Bulk Selection
... NILs in Table 1 (below). The multiline was divided into two parts and one part was advanced through four generations with fungicide applications to control rust, and the second part was advanced through four generations under human enhanced rust epiphytotics. Overall, the NILs had similar phenotypes ...
... NILs in Table 1 (below). The multiline was divided into two parts and one part was advanced through four generations with fungicide applications to control rust, and the second part was advanced through four generations under human enhanced rust epiphytotics. Overall, the NILs had similar phenotypes ...
Genetic Variation of Multilocus Traits
... will denote by (αδ) with subscripts for the alleles at one of the loci (for the additive effects) and the genotypes at the other locus (for the dominance effects) There third is dominance × dominance interaction, which we will denote by (δδ) with subscripts for the genotypes at the two loci. How man ...
... will denote by (αδ) with subscripts for the alleles at one of the loci (for the additive effects) and the genotypes at the other locus (for the dominance effects) There third is dominance × dominance interaction, which we will denote by (δδ) with subscripts for the genotypes at the two loci. How man ...
file
... condition of both males and females (see table 1 for a list of symbols). Condition in turn determines viability, and in the case of males it can also have an influence on their sexual appearance. We introduce female choice by considering a second locus with two possible alleles, B involving choosy b ...
... condition of both males and females (see table 1 for a list of symbols). Condition in turn determines viability, and in the case of males it can also have an influence on their sexual appearance. We introduce female choice by considering a second locus with two possible alleles, B involving choosy b ...
the long-term evolution of multilocus traits under frequency
... These observations agree with analytical results (Geritz et al. 1998; Kisdi and Geritz 1999) that predict the strategy z* ⫽ 0 to be both convergence stable and evolutionarily stable for ⬍ . The former implies that evolution through small phenotypic steps will proceed toward z* ⫽ 0, with each step ...
... These observations agree with analytical results (Geritz et al. 1998; Kisdi and Geritz 1999) that predict the strategy z* ⫽ 0 to be both convergence stable and evolutionarily stable for ⬍ . The former implies that evolution through small phenotypic steps will proceed toward z* ⫽ 0, with each step ...
File
... The symbol D represents the dominant allele for the disorder. The symbol d represents the recessive allele. Fiona has the pair of alleles dd. Write the correct pairs of alleles in the boxes. ...
... The symbol D represents the dominant allele for the disorder. The symbol d represents the recessive allele. Fiona has the pair of alleles dd. Write the correct pairs of alleles in the boxes. ...
Mendelian genetics
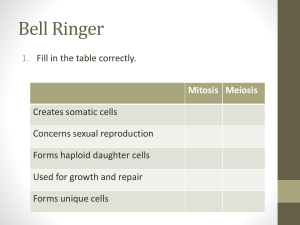
... Mitosis Meiosis Creates somatic cells Concerns sexual reproduction Forms haploid daughter cells Used for growth and repair ...
... Mitosis Meiosis Creates somatic cells Concerns sexual reproduction Forms haploid daughter cells Used for growth and repair ...
Document
... who is homozygous recessive for both traits, then all his children will have dominant phenotypes. • If a man is heterozygous for both traits, then each child has a 25% chance of showing either one or both recessive traits. – 4 phenotypes at a ratio of 1:1:1:1 ...
... who is homozygous recessive for both traits, then all his children will have dominant phenotypes. • If a man is heterozygous for both traits, then each child has a 25% chance of showing either one or both recessive traits. – 4 phenotypes at a ratio of 1:1:1:1 ...
TEKS 8.11 C
... parents with known genotypes. The Punnett square is named after Reginald Punnett, an English geneticist who discovered some basic principles about sex linkage and sex determination while researching the feather color of chickens as a predictor of gender. The monohybrid cross is used to investigate t ...
... parents with known genotypes. The Punnett square is named after Reginald Punnett, an English geneticist who discovered some basic principles about sex linkage and sex determination while researching the feather color of chickens as a predictor of gender. The monohybrid cross is used to investigate t ...
Pedigrees - Wikispaces
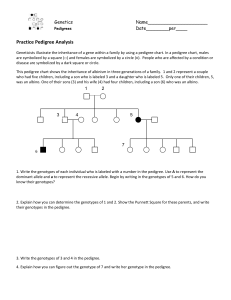
... Pedigrees Pedigree charts show a record of the family of an individual. It can be used to study the transmission of a hereditary condition. It is particularly useful when there are large families and a good family record over several generations. You cannot make humans of different types breed to ...
... Pedigrees Pedigree charts show a record of the family of an individual. It can be used to study the transmission of a hereditary condition. It is particularly useful when there are large families and a good family record over several generations. You cannot make humans of different types breed to ...
Correlation of length of VNTR alleles at the X
... the effects were major, they would result in single gene rather than polygenic disorders. X-linked genes form a unique vehicle to examine this hypothesis and search for subtle effects since, at least in males, each allele is hemizygously present thus eliminating the confounding factor of heterozygos ...
... the effects were major, they would result in single gene rather than polygenic disorders. X-linked genes form a unique vehicle to examine this hypothesis and search for subtle effects since, at least in males, each allele is hemizygously present thus eliminating the confounding factor of heterozygos ...
Chapter 5: Patterns of Inheritance - ahs
... Example 1: P generation of male yellow-pea-producing plant and female green-pea-producing plant P generation cross results: All offspring (F1 generation) were the same seed colour: yellow, i.e., one parent’s seed colour trait seemed to disappear. This result was the same for each of the seven traits ...
... Example 1: P generation of male yellow-pea-producing plant and female green-pea-producing plant P generation cross results: All offspring (F1 generation) were the same seed colour: yellow, i.e., one parent’s seed colour trait seemed to disappear. This result was the same for each of the seven traits ...
Mating ecology explains patterns of genome elimination
... in the citrus mealybug Planococcus citri, a male’s sperm carry only the chromosomes he inherited from his mother, all paternal chromosomes having been eliminated, whereas a female’s oocytes carry chromosomes from both of her parents. This ‘genome elimination’ (GE) is a whole-genome form of meiotic d ...
... in the citrus mealybug Planococcus citri, a male’s sperm carry only the chromosomes he inherited from his mother, all paternal chromosomes having been eliminated, whereas a female’s oocytes carry chromosomes from both of her parents. This ‘genome elimination’ (GE) is a whole-genome form of meiotic d ...
Unequal allelic frequencies at the self
... effect of random genetic drift within a panmictic population, and that of population structure, in causing departure from isoplethic equilibrium at the S-locus in samples from natural populations of a tree species with GSI, Prunus avium L. (Rosaceae). We used previously published data on microsatell ...
... effect of random genetic drift within a panmictic population, and that of population structure, in causing departure from isoplethic equilibrium at the S-locus in samples from natural populations of a tree species with GSI, Prunus avium L. (Rosaceae). We used previously published data on microsatell ...
Presentation
... (universal donor), but can only receive type O- blood. People with type AB+ blood can receive blood from anyone (universal recipient), but can only donate to someone who is type AB+. ...
... (universal donor), but can only receive type O- blood. People with type AB+ blood can receive blood from anyone (universal recipient), but can only donate to someone who is type AB+. ...
Introduction
... c) What can you conclude about the children if both parents are affected with an X-linked recessive trait? d) How does this conclusion compare with the one you made earlier if about both parents being affected by an autosomal recessive trait? e. What can you conclude about the number of males that w ...
... c) What can you conclude about the children if both parents are affected with an X-linked recessive trait? d) How does this conclusion compare with the one you made earlier if about both parents being affected by an autosomal recessive trait? e. What can you conclude about the number of males that w ...
NAME: 07/23 SSA Science NATURAL SELECTION VIRTUAL LAB
... 2. This simulation is investigating the effect of ___ on certain phenotypes. 3. By placing pressure on these specific phenotypes, what will change? 4. What can natural selection alter in a population’s gene pool over time? 5. So how can evolution be described when referring to changes in gene pools? ...
... 2. This simulation is investigating the effect of ___ on certain phenotypes. 3. By placing pressure on these specific phenotypes, what will change? 4. What can natural selection alter in a population’s gene pool over time? 5. So how can evolution be described when referring to changes in gene pools? ...
Do progeny inherit traits from their parents in predictable ways?
... was bred to a black-nosed Ridgeback female (Mizani). Both parents had obvious back ridges and were negative for a defect called dermoid sinus, which often occurs in this breed of dogs. (All Ridgebacks that lack a ridge or have dermoid sinus are neutered by breeders.) What can you deduce about the in ...
... was bred to a black-nosed Ridgeback female (Mizani). Both parents had obvious back ridges and were negative for a defect called dermoid sinus, which often occurs in this breed of dogs. (All Ridgebacks that lack a ridge or have dermoid sinus are neutered by breeders.) What can you deduce about the in ...
X r Y
... – The factors separated when the gametes were formed during meiosis, each gamete would get either the tall or short gene. – When random fusion of the gametes occurred during fertilization, the combinations were brought together in a 3:1 ratio, as indicated by the Punnett square. ...
... – The factors separated when the gametes were formed during meiosis, each gamete would get either the tall or short gene. – When random fusion of the gametes occurred during fertilization, the combinations were brought together in a 3:1 ratio, as indicated by the Punnett square. ...
Chapter 14
... – There are many varieties with distinct heritable features, or characters (such as flower color); character variants (such as purple or white flowers) are called traits. – Mating of plants can be controlled. – Each pea plant has sperm-producing organs (stamens) and egg-producing organs (carpels). – ...
... – There are many varieties with distinct heritable features, or characters (such as flower color); character variants (such as purple or white flowers) are called traits. – Mating of plants can be controlled. – Each pea plant has sperm-producing organs (stamens) and egg-producing organs (carpels). – ...
Supplementary Information (doc 224K)
... Criteria of STR marker eligibility for quantitative chimerism testing (RSD code) Judicious selection of appropriate microsatellite markers is an essential prerequisite for reliable monitoring of post-transplant chimerism. The requirements of quantitative chimerism analysis by STR-PCR show important ...
... Criteria of STR marker eligibility for quantitative chimerism testing (RSD code) Judicious selection of appropriate microsatellite markers is an essential prerequisite for reliable monitoring of post-transplant chimerism. The requirements of quantitative chimerism analysis by STR-PCR show important ...
parts
... close to the predicted results must the data be for you to be confident that they support the hypothesis? A coin toss is a good way to make and test predictions. You and a partner will each toss a coin. Then you will record the results to show whether or not either of the two coins has turned up hea ...
... close to the predicted results must the data be for you to be confident that they support the hypothesis? A coin toss is a good way to make and test predictions. You and a partner will each toss a coin. Then you will record the results to show whether or not either of the two coins has turned up hea ...
Plant Genetics 2003 - Biology Department | UNC Chapel Hill
... • What is the effect of study power on – The # DQTL per trait? – The effect sizes of the DQTL? ...
... • What is the effect of study power on – The # DQTL per trait? – The effect sizes of the DQTL? ...
Mendelian Genetics Chapter 12 Reading Mendellian Genetics
... he taught high school and cared for a garden. It was in this garden that he completed his important experiments. Most of Mendel’s experiments involved crossing different types of pea plants. In this case, the word cross means “to mate or breed two individuals.” Mendel crossed a type of garden pea pl ...
... he taught high school and cared for a garden. It was in this garden that he completed his important experiments. Most of Mendel’s experiments involved crossing different types of pea plants. In this case, the word cross means “to mate or breed two individuals.” Mendel crossed a type of garden pea pl ...