AP Bio Steps Wednesday February 25 SWBAT - APICA
... Describe the inheritance of color blindness and hemophilia as examples of sex linkage. State that a human female can be homozygous or heterozygous with respect to sex-linked genes. Explain that female carriers are heterozygous for X-linked recessive alleles. Predict the genotypic and phenotypic rati ...
... Describe the inheritance of color blindness and hemophilia as examples of sex linkage. State that a human female can be homozygous or heterozygous with respect to sex-linked genes. Explain that female carriers are heterozygous for X-linked recessive alleles. Predict the genotypic and phenotypic rati ...
Lecture 13: Speciation Continued
... linked with right alleles for host selection. These conditions are Exceptional Circumstances!!! ...
... linked with right alleles for host selection. These conditions are Exceptional Circumstances!!! ...
Mutations
... Sickle Cell Anemia had change in the polypeptide chain: Glutamic acid is changed to Valine ...
... Sickle Cell Anemia had change in the polypeptide chain: Glutamic acid is changed to Valine ...
D0794983_C11_L01_Lesson_Review_Workbook_A
... Mendel founded modern genetics with his experiments on a convenient model system, pea plants: Fertilization is the process in which reproductive cells (egg from the female and sperm from the male) join to produce a new cell. A trait is a specific characteristic, such as (in peas) seed color or plant ...
... Mendel founded modern genetics with his experiments on a convenient model system, pea plants: Fertilization is the process in which reproductive cells (egg from the female and sperm from the male) join to produce a new cell. A trait is a specific characteristic, such as (in peas) seed color or plant ...
11.1 Worksheet - Merrillville Community School
... Mendel founded modern genetics with his experiments on a convenient model system, pea plants: Fertilization is the process in which reproductive cells (egg from the female and sperm from the male) join to produce a new cell. A trait is a specific characteristic, such as (in peas) seed color or plant ...
... Mendel founded modern genetics with his experiments on a convenient model system, pea plants: Fertilization is the process in which reproductive cells (egg from the female and sperm from the male) join to produce a new cell. A trait is a specific characteristic, such as (in peas) seed color or plant ...
Heterosis East, E. M. 1936. Genetics, 21
... was given a purely formal solution some twenty-five years ago when a series of analyses of the effects of inbreeding in maize, supplemented by studies of the results obtained when these inbred lines were crossed, made it possible to regard heterosis as something incident to the operation of genetic ...
... was given a purely formal solution some twenty-five years ago when a series of analyses of the effects of inbreeding in maize, supplemented by studies of the results obtained when these inbred lines were crossed, made it possible to regard heterosis as something incident to the operation of genetic ...
PUNNETT SQUARE Webquest
... to perform the following activities that teach about Dominance, Incomplete Dominance and Codominance. Then, answer the questions below in complete sentences. ...
... to perform the following activities that teach about Dominance, Incomplete Dominance and Codominance. Then, answer the questions below in complete sentences. ...
5163 Demonstrate knowledge of, and respond to client requests for
... The following areas of knowledge underpin performance of the elements in this unit standard: Element 1 Gene, homozygous, heterozygous, dominant/recessive, phenotype/genotype, allele's, gene locus, filial generation, lethal factors Mendel's first and second laws of inheritance Sex linked genes/charac ...
... The following areas of knowledge underpin performance of the elements in this unit standard: Element 1 Gene, homozygous, heterozygous, dominant/recessive, phenotype/genotype, allele's, gene locus, filial generation, lethal factors Mendel's first and second laws of inheritance Sex linked genes/charac ...
Jeopardy
... that shows all the possible alleles (or versions of a gene) that can be inherited by the offspring of two parents. • If a heterozygous blue-tailed critter (Bb) is crossed with a homozygous orange-tailed critter (bb), what is the probability of bluetailed to orange-tailed offspring being born. • Answ ...
... that shows all the possible alleles (or versions of a gene) that can be inherited by the offspring of two parents. • If a heterozygous blue-tailed critter (Bb) is crossed with a homozygous orange-tailed critter (bb), what is the probability of bluetailed to orange-tailed offspring being born. • Answ ...
HOMEWORK PACKET: (11.1) The Work of Gregor Mendel
... Mendel founded modern genetics with his experiments on a convenient model system, pea plants: Fertilization is the process in which reproductive cells (egg from the female and sperm from the male) join to produce a new cell. A trait is a specific characteristic, such as (in peas) seed color or plant ...
... Mendel founded modern genetics with his experiments on a convenient model system, pea plants: Fertilization is the process in which reproductive cells (egg from the female and sperm from the male) join to produce a new cell. A trait is a specific characteristic, such as (in peas) seed color or plant ...
Title
... phenotype if they are ___________. a. homozygous, heterozygous b. heterozygous, homozygous c. homozygous, hemizygous ...
... phenotype if they are ___________. a. homozygous, heterozygous b. heterozygous, homozygous c. homozygous, hemizygous ...
Meiosis and Mendel
... c. Allowed F1 generation to self-pollinate 1). Produced F2 generation that had both plants with purple and white flowers) 2). Trait for white had been “hidden”, it did not disappear. ...
... c. Allowed F1 generation to self-pollinate 1). Produced F2 generation that had both plants with purple and white flowers) 2). Trait for white had been “hidden”, it did not disappear. ...
Document
... In eukaryotes, nuclear chromosomes are packaged by proteins into a condensed structure called chromatin. This allows the very long DNA molecules to fit into the cell nucleus. The structure of chromosomes and chromatin varies through the cell cycle. Chromosomes are the essential unit for cellular div ...
... In eukaryotes, nuclear chromosomes are packaged by proteins into a condensed structure called chromatin. This allows the very long DNA molecules to fit into the cell nucleus. The structure of chromosomes and chromatin varies through the cell cycle. Chromosomes are the essential unit for cellular div ...
Unit 3- study guide Test 1
... In humans, our diploid number is 46 and our haploid number is 23 18. Why is crossing over important? When does it happen? Crossing over is where the paternal and maternal chromsomes “cross over” each other and exchange genetic information to create a new chromosome, with some of both parent’s DNA. T ...
... In humans, our diploid number is 46 and our haploid number is 23 18. Why is crossing over important? When does it happen? Crossing over is where the paternal and maternal chromsomes “cross over” each other and exchange genetic information to create a new chromosome, with some of both parent’s DNA. T ...
Study Guide
... Note: The result of Meiosis I is _____ new daughter cells. The two new cells have sets of chromosomes and alleles that are ____________________ from each other and from the parent ...
... Note: The result of Meiosis I is _____ new daughter cells. The two new cells have sets of chromosomes and alleles that are ____________________ from each other and from the parent ...
Presentation
... their height. The alleles for that gene are short and tall. The pea plants had two genes for flower color. The alleles for that gene are purple and white. The pea plants had two genes for their seed shape. The alleles for that gene are round and wrinkled. ...
... their height. The alleles for that gene are short and tall. The pea plants had two genes for flower color. The alleles for that gene are purple and white. The pea plants had two genes for their seed shape. The alleles for that gene are round and wrinkled. ...
Station 1 Gregor Mendel Who was Gregor Mendel? Where did he do
... the study of heredity. Heredity is the passing of physical characteristics from parents to offspring. Mendel wondered why different pea plants had different characteristics. Some pea plants grew tall, while others were short. Some plants produced green seeds, while others had yellow seeds. Each diff ...
... the study of heredity. Heredity is the passing of physical characteristics from parents to offspring. Mendel wondered why different pea plants had different characteristics. Some pea plants grew tall, while others were short. Some plants produced green seeds, while others had yellow seeds. Each diff ...
Lesson 1 | Mendel and His Peas - Kapuk`s E
... sentence. NOTE: You may need to change a term to its plural form. ...
... sentence. NOTE: You may need to change a term to its plural form. ...
Notes 5-1 & 5-2
... If a gene has both dominant alleles, it is homozygous dominant (TT) If a gene has both recessive alleles, it is homozygous recessive (tt) If a gene has 1 dominant and 1 recessive allele, it is heterozygous (Tt) ...
... If a gene has both dominant alleles, it is homozygous dominant (TT) If a gene has both recessive alleles, it is homozygous recessive (tt) If a gene has 1 dominant and 1 recessive allele, it is heterozygous (Tt) ...
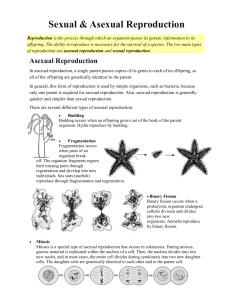
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
... Sexual Reproduction In sexual reproduction, two parents each contribute genetic material to their offspring. Because both parents contribute genetic material, the offspring have traits of both parents, but they are not exactly like either parent. For sexual reproduction to occur, each parent must f ...
... Sexual Reproduction In sexual reproduction, two parents each contribute genetic material to their offspring. Because both parents contribute genetic material, the offspring have traits of both parents, but they are not exactly like either parent. For sexual reproduction to occur, each parent must f ...
Genetics Powerpoint for Bio. I
... same gene Dominant – gene that is seen Recessive – only seen if with another recessive allele Homozygous – having 2 like alleles Heterozygous – having 2 different alleles Genotypes – actual gene make-up for a particular locus or trait Phenotypes – visible trait ...
... same gene Dominant – gene that is seen Recessive – only seen if with another recessive allele Homozygous – having 2 like alleles Heterozygous – having 2 different alleles Genotypes – actual gene make-up for a particular locus or trait Phenotypes – visible trait ...
Integrative taxonomy – Methods and Applications
... of cichlid fishes, adaptive radiation is associated with strong divergent selection on morphological traits whereas these differences in morphological traits were not associated with strong reproductive isolation. Integration by cumulation is based on the principle that divergence in any one of the ...
... of cichlid fishes, adaptive radiation is associated with strong divergent selection on morphological traits whereas these differences in morphological traits were not associated with strong reproductive isolation. Integration by cumulation is based on the principle that divergence in any one of the ...
Hybrid (biology)

In biology a hybrid, also known as cross breed, is the result of mixing, through sexual reproduction, two animals or plants of different breeds, varieties, species or genera. Using genetic terminology, it may be defined as follows. Hybrid generally refers to any offspring resulting from the breeding of two genetically distinct individuals, which usually will result in a high degree of heterozygosity, though hybrid and heterozygous are not, strictly speaking, synonymous. a genetic hybrid carries two different alleles of the same gene a structural hybrid results from the fusion of gametes that have differing structure in at least one chromosome, as a result of structural abnormalities a numerical hybrid results from the fusion of gametes having different haploid numbers of chromosomes a permanent hybrid is a situation where only the heterozygous genotype occurs, because all homozygous combinations are lethal.From a taxonomic perspective, hybrid refers to: Offspring resulting from the interbreeding between two animal species or plant species. See also hybrid speciation. Hybrids between different subspecies within a species (such as between the Bengal tiger and Siberian tiger) are known as intra-specific hybrids. Hybrids between different species within the same genus (such as between lions and tigers) are sometimes known as interspecific hybrids or crosses. Hybrids between different genera (such as between sheep and goats) are known as intergeneric hybrids. Extremely rare interfamilial hybrids have been known to occur (such as the guineafowl hybrids). No interordinal (between different orders) animal hybrids are known. The third type of hybrid consists of crosses between populations, breeds or cultivars within a single species. This meaning is often used in plant and animal breeding, where hybrids are commonly produced and selected, because they have desirable characteristics not found or inconsistently present in the parent individuals or populations.↑ ↑ ↑ ↑