video slide - Point Pleasant Beach School District
... independent assortment of alleles, but crossing over also mixes up alleles on homologous chromosomes before distribution “Therefore, in humans with 23 pairs of chromosomes, a gamete (egg or sperm) could have 223 or 8,388,604 possible combinations of chromosomes from that parent. Any couple could hav ...
... independent assortment of alleles, but crossing over also mixes up alleles on homologous chromosomes before distribution “Therefore, in humans with 23 pairs of chromosomes, a gamete (egg or sperm) could have 223 or 8,388,604 possible combinations of chromosomes from that parent. Any couple could hav ...
The genetics of deafness - Archives of Disease in Childhood
... accounting for 70-85% of genetic non-syndromic deafness.34 Genes acting in an autosomal dominant manner account for 12-25%3 of such cases and sex linked genes account for approximately 3%.' Although it may be possible to recognise the autosomal dominant and sex linked types on the basis of the inher ...
... accounting for 70-85% of genetic non-syndromic deafness.34 Genes acting in an autosomal dominant manner account for 12-25%3 of such cases and sex linked genes account for approximately 3%.' Although it may be possible to recognise the autosomal dominant and sex linked types on the basis of the inher ...
VI. Levels of Selection
... 3. 'Selfish' Genes (Richard Dawkins) - genes are the fundamental replicators - genes which confer an advantage, when averaged across other genetic backgrounds, will be selected for. Analogy of 'crews') - co-adaptive assemblages and non-additive effects are not explained ...
... 3. 'Selfish' Genes (Richard Dawkins) - genes are the fundamental replicators - genes which confer an advantage, when averaged across other genetic backgrounds, will be selected for. Analogy of 'crews') - co-adaptive assemblages and non-additive effects are not explained ...
chapter 11 section 1 notes
... Mendel’s garden had several stocks of pea plants that were “truebreeding,” meaning that they were self-pollinating, and would produce offspring with identical traits to themselves. In other words, the traits of each successive generation would be the same. A trait is a specific characteristic of an ...
... Mendel’s garden had several stocks of pea plants that were “truebreeding,” meaning that they were self-pollinating, and would produce offspring with identical traits to themselves. In other words, the traits of each successive generation would be the same. A trait is a specific characteristic of an ...
Multivariate Analysis of Genotype–Phenotype Association
... ABSTRACT With the advent of modern imaging and measurement technology, complex phenotypes are increasingly represented by large numbers of measurements, which may not bear biological meaning one by one. For such multivariate phenotypes, studying the pairwise associations between all measurements and ...
... ABSTRACT With the advent of modern imaging and measurement technology, complex phenotypes are increasingly represented by large numbers of measurements, which may not bear biological meaning one by one. For such multivariate phenotypes, studying the pairwise associations between all measurements and ...
Genetic Algorithms: Genetic Algorithm Applications to Actuarial Problems ARC 2012
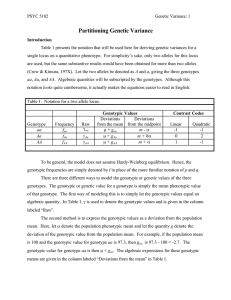
... § Blind Robby – deterministic gene string with 7 possible actions for each gene § Robby with vision – adapts to environment and chooses actions (from 7) § Provider network – deterministic gene string, simple IN or OUT of network ...
... § Blind Robby – deterministic gene string with 7 possible actions for each gene § Robby with vision – adapts to environment and chooses actions (from 7) § Provider network – deterministic gene string, simple IN or OUT of network ...
The genetic causes of convergent evolution
... alleles can be selected even if alternative alleles would have provided superior fitness improvements12. In some cases, alleles that have been selected during previous bouts of selection can accumulate additional mutations that enhance their beneficial phenotypic effects and/or ameliorate deleteriou ...
... alleles can be selected even if alternative alleles would have provided superior fitness improvements12. In some cases, alleles that have been selected during previous bouts of selection can accumulate additional mutations that enhance their beneficial phenotypic effects and/or ameliorate deleteriou ...
Lecture 32 – PDF
... treated as if they were alleles at a single genetic locus. (iv) Inversions historically are called “crossover suppressers.” This is a misnomer, as recombination (not crossing over) is actually suppressed. b) Inversions permit the build-up and maintenance of co-adapted gene complexes. (i) The region ...
... treated as if they were alleles at a single genetic locus. (iv) Inversions historically are called “crossover suppressers.” This is a misnomer, as recombination (not crossing over) is actually suppressed. b) Inversions permit the build-up and maintenance of co-adapted gene complexes. (i) The region ...
Polygenic inheritance of fruit size in red pepper
... amlyais of them will serve ss an illustration of aethods toy which actions of the polygenes can toe determined. As the ntxmtoer of genes affecting a polygenic character is large, it is impossitole to single them out individually, A suggestion for simplifiestion would toe to study then in small group ...
... amlyais of them will serve ss an illustration of aethods toy which actions of the polygenes can toe determined. As the ntxmtoer of genes affecting a polygenic character is large, it is impossitole to single them out individually, A suggestion for simplifiestion would toe to study then in small group ...
Short Tandem Repeat Polymorphism and Cancer Risk: Influence of
... vary with the length of CAG repeats due to the role of androgen receptor in the disease. This speculation has been supported by some epidemiologic studies in which longer CAG repeats are found to be associated with lower risk of prostate cancer. However, not all epidemiologic studies have found evid ...
... vary with the length of CAG repeats due to the role of androgen receptor in the disease. This speculation has been supported by some epidemiologic studies in which longer CAG repeats are found to be associated with lower risk of prostate cancer. However, not all epidemiologic studies have found evid ...
Genetic correlations between adults and larvae in a marine fish
... our knowledge, existing measures of phenotypic correlations do not separate genetic resemblance from sizedependent maternal effects, and the actual magnitudes of size-dependent maternal effects are unclear. However, the presence of strong phenotypic correlations between maternal and offspring size s ...
... our knowledge, existing measures of phenotypic correlations do not separate genetic resemblance from sizedependent maternal effects, and the actual magnitudes of size-dependent maternal effects are unclear. However, the presence of strong phenotypic correlations between maternal and offspring size s ...
Genetic linkage studies in the pseudoautosomal
... the role of specific genes, specific environmental factors, and interactions between genes and environment in determining a particular trait of interest. This trait can be either a binary trait such as a particular disease (schizophrenia, breast cancer) or a quantitative trait (serum cholesterol lev ...
... the role of specific genes, specific environmental factors, and interactions between genes and environment in determining a particular trait of interest. This trait can be either a binary trait such as a particular disease (schizophrenia, breast cancer) or a quantitative trait (serum cholesterol lev ...
Parameter Control in Evolutionary Algorithms:Trends and Challenges
... 2) Provide an extensive review of related work. 3) Observe main clusters of work and analyze the corresponding research trends. 4) Identify the most prominent challenges for future developments. The rest of the paper is organized as follows. The next section gives a short overview of the development ...
... 2) Provide an extensive review of related work. 3) Observe main clusters of work and analyze the corresponding research trends. 4) Identify the most prominent challenges for future developments. The rest of the paper is organized as follows. The next section gives a short overview of the development ...
Chapter 5 Gases - Saint Demetrios Astoria School
... Humans? (cont’d.) • Types of genetic mutations – Single genes that follow Mendelian inheritance patterns govern more than 6,000 genetic abnormalities and disorders – Most human traits are polygenic, or influenced by multiple genes – Traits can be influenced by environmental ...
... Humans? (cont’d.) • Types of genetic mutations – Single genes that follow Mendelian inheritance patterns govern more than 6,000 genetic abnormalities and disorders – Most human traits are polygenic, or influenced by multiple genes – Traits can be influenced by environmental ...
Chapter 14 PPT Mendelian Genetics..
... segregation, states that the two alleles for a heritable character separate (segregate) during gamete formation and end up in different gametes • Thus, an egg or a sperm gets only one of the two alleles that are present in the somatic cells of an organism • This segregation of alleles corresponds to ...
... segregation, states that the two alleles for a heritable character separate (segregate) during gamete formation and end up in different gametes • Thus, an egg or a sperm gets only one of the two alleles that are present in the somatic cells of an organism • This segregation of alleles corresponds to ...
Obtaining genetic testing in pediatric epilepsy
... NGS does not provide a panacea for genetic diagnosis. Mutations in noncoding areas and introns are not covered by NGS technology as applied to WES. Triplet repeats, as in fragile X, abnormal methylation, as in Angelman syndrome, and some large insertions, deletions, and duplications can be missed by ...
... NGS does not provide a panacea for genetic diagnosis. Mutations in noncoding areas and introns are not covered by NGS technology as applied to WES. Triplet repeats, as in fragile X, abnormal methylation, as in Angelman syndrome, and some large insertions, deletions, and duplications can be missed by ...
Mendelian genetics power point
... For example, for the cross PpYyRr Ppyyrr, we can calculate the probability of offspring showing at least two recessive traits ...
... For example, for the cross PpYyRr Ppyyrr, we can calculate the probability of offspring showing at least two recessive traits ...
Chapter 15
... The Chromosome Theory of Inheritance: genes (allele pairs) are on chromosomes and homologous chromosomes segregate during meiosis (principle of segregation) and reunite during fertilization. If allele pairs are on different chromosomes they will sort independently (principle of independent assortme ...
... The Chromosome Theory of Inheritance: genes (allele pairs) are on chromosomes and homologous chromosomes segregate during meiosis (principle of segregation) and reunite during fertilization. If allele pairs are on different chromosomes they will sort independently (principle of independent assortme ...
as a PDF
... F1 hybrids. This pattern, referred to as isolation asymmetry or Darwin’s corollary to Haldane’s rule, is a general feature of reproductive isolation in plants, yet factors determining its magnitude and direction remain unclear. We evaluated reciprocal species crosses between two naturally hybridizin ...
... F1 hybrids. This pattern, referred to as isolation asymmetry or Darwin’s corollary to Haldane’s rule, is a general feature of reproductive isolation in plants, yet factors determining its magnitude and direction remain unclear. We evaluated reciprocal species crosses between two naturally hybridizin ...
0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0
... • Biological Problem: For disease association studies, haplotype data is more valuable than genotype data, but haplotype data is hard to collect. Genotype data is easy to collect. • Computational Problem: Given a set of n genotypes, determine the original set of n haplotype pairs that generated the ...
... • Biological Problem: For disease association studies, haplotype data is more valuable than genotype data, but haplotype data is hard to collect. Genotype data is easy to collect. • Computational Problem: Given a set of n genotypes, determine the original set of n haplotype pairs that generated the ...
Genetic drift

Genetic drift (or allelic drift) is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces. A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation.When there are few copies of an allele, the effect of genetic drift is larger, and when there are many copies the effect is smaller. In the early twentieth century vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at the most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims that most instances where a genetic change spreads across a population (although not necessarily changes in phenotypes) are caused by genetic drift. There is currently a scientific debate about how much of evolution has been caused by natural selection, and how much by genetic drift.