File - singhscience
... A molecule found in the nucleus of cells, it’s job is to give instruction to make proteins. ...
... A molecule found in the nucleus of cells, it’s job is to give instruction to make proteins. ...
Week 7 - Natural Selection and Genetic Variation for Allozymes
... individuals that possess certain combinations of traits have a greater lifetime reproductive success (usually measured as survival, mating success, or fecundity), than those that possess other combinations of traits. To determine whether natural selection has occurred, one usually measures features ...
... individuals that possess certain combinations of traits have a greater lifetime reproductive success (usually measured as survival, mating success, or fecundity), than those that possess other combinations of traits. To determine whether natural selection has occurred, one usually measures features ...
Bio112_Ex2StudyGuide_F16
... 42. Parapatric speciation would be expected to occur most often a. in the same homeland. b. near a common border between two populations. c. within a group of interbreeding populations. d. across obvious geographical barriers. e. by divergence from a common interbreeding population. 43. Microevoluti ...
... 42. Parapatric speciation would be expected to occur most often a. in the same homeland. b. near a common border between two populations. c. within a group of interbreeding populations. d. across obvious geographical barriers. e. by divergence from a common interbreeding population. 43. Microevoluti ...
Ch_23 Population Genetics
... Sex & Variation Sex spreads variation one ancestor can have many descendants sex causes recombination offspring have new combinations of traits = new phenotypes ...
... Sex & Variation Sex spreads variation one ancestor can have many descendants sex causes recombination offspring have new combinations of traits = new phenotypes ...
RAFT: Genetics - Catawba County Schools
... Investigate and understand that organisms reproduce and transmit genetic information to new generations Utilize appropriate information systems to build an understanding of heredity and genetics Objectives: The students will KNOW Vocabulary: gene, DNA, RNA, recessive trait, dominant trait, bac ...
... Investigate and understand that organisms reproduce and transmit genetic information to new generations Utilize appropriate information systems to build an understanding of heredity and genetics Objectives: The students will KNOW Vocabulary: gene, DNA, RNA, recessive trait, dominant trait, bac ...
Answers - WordPress.com
... SECTION 1. GENETIC VARIATION WITHIN POPULATIONS 1. genetic variation 2. A wide range of phenotypes increases the likelihood that some individuals will have traits that allow them to survive in new environmental conditions. 3. gene pool 4. the combined alleles of all individuals in a population 5. al ...
... SECTION 1. GENETIC VARIATION WITHIN POPULATIONS 1. genetic variation 2. A wide range of phenotypes increases the likelihood that some individuals will have traits that allow them to survive in new environmental conditions. 3. gene pool 4. the combined alleles of all individuals in a population 5. al ...
The population memetics of DarwinTunes
... The initial population All the songs in a DarwinTunes population are descended from a single pair of randomly generated songs – an Adam and Eve as it were – except that our songs don’t have genders. These songs were then allowed to mutate, recombine and reproduce to form a population of 100 descenda ...
... The initial population All the songs in a DarwinTunes population are descended from a single pair of randomly generated songs – an Adam and Eve as it were – except that our songs don’t have genders. These songs were then allowed to mutate, recombine and reproduce to form a population of 100 descenda ...
Chemistry Revision
... Mutation- A permanent mistake in a section of DNA within an organism Dominant- An allele where only one copy is required for it to be expressed over the recessive allele Recessive- An allele where two copies are required for the characteristic to be expressed ...
... Mutation- A permanent mistake in a section of DNA within an organism Dominant- An allele where only one copy is required for it to be expressed over the recessive allele Recessive- An allele where two copies are required for the characteristic to be expressed ...
Part C: Genetics
... In nature we rarely observe an exact phenotypic ratio of 3 dominant allele to 1 recessive allele as the result of a heterozygous monohybrid cross. The larger the sample size, the more likely we are to be closer to the expected ratio. Family trees may be used to trace the inheritance of dominant and ...
... In nature we rarely observe an exact phenotypic ratio of 3 dominant allele to 1 recessive allele as the result of a heterozygous monohybrid cross. The larger the sample size, the more likely we are to be closer to the expected ratio. Family trees may be used to trace the inheritance of dominant and ...
Chapter 15 The Theory of Evolution
... – 200 alleles total R’R’= q2 = 0.22 = 0.04 2RR’= 2pq = 2(.8)(.2) = 0.32 • R alleles = 160/200 = 0.8 = p • R’ alleles = 40/200 = 0.2 = q ...
... – 200 alleles total R’R’= q2 = 0.22 = 0.04 2RR’= 2pq = 2(.8)(.2) = 0.32 • R alleles = 160/200 = 0.8 = p • R’ alleles = 40/200 = 0.2 = q ...
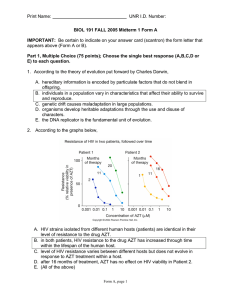
UNR ID Number: BIOL 191 FALL 2005 Midterm 1 Form A
... 5. Alleles that increase their transmission to the next generation by sabotaging gametes carrying alternative alleles A. are unknown in nature because selection always acts for the good of the species. B. are called meiotic drive alleles. C. are called genomically-imprinted genes. D. are called tran ...
... 5. Alleles that increase their transmission to the next generation by sabotaging gametes carrying alternative alleles A. are unknown in nature because selection always acts for the good of the species. B. are called meiotic drive alleles. C. are called genomically-imprinted genes. D. are called tran ...
Evolution Test Review
... 22. What are the 2 main sources of genetic variation? 23. A single-gene trait that has two alleles and that shows a simple dominant-recessive pattern will result in how many phenotypes? 24. The number of phenotypes produced for a given trait depends upon number of ___________that control a trait. 25 ...
... 22. What are the 2 main sources of genetic variation? 23. A single-gene trait that has two alleles and that shows a simple dominant-recessive pattern will result in how many phenotypes? 24. The number of phenotypes produced for a given trait depends upon number of ___________that control a trait. 25 ...
Document
... •Use Hardy-Weinberg to calculate allele frequencies based on the number of homozygous recessive individuals. If q2 = 0.0043, then q = 0.065; p = 1 - q = 0.935 p2 = 0.8742, 2pq = 0.1216 ...
... •Use Hardy-Weinberg to calculate allele frequencies based on the number of homozygous recessive individuals. If q2 = 0.0043, then q = 0.065; p = 1 - q = 0.935 p2 = 0.8742, 2pq = 0.1216 ...
0534997295_32346
... Explain density-dependent population controls and density-independent population controls. ...
... Explain density-dependent population controls and density-independent population controls. ...
Population Genetics Outline Population Genetics Allele Frequency
... Mutation • Mutation – Any event that changes genetic structure • Mutation from A to a will lead freq(A) to decrease, freq(a) to increase. – Mutation rate is low in animals and plants (1 mutation in 100,000 genes per generation) ...
... Mutation • Mutation – Any event that changes genetic structure • Mutation from A to a will lead freq(A) to decrease, freq(a) to increase. – Mutation rate is low in animals and plants (1 mutation in 100,000 genes per generation) ...
Hardy Weinberg Problem Set
... 3. There are 100 students in a class. Ninety-six did well in the course whereas four blew it totally and received a grade of F. Sorry. In the highly unlikely event that t hese traits are genetic rather than environmental, if these traits involve dominant and recessive alleles, and if the four (4%) ...
... 3. There are 100 students in a class. Ninety-six did well in the course whereas four blew it totally and received a grade of F. Sorry. In the highly unlikely event that t hese traits are genetic rather than environmental, if these traits involve dominant and recessive alleles, and if the four (4%) ...
Unit 5 - Evolution Vocab updated2
... The long-term process through which a population of organisms accumulates genetic changes that enable its members to successfully adapt to environmental conditions and to better exploit food ...
... The long-term process through which a population of organisms accumulates genetic changes that enable its members to successfully adapt to environmental conditions and to better exploit food ...
Genetic drift

Genetic drift (or allelic drift) is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces. A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation.When there are few copies of an allele, the effect of genetic drift is larger, and when there are many copies the effect is smaller. In the early twentieth century vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at the most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims that most instances where a genetic change spreads across a population (although not necessarily changes in phenotypes) are caused by genetic drift. There is currently a scientific debate about how much of evolution has been caused by natural selection, and how much by genetic drift.