals has an equal probability of becoming a parent then that process is indiscriminate sampling. Less abs ...
... the urn has an equal probability of being pulled. In the biological case, imagine a population of 1,000 individuals, only 100 of which will get to mate and reproduce. If each of the 1,000 individuals has an equal probability of becoming a parent then that process is indiscriminate sampling. Less abs ...
PowerPoint - The Science Queen
... genetic cross. To be able to draw a Punnett Square, you must know the genotype of both parents. ...
... genetic cross. To be able to draw a Punnett Square, you must know the genotype of both parents. ...
Whose got Genes?
... gene from each parent) they are said to be homozygous dominant When offspring inherit two recessive genes, (one recessive gene from each parent) they are said to be homozygous recessive Baker 2003/2004 ...
... gene from each parent) they are said to be homozygous dominant When offspring inherit two recessive genes, (one recessive gene from each parent) they are said to be homozygous recessive Baker 2003/2004 ...
Evolutionary Reproduction of Dutch Masters: The Mondriaan and Escher Evolvers
... crossover, random change mutation, tournament selection, and generational replacement. After having gained experience with the resulting system we had to conclude none of these choices was the right one, and we chose alternatives for all of them. We briefly discuss the four main operators below. N-p ...
... crossover, random change mutation, tournament selection, and generational replacement. After having gained experience with the resulting system we had to conclude none of these choices was the right one, and we chose alternatives for all of them. We briefly discuss the four main operators below. N-p ...
local selection underlies the geographic distribution of sexratio drive
... in Carvalho and Vaz 1999; Jaenike 2001). First, balancing selection due to linkage of SR with deleterious mutations can occur: if multiple genes are necessary for the expression of drive, and inversions that maintain linkage among these genes capture linked recessive alleles, these linked mutations ...
... in Carvalho and Vaz 1999; Jaenike 2001). First, balancing selection due to linkage of SR with deleterious mutations can occur: if multiple genes are necessary for the expression of drive, and inversions that maintain linkage among these genes capture linked recessive alleles, these linked mutations ...
17.2 McClintock Found That Chromosomes of Corn
... movement of the Ds locus out of its original location may occasionally cause a chromosome to break, and the distal part of this chromosome is lost. This chromosome breakage may happen in several cells, which continue to divide and grow as the kernel becomes larger. This process produces a sectoring ...
... movement of the Ds locus out of its original location may occasionally cause a chromosome to break, and the distal part of this chromosome is lost. This chromosome breakage may happen in several cells, which continue to divide and grow as the kernel becomes larger. This process produces a sectoring ...
Genetics
... certain species of mouse with black fur is crossed with a mouse with white fur and all of the offspring have grey fur. ...
... certain species of mouse with black fur is crossed with a mouse with white fur and all of the offspring have grey fur. ...
Real Coded Genetic Algorithm for Jiles–Atherton Model Parameters
... algorithm starts with a set of solutions called population. Solutions from a population are used to form a new population. This is motivated by the hope that the new population will be better than the old one. Solutions that will form new solutions are selected according to their fitness: the more s ...
... algorithm starts with a set of solutions called population. Solutions from a population are used to form a new population. This is motivated by the hope that the new population will be better than the old one. Solutions that will form new solutions are selected according to their fitness: the more s ...
Combining genotypic and phenotypic predictions of invasive
... ramorum lineages have different mating types: NA1 and d NA2 are A2 while ...
... ramorum lineages have different mating types: NA1 and d NA2 are A2 while ...
Positive Heuristics in Evolutionary Biology
... intensify. However, its resolution really has no direct bearing on the issues under discussion here. On the surface, Stanley's claim appears to undermine the gene frequency approach, since the formal results of population genetics are usually associated with phyletic evolution. However, on closer an ...
... intensify. However, its resolution really has no direct bearing on the issues under discussion here. On the surface, Stanley's claim appears to undermine the gene frequency approach, since the formal results of population genetics are usually associated with phyletic evolution. However, on closer an ...
PDF - Oxford Academic - Oxford University Press
... transcribed 2–10 times more efficiently than alleles of 3 and 5 copies, suggesting an optimal length for the regulatory region. Deckert et al. (1999) replicated these results but found that allele 5 also had high transcriptional activity. We wanted to examine whether different alleles at this polymo ...
... transcribed 2–10 times more efficiently than alleles of 3 and 5 copies, suggesting an optimal length for the regulatory region. Deckert et al. (1999) replicated these results but found that allele 5 also had high transcriptional activity. We wanted to examine whether different alleles at this polymo ...
Mendel and punnetts squares notes
... The results for the entire class should be even closer to the number predicted by the rules of probability. ...
... The results for the entire class should be even closer to the number predicted by the rules of probability. ...
Genome-wide scans for loci under selection in
... balancing selection, as these have been the primary types of selection that current genome-wide scans have studied. Positive selection acts to increase the frequency of advantageous alleles in a population. Strongly advantageous mutations are rapidly swept to fixation, hence the term ‘selective sweep ...
... balancing selection, as these have been the primary types of selection that current genome-wide scans have studied. Positive selection acts to increase the frequency of advantageous alleles in a population. Strongly advantageous mutations are rapidly swept to fixation, hence the term ‘selective sweep ...
Genetic drift

Genetic drift (or allelic drift) is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces. A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation.When there are few copies of an allele, the effect of genetic drift is larger, and when there are many copies the effect is smaller. In the early twentieth century vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at the most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims that most instances where a genetic change spreads across a population (although not necessarily changes in phenotypes) are caused by genetic drift. There is currently a scientific debate about how much of evolution has been caused by natural selection, and how much by genetic drift.