File
... microevolution might be responsible for the pattern, and part of the scientist's job is to figure out which of these mechanisms caused the change ...
... microevolution might be responsible for the pattern, and part of the scientist's job is to figure out which of these mechanisms caused the change ...
Lecture 3 Human Genetics
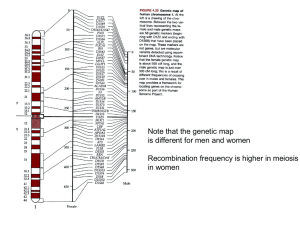
... Now consider that a disease mutation arises between C and D Just like the SNPs, it is likely to have arisen once And it is in only one of the common 7 haplotypes ...
... Now consider that a disease mutation arises between C and D Just like the SNPs, it is likely to have arisen once And it is in only one of the common 7 haplotypes ...
91157 Demonstrate understanding of genetic variation and
... Biological ideas and processes relating to sources of variation within a gene pool are selected from: mutation as a source of new alleles independent assortment, segregation and crossing over during meiosis monohybrid inheritance to show the effect of co-dominance, incomplete dominance, lethal ...
... Biological ideas and processes relating to sources of variation within a gene pool are selected from: mutation as a source of new alleles independent assortment, segregation and crossing over during meiosis monohybrid inheritance to show the effect of co-dominance, incomplete dominance, lethal ...
Assessment Schedule 2010 AS 90459 (Biology 2.3) Describe
... Natural selection – changes in the environment cause change in selection pressures on robins so favourable alleles will be selected for and increase in frequency in gene pool. ...
... Natural selection – changes in the environment cause change in selection pressures on robins so favourable alleles will be selected for and increase in frequency in gene pool. ...
Hardy-Weinberg Practice Problems
... equilibrium reveals that 910 are yellow and 90 are white. What are the frequencies of the yellow and white alleles in this population? What is the percentage of heterozygotes in this population? ...
... equilibrium reveals that 910 are yellow and 90 are white. What are the frequencies of the yellow and white alleles in this population? What is the percentage of heterozygotes in this population? ...
Population Genetics and Hardy-Weinberg Populations Lab General
... We will be starting with initial populations in equilibrium (even distributed frequencies of alleles) and looking at the effects of various changes on the equilibrium. For the work I have provided a spreadsheet to calculate the allele frequencies and successive generations. Each population should s ...
... We will be starting with initial populations in equilibrium (even distributed frequencies of alleles) and looking at the effects of various changes on the equilibrium. For the work I have provided a spreadsheet to calculate the allele frequencies and successive generations. Each population should s ...
genetic variation
... (Jelinski, 1997), and can be maintained through arboreal reproduction if the diversity was acquired through recombination, introgression, or somatic mutation (Rasmussen and Kollmann, 2007). The variation is regulated by differential selection pressures such as climate, soil, disturbance, geographica ...
... (Jelinski, 1997), and can be maintained through arboreal reproduction if the diversity was acquired through recombination, introgression, or somatic mutation (Rasmussen and Kollmann, 2007). The variation is regulated by differential selection pressures such as climate, soil, disturbance, geographica ...
The Making of the Fittest - 5 Short Films Watch any 4 of the 5 short
... 4. Near the end of the film, Dr. Sean B. Carroll states that “while mutation is random, natural selection is not.” In your own words, explain how this is possible. Video #2: The Birth and Death of Genes (http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/making-fittest-birth-and-death-genes) 1. Explain how a change ...
... 4. Near the end of the film, Dr. Sean B. Carroll states that “while mutation is random, natural selection is not.” In your own words, explain how this is possible. Video #2: The Birth and Death of Genes (http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/making-fittest-birth-and-death-genes) 1. Explain how a change ...
Population genetics is based on statistical models: “A model is an
... Acts on the locus subject to selection, and those loci linked to it ...
... Acts on the locus subject to selection, and those loci linked to it ...
No Slide Title
... Genetic Drift • Genetic drift is a change in allele frequencies due to random events. • Genetic drift operates most strongly in small populations, but genetic equilibrium happens in large populations because a change is less effective – Small population, one organism doesn’t mate it could be catastr ...
... Genetic Drift • Genetic drift is a change in allele frequencies due to random events. • Genetic drift operates most strongly in small populations, but genetic equilibrium happens in large populations because a change is less effective – Small population, one organism doesn’t mate it could be catastr ...
Mendelian Genetics and Extensions to Mendelism
... A gene may have more than two alleles Mutiple alleles(复等位基因) A condition in which a particular gene occurs in three or more allelic forms in a population of organisms ABO blood types: I A , I B , i IA ...
... A gene may have more than two alleles Mutiple alleles(复等位基因) A condition in which a particular gene occurs in three or more allelic forms in a population of organisms ABO blood types: I A , I B , i IA ...
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
... the magnitude of the effects of migration is based on two factors the proportion of migrants in the population the difference in allele frequencies between the migrants and the original population ...
... the magnitude of the effects of migration is based on two factors the proportion of migrants in the population the difference in allele frequencies between the migrants and the original population ...
The Theory of Evolution
... extreme variations in traits within a population. A useful example can be found in the breeding of the greyhound dog. Early breeders were interested in dog with the greatest speed. They carefully selected from a group of hounds those who ran the fastest. From their offspring, the greyhound breeders ...
... extreme variations in traits within a population. A useful example can be found in the breeding of the greyhound dog. Early breeders were interested in dog with the greatest speed. They carefully selected from a group of hounds those who ran the fastest. From their offspring, the greyhound breeders ...
Slides-Brian_Charlesworth-Sex_and_molecular_evolution
... transmission of a chromosome from parent to offspring. • Natural selection– differences in fitness (survival and reproductive success) between individuals with different genetic ...
... transmission of a chromosome from parent to offspring. • Natural selection– differences in fitness (survival and reproductive success) between individuals with different genetic ...
Association Studies and High-throughput Genotyping Technologies
... Association Studies Can Identify Variants with High or Low Penetrance • Case / control groups • Not limited to high penetrance alleles • Amenable to the study of gene-environment interactions • A preferred approach for the majority of complex genetic disorders ...
... Association Studies Can Identify Variants with High or Low Penetrance • Case / control groups • Not limited to high penetrance alleles • Amenable to the study of gene-environment interactions • A preferred approach for the majority of complex genetic disorders ...
Chapter 5 PPT Review
... where the father is heterozygous for dominate dimples and the mother is heterozygous for dominate ...
... where the father is heterozygous for dominate dimples and the mother is heterozygous for dominate ...
Adaptive evolution
... Balancing Selection Case in which natural selection maintains genetic variation at frequencies above levels of mutation. …in this case, balancing selection makes the population as a whole more resistant to malaria ...
... Balancing Selection Case in which natural selection maintains genetic variation at frequencies above levels of mutation. …in this case, balancing selection makes the population as a whole more resistant to malaria ...
Genetic drift

Genetic drift (or allelic drift) is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces. A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation.When there are few copies of an allele, the effect of genetic drift is larger, and when there are many copies the effect is smaller. In the early twentieth century vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at the most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims that most instances where a genetic change spreads across a population (although not necessarily changes in phenotypes) are caused by genetic drift. There is currently a scientific debate about how much of evolution has been caused by natural selection, and how much by genetic drift.