Patterns of Single gene disorders
... Genetic isolates: groups in which the frequency of rare recessive genes is quite different from that in the general population Although such populations are not consanguineous, the chance of mating with another carrier of a particular recessive condition may be as high as observed in cousin ...
... Genetic isolates: groups in which the frequency of rare recessive genes is quite different from that in the general population Although such populations are not consanguineous, the chance of mating with another carrier of a particular recessive condition may be as high as observed in cousin ...
One parent is heterozygous for the faulty allele
... 3. Listen and decide whether the statements are true or false. (timing 28:30) Tay Sachs Disease a. Among Orthodox Jews, among Ashkenazi Jews between 2% and 3% of the population carries an allele for Tay-Sachs disease which is phenotypically silent in the heterozygous state but in the homozygous stat ...
... 3. Listen and decide whether the statements are true or false. (timing 28:30) Tay Sachs Disease a. Among Orthodox Jews, among Ashkenazi Jews between 2% and 3% of the population carries an allele for Tay-Sachs disease which is phenotypically silent in the heterozygous state but in the homozygous stat ...
Bioinformatics Factsheet
... On the other hand, a recessive allele will be expressed only if there are two identical copies of that allele, or for a male, if one copy is present on the X chromosome. The phenotype of a recessive allele is only seen when both alleles are the same. When an individual has one dominant allele and on ...
... On the other hand, a recessive allele will be expressed only if there are two identical copies of that allele, or for a male, if one copy is present on the X chromosome. The phenotype of a recessive allele is only seen when both alleles are the same. When an individual has one dominant allele and on ...
Name
... 3. Sunlight can cause a person’s hair to become lighter in color. Is this an example of an interaction between genes and the environment? Why or why not? ...
... 3. Sunlight can cause a person’s hair to become lighter in color. Is this an example of an interaction between genes and the environment? Why or why not? ...
Document
... 1. Assuming independent assortment, which of the crosses below will give a 3:3:1:1 ratio? A) AABB x aabb B) AaBb x Aabb C) AaBb x aabb D) AaBB x aaBb E) Aabb x aaBb 2. Suppose that a husband and wife are both heterozygous for a recessive allele that defines albinism. If they have dizygotic (twoegg) ...
... 1. Assuming independent assortment, which of the crosses below will give a 3:3:1:1 ratio? A) AABB x aabb B) AaBb x Aabb C) AaBb x aabb D) AaBB x aaBb E) Aabb x aaBb 2. Suppose that a husband and wife are both heterozygous for a recessive allele that defines albinism. If they have dizygotic (twoegg) ...
Estimating Genetic Penetrance - Dept. of Statistics, Texas
... Use the conditional logistic regression function to determine probability of transmission of the genes • The parents determine the 4 possible children • Treat each child as a category in a multinomial distribution • Calculate the probability of each child using a conditional logistic regression func ...
... Use the conditional logistic regression function to determine probability of transmission of the genes • The parents determine the 4 possible children • Treat each child as a category in a multinomial distribution • Calculate the probability of each child using a conditional logistic regression func ...
Natural selection student guides
... name and eye color as quickly as you can, then record that information in the data table found in your Student Journal. 3. Once you have recorded all of your data, complete the questions found below the data table in your Student Journal. ...
... name and eye color as quickly as you can, then record that information in the data table found in your Student Journal. 3. Once you have recorded all of your data, complete the questions found below the data table in your Student Journal. ...
uh-lee-uls
... appeared in the F1 generation. However, in the F2 generation, the “lost” form of the trait always reappeared in about one fourth of the plants. ...
... appeared in the F1 generation. However, in the F2 generation, the “lost” form of the trait always reappeared in about one fourth of the plants. ...
Early History The Composition of a Human Cell
... Practical Implications of Genetic Variation: The Story of Blood Types Blood can be distinguished into types according to different molecules associated with red blood cells. One system of typing human blood can be instructive in understanding the concept of genetic inheritance. On one of our chromos ...
... Practical Implications of Genetic Variation: The Story of Blood Types Blood can be distinguished into types according to different molecules associated with red blood cells. One system of typing human blood can be instructive in understanding the concept of genetic inheritance. On one of our chromos ...
award
... or GxE) to AD/HD is likely a key component to unlocking the specific processes that cause the disorder. While many environmental factors have been linked to AD/HD, marital conflict has been shown to be a strong predictor of child adjustment. Further, children’s perceptions of conflict, specifically ...
... or GxE) to AD/HD is likely a key component to unlocking the specific processes that cause the disorder. While many environmental factors have been linked to AD/HD, marital conflict has been shown to be a strong predictor of child adjustment. Further, children’s perceptions of conflict, specifically ...
Slide 1
... • The trait that is observed in the F1 offspring is the dominant trait (uppercase) • The trait that disappears in the offspring is the recessive trait (lowercase) ...
... • The trait that is observed in the F1 offspring is the dominant trait (uppercase) • The trait that disappears in the offspring is the recessive trait (lowercase) ...
December 2013 Newsletter - SDSU Department of Psychology
... A: I have found that the process of getting people good cancer care can be complex and that interventions should be very targeted to best help people. I have found that interventions do not always work and so it is important to approach the design of them systematically and evaluate them with strong ...
... A: I have found that the process of getting people good cancer care can be complex and that interventions should be very targeted to best help people. I have found that interventions do not always work and so it is important to approach the design of them systematically and evaluate them with strong ...
The Number of Alleles that Can Be Maintained in a Finite Population
... The complexity of the conditions, however,does not change the generalconclusion that overdominance is a potent factor for maintaining apolymorphism in alarge population. Recently the behavior of overdominant genes in a finite population has been some mathematicalresults of investigated by ROBERTSON( ...
... The complexity of the conditions, however,does not change the generalconclusion that overdominance is a potent factor for maintaining apolymorphism in alarge population. Recently the behavior of overdominant genes in a finite population has been some mathematicalresults of investigated by ROBERTSON( ...
Topic 4.3: Theoretical genetics
... 1. Carrier: An individual who has a recessive allele of a gene that does not have an effect on their phenotype 2. Test Cross: Testing a suspected heterozygote plant or animal by crossing it with a known homozygous recessive. (aa) Since a recessive allele can be masked, it is often impossible to tell ...
... 1. Carrier: An individual who has a recessive allele of a gene that does not have an effect on their phenotype 2. Test Cross: Testing a suspected heterozygote plant or animal by crossing it with a known homozygous recessive. (aa) Since a recessive allele can be masked, it is often impossible to tell ...
Case Study: Genetic Disorders as Models for Evolution
... The lifestyle of the Ashkenazim has been unique among the world’s ethnic groups. As a result of certain events over the past several thousand years, including war and various forms of persecution, the population has remained isolated from the general European population. Some reports suggest that t ...
... The lifestyle of the Ashkenazim has been unique among the world’s ethnic groups. As a result of certain events over the past several thousand years, including war and various forms of persecution, the population has remained isolated from the general European population. Some reports suggest that t ...
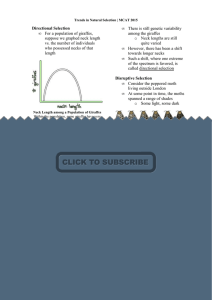
Directional Selection • For a population of giraffes, suppose we
... dominant allele (AA) will not suffer from sicklecell anemia, but will have vulnerability to malaria. An individual who is homozygous for the recessive allele (SS) will have resistance to malaria, but will suffer from sickle-cell anemia. The heterozygous individual (AS) has normal red blood cells and ...
... dominant allele (AA) will not suffer from sicklecell anemia, but will have vulnerability to malaria. An individual who is homozygous for the recessive allele (SS) will have resistance to malaria, but will suffer from sickle-cell anemia. The heterozygous individual (AS) has normal red blood cells and ...
Mendel, Alleles, Punnentt squares Complex Punnett Squares VOCAB:
... Probability is the fraction of how many boxes contain the genotype of phenotype. Ratio (2:2) will always equal the number of boxes in the Punnett square and you count the boxes for the phenotypes or genotypes. Dihybrid Cross: A cross where you track 2 alleles. Boxes will have 4 letters. KEEP THE LET ...
... Probability is the fraction of how many boxes contain the genotype of phenotype. Ratio (2:2) will always equal the number of boxes in the Punnett square and you count the boxes for the phenotypes or genotypes. Dihybrid Cross: A cross where you track 2 alleles. Boxes will have 4 letters. KEEP THE LET ...
F94L – A Muscling Mutation in Limousin Cattle
... polymorphism’ (SNP). It is where one single letter in the genetic code gets changed to a different letter. In the case of the F94L mutation, a ‘C’ has been changed to an ‘A’. The change in the genetic code is a natural process that sometimes spontaneously takes place during cell replication. When th ...
... polymorphism’ (SNP). It is where one single letter in the genetic code gets changed to a different letter. In the case of the F94L mutation, a ‘C’ has been changed to an ‘A’. The change in the genetic code is a natural process that sometimes spontaneously takes place during cell replication. When th ...
Are there genetic factors associated with male infertility?
... essence, an infertile male represents the end of that genetic line. In nature, infertility is a “genetic lethal” condition as the defective genes causing infertility (and perhaps genetic syndromes) cannot be passed on to future generations. Assisted reproductive technologies now bypass this evolutio ...
... essence, an infertile male represents the end of that genetic line. In nature, infertility is a “genetic lethal” condition as the defective genes causing infertility (and perhaps genetic syndromes) cannot be passed on to future generations. Assisted reproductive technologies now bypass this evolutio ...
Bikini Bottom Genetics
... Concept 10.2 Mendel discovered that inheritance follows rules of chance. (p. 208-214) The offspring of 2 true-breeding plants are called ______________. Mendel performed _______________ crosses, which are matings between plants that differ in only one character. Mendel developed the following 4 hyp ...
... Concept 10.2 Mendel discovered that inheritance follows rules of chance. (p. 208-214) The offspring of 2 true-breeding plants are called ______________. Mendel performed _______________ crosses, which are matings between plants that differ in only one character. Mendel developed the following 4 hyp ...
Biology 12AP Genetics
... Mendel made when he crossed two strains of pure-breeding peas and observed a particular characteristic that showed two traits, such as purple and white flowers? ...
... Mendel made when he crossed two strains of pure-breeding peas and observed a particular characteristic that showed two traits, such as purple and white flowers? ...
4. Chromosomes and Inheritance
... c. Based on the actual results of this cross, do you think these 2 gene loci are linked or unlinked? Explain your answer. d. Assuming that your answer to part C is correct, why don’t the actual results of the cross agree more closely with your predicted results? Describe as many possible reasons as ...
... c. Based on the actual results of this cross, do you think these 2 gene loci are linked or unlinked? Explain your answer. d. Assuming that your answer to part C is correct, why don’t the actual results of the cross agree more closely with your predicted results? Describe as many possible reasons as ...
BI 102 – General Biology Instructor: Waite Quiz 3 Study Guide Quiz
... BI 102 – General Biology Instructor: Waite ...
... BI 102 – General Biology Instructor: Waite ...
Genetic drift

Genetic drift (or allelic drift) is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces. A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation.When there are few copies of an allele, the effect of genetic drift is larger, and when there are many copies the effect is smaller. In the early twentieth century vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at the most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims that most instances where a genetic change spreads across a population (although not necessarily changes in phenotypes) are caused by genetic drift. There is currently a scientific debate about how much of evolution has been caused by natural selection, and how much by genetic drift.