whatisgeneticsnotes2008
... Therefore, Dad must have the Bb genotype, because he must have given her the “b” allele. His “b” allele is masked by his “B”/dominant allele. ...
... Therefore, Dad must have the Bb genotype, because he must have given her the “b” allele. His “b” allele is masked by his “B”/dominant allele. ...
Notes - Bruce Owen
... − but continuously varying traits are controlled by many pairs of alleles (many loci), with each pair partially influencing the trait − traits that are controlled by multiple pairs of alleles (multiple loci) are called polygenic traits − there are also alleles that affect more than one trait, or in ...
... − but continuously varying traits are controlled by many pairs of alleles (many loci), with each pair partially influencing the trait − traits that are controlled by multiple pairs of alleles (multiple loci) are called polygenic traits − there are also alleles that affect more than one trait, or in ...
Study Guide
... In the space below, draw a pair of homologous chromosomes. Label the chromosomes with two sets of genes, one with homozygous alleles (Gene A, Gene A) and one with heterozygous alleles (Gene B, Gene b). c> G o E o (J ...
... In the space below, draw a pair of homologous chromosomes. Label the chromosomes with two sets of genes, one with homozygous alleles (Gene A, Gene A) and one with heterozygous alleles (Gene B, Gene b). c> G o E o (J ...
the Note
... Amniocentesis: this procedure takes place at 15 to 16 weeks of pregnancy. The pregnancy will have progressed to six months by the time results are available. Termination of the foetus at 6 months can be physically dangerous for the mother and also emotionally very traumatic. Gene probes and DNA ...
... Amniocentesis: this procedure takes place at 15 to 16 weeks of pregnancy. The pregnancy will have progressed to six months by the time results are available. Termination of the foetus at 6 months can be physically dangerous for the mother and also emotionally very traumatic. Gene probes and DNA ...
Biology-studytargetsforsemesterII
... 2. I can describe how natural selection is a mechanism for evolution by explaining how a new species originates. 3. I can explain how natural selection leads to organisms that are well suited for their environment. 4. I can explain how genetic variation is preserved or eliminated from a population t ...
... 2. I can describe how natural selection is a mechanism for evolution by explaining how a new species originates. 3. I can explain how natural selection leads to organisms that are well suited for their environment. 4. I can explain how genetic variation is preserved or eliminated from a population t ...
RF (mu) = NPD + ½(T)/total x 100
... produced if an individual is heterozygous for alleles at only one locus per chromosome and has 22 somatic chromosome pairs? A: 2 alleles on each of 22 chromosome pairs = 222 ...
... produced if an individual is heterozygous for alleles at only one locus per chromosome and has 22 somatic chromosome pairs? A: 2 alleles on each of 22 chromosome pairs = 222 ...
Disease Resistance Procedure
... maximizing resistance to feline distemper by increasing the presence of the hypothetical resistance gene (dd) in the population. Theoretically, a disease resistant population would be more successful in the wild. Students must also be aware, however, of inbreeding in their population. A high total i ...
... maximizing resistance to feline distemper by increasing the presence of the hypothetical resistance gene (dd) in the population. Theoretically, a disease resistant population would be more successful in the wild. Students must also be aware, however, of inbreeding in their population. A high total i ...
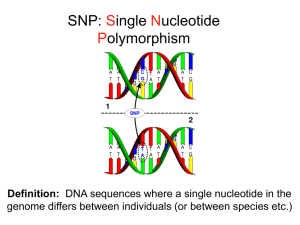
SNP presentation
... heart disease, breast cancer) • May be interested in genetic risks in pregnancy ...
... heart disease, breast cancer) • May be interested in genetic risks in pregnancy ...
Key Points on Allele Dominance
... 1. Most traits are determined by ______________ __________ that act together. 2. Some traits such as the ability to __________ certain substances and the presence or absence of dimples are controlled by a __________ __________. 3. Organisms have ______ alleles for each gene; one allele comes from __ ...
... 1. Most traits are determined by ______________ __________ that act together. 2. Some traits such as the ability to __________ certain substances and the presence or absence of dimples are controlled by a __________ __________. 3. Organisms have ______ alleles for each gene; one allele comes from __ ...
Genetic screening: any kind of test performed for the systematic
... targets, can they be ligated into a complete probe. The advantage of splitting the probe into two parts is that only the ligated oligonucleotides, but not the unbound probe oligonucleotides, are amplified. If the probes were not split in this way, the primer sequences at either end would cause the p ...
... targets, can they be ligated into a complete probe. The advantage of splitting the probe into two parts is that only the ligated oligonucleotides, but not the unbound probe oligonucleotides, are amplified. If the probes were not split in this way, the primer sequences at either end would cause the p ...
MCB 371/372 - Gogarten Lab | UConn
... of providing a selective advantage. Some items are removed quickly (purifying selection), some are useful under some conditions, but most things do not alter the fitness. ...
... of providing a selective advantage. Some items are removed quickly (purifying selection), some are useful under some conditions, but most things do not alter the fitness. ...
Extending Mendel Genetics
... In cats, the gene that controls the color of coat spots is located on the X-Chromosome – expressing (or not) either black or orange or possibly both if there are 2 X chromosomes. Calico cats are white with patches of black & orange. Tortoiseshell cats are black & orange with sparse to no patches of ...
... In cats, the gene that controls the color of coat spots is located on the X-Chromosome – expressing (or not) either black or orange or possibly both if there are 2 X chromosomes. Calico cats are white with patches of black & orange. Tortoiseshell cats are black & orange with sparse to no patches of ...
Answers: Chapter 13 – Genetic Change Through Selection (Thomas
... considered is small AND when only a small percentage of offspring is needed to replace the parents. Method that recognizes the value of multiple traits and places an economic weighting on the traits of importance. Allows an overall ranking of the animals from best to worst – utilizing a highly objec ...
... considered is small AND when only a small percentage of offspring is needed to replace the parents. Method that recognizes the value of multiple traits and places an economic weighting on the traits of importance. Allows an overall ranking of the animals from best to worst – utilizing a highly objec ...
1 - College of Computer, Mathematical, and Natural Sciences
... c. average heterozygosity was declining steadily over time d. individual populations were polymorphic for several loci and most populations were genetically similar to one another. ...
... c. average heterozygosity was declining steadily over time d. individual populations were polymorphic for several loci and most populations were genetically similar to one another. ...
Meiosis and Genetic Variation
... combinations of chromosomes (223). – Sexual reproduction, fertilization, produces offspring from the random combination of two gametes. In humans, the total number of possible chromosome combinations is more than 70 trillion (223 X 223). ...
... combinations of chromosomes (223). – Sexual reproduction, fertilization, produces offspring from the random combination of two gametes. In humans, the total number of possible chromosome combinations is more than 70 trillion (223 X 223). ...
Genetic drift

Genetic drift (or allelic drift) is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces. A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation.When there are few copies of an allele, the effect of genetic drift is larger, and when there are many copies the effect is smaller. In the early twentieth century vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at the most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims that most instances where a genetic change spreads across a population (although not necessarily changes in phenotypes) are caused by genetic drift. There is currently a scientific debate about how much of evolution has been caused by natural selection, and how much by genetic drift.