Lab 10: Population Genetics
... Genetic changes that occur in generations of populations over long periods of time are the basis for evolution of a species. In a population of any species, there are typically individuals that show differences in phenotype for a particular trait. These differences may represent genetic variation in ...
... Genetic changes that occur in generations of populations over long periods of time are the basis for evolution of a species. In a population of any species, there are typically individuals that show differences in phenotype for a particular trait. These differences may represent genetic variation in ...
Nerve activates contraction
... frequencies from one generation to another occur because of chance events (sampling errors) that occur when populations are finite in size. • For example, one would not be too surprised if a coin produced seven heads and three tails in ten tosses, but you would be surprised if you saw 700 heads and ...
... frequencies from one generation to another occur because of chance events (sampling errors) that occur when populations are finite in size. • For example, one would not be too surprised if a coin produced seven heads and three tails in ten tosses, but you would be surprised if you saw 700 heads and ...
chapter14
... – Each character (but one) is controlled by a single gene. – Each gene has only two alleles, one of which is completely dominant to the other. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... – Each character (but one) is controlled by a single gene. – Each gene has only two alleles, one of which is completely dominant to the other. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Pedigree Analysis
... know one of the genes (letters), use a "?" for the unknown letter. If possible, write the genotype of the three recessive individuals next to their symbols. As you attempt to write the genotypes, keep in mind that the pedigree may not be possible for a dominant trait; it may not be possible to write ...
... know one of the genes (letters), use a "?" for the unknown letter. If possible, write the genotype of the three recessive individuals next to their symbols. As you attempt to write the genotypes, keep in mind that the pedigree may not be possible for a dominant trait; it may not be possible to write ...
Lecture PDF - Carol Eunmi LEE
... 2) Not heritable (Not inherited) 3) Short term or developmental response within a single generation 4) Arises through differential gene expression or other regulatory mechanism rather than natural selection ...
... 2) Not heritable (Not inherited) 3) Short term or developmental response within a single generation 4) Arises through differential gene expression or other regulatory mechanism rather than natural selection ...
Lecture PPT - Carol Eunmi LEE
... 2) Not heritable (Not inherited) 3) Short term or developmental response within a single generation 4) Arises through differential gene expression or other regulatory mechanism rather than natural selection ...
... 2) Not heritable (Not inherited) 3) Short term or developmental response within a single generation 4) Arises through differential gene expression or other regulatory mechanism rather than natural selection ...
Relatedness in the post-genomic era: is it still
... levels of relatedness. We used a Type B simulation (see Supplementary information S1 (box)). From the current generation, we drew 4 samples of 1,250 individuals, first with no filtering so that siblings were included, followed by filtering to exclude close relatives (the x axis labels indicate the ...
... levels of relatedness. We used a Type B simulation (see Supplementary information S1 (box)). From the current generation, we drew 4 samples of 1,250 individuals, first with no filtering so that siblings were included, followed by filtering to exclude close relatives (the x axis labels indicate the ...
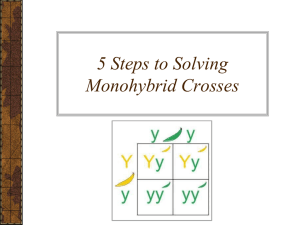
Chap 13
... – Started with garden pea plants that “bred true” for a particular trait – the trait stayed the same generation after generation – Cross-fertilized pea plants with different traits and offspring appeared in predictable patterns – Concluded that hereditary information is passed in discrete units ...
... – Started with garden pea plants that “bred true” for a particular trait – the trait stayed the same generation after generation – Cross-fertilized pea plants with different traits and offspring appeared in predictable patterns – Concluded that hereditary information is passed in discrete units ...
Sympatric Speciation
... the occurrence of mating is determined by the female. The main difficulty is to imagine how a gene B could influence mating in this way; in effect, B is a gene which causes courting individuals to be influenced by the difference between A and a, which.bb individuals ignore. If such genes exist, woul ...
... the occurrence of mating is determined by the female. The main difficulty is to imagine how a gene B could influence mating in this way; in effect, B is a gene which causes courting individuals to be influenced by the difference between A and a, which.bb individuals ignore. If such genes exist, woul ...
How to minimize “bubble-ascus” abortion in crosses for cytology. Background
... have shown that vegetatively normal haploid isolates from natural populations carry on average one or more deleterious recessive mutations that can be detected when made homozygous by backcrossing. In constructing the widely used Oak Ridge N. crassa wild type strains for use as standards, backcrosse ...
... have shown that vegetatively normal haploid isolates from natural populations carry on average one or more deleterious recessive mutations that can be detected when made homozygous by backcrossing. In constructing the widely used Oak Ridge N. crassa wild type strains for use as standards, backcrosse ...
Basic Mendellian Genetic
... of hair = b. However, sometimes it won't and you will have to give them names. Dominant alleles are given capital letters, such as "A, B or C." Recessive alleles are given small case letters, such as "a, b or c." If the problem involves multiple alleles, the best way to name them is to use a single ...
... of hair = b. However, sometimes it won't and you will have to give them names. Dominant alleles are given capital letters, such as "A, B or C." Recessive alleles are given small case letters, such as "a, b or c." If the problem involves multiple alleles, the best way to name them is to use a single ...
A Century of Hardy–Weinberg Equilibrium
... the case where ascertainment was incomplete. In developing these methods, Weinberg was drawing on his experience of working with poor families, both in public employment and privately, recognizing how genetical studies were often not the mainspring for data collection, and how, consequently, data mi ...
... the case where ascertainment was incomplete. In developing these methods, Weinberg was drawing on his experience of working with poor families, both in public employment and privately, recognizing how genetical studies were often not the mainspring for data collection, and how, consequently, data mi ...
A Century of Hardy–Weinberg Equilibrium
... the case where ascertainment was incomplete. In developing these methods, Weinberg was drawing on his experience of working with poor families, both in public employment and privately, recognizing how genetical studies were often not the mainspring for data collection, and how, consequently, data mi ...
... the case where ascertainment was incomplete. In developing these methods, Weinberg was drawing on his experience of working with poor families, both in public employment and privately, recognizing how genetical studies were often not the mainspring for data collection, and how, consequently, data mi ...
Inherited Lethal Genes - Iowa State University Digital Repository
... during their maturation. When fertilization occurs, one factor from each parent comes together in the new individual. Figure 1 shows how a recessive defect is inherited. Both sire and dam appeared normal, yet both carried the recessive factor for the defect as well as the factor for the normal. Out ...
... during their maturation. When fertilization occurs, one factor from each parent comes together in the new individual. Figure 1 shows how a recessive defect is inherited. Both sire and dam appeared normal, yet both carried the recessive factor for the defect as well as the factor for the normal. Out ...
Selection against Accumulating Mutations in Niche
... Exploiter perception and the ANN. The signals are ‘perceived’ by exploiter perceptrons: a feed-forward ANN (Fig. 2) capable of non-linear discrimination if the number of layers are at least three. ANNs are models of biological neural circuits with nodes having the functionality of a neural cell [35] ...
... Exploiter perception and the ANN. The signals are ‘perceived’ by exploiter perceptrons: a feed-forward ANN (Fig. 2) capable of non-linear discrimination if the number of layers are at least three. ANNs are models of biological neural circuits with nodes having the functionality of a neural cell [35] ...
6.3 Mendel and Heredity
... • Probability is the likelihood that something will happen • Predicts an average number of occurrences, not an exact number of occurrences. ...
... • Probability is the likelihood that something will happen • Predicts an average number of occurrences, not an exact number of occurrences. ...
Using Computer Simulation to Understand Mutation
... linkage blocks, number of chromosomes, genome size, mutation effect combining method, heritability of genotypic fitness, type of selection, number of generations, and population size. Mendel’s output report is provided at regular generation intervals and includes summary statistics on number and typ ...
... linkage blocks, number of chromosomes, genome size, mutation effect combining method, heritability of genotypic fitness, type of selection, number of generations, and population size. Mendel’s output report is provided at regular generation intervals and includes summary statistics on number and typ ...
Understanding Genetics and the Sire Summaries
... What color eyes do you have? What is your hair color? How tall are you? How fast can you run? If you have siblings, you know that you are all different in many ways, but you can also probably notice some similarities in your appearance and abilities. It’s also likely that some of those similarities ...
... What color eyes do you have? What is your hair color? How tall are you? How fast can you run? If you have siblings, you know that you are all different in many ways, but you can also probably notice some similarities in your appearance and abilities. It’s also likely that some of those similarities ...
(2014) On the origin of sex chromosomes from meiotic drive
... self-defeating, as its spread will enrich the population for the sex that it determines [8]. That said, some sex-determining alleles do achieve high frequencies. What makes these alleles different? What benefits do they receive that others may not? Two previous theories for the origin of sex chromos ...
... self-defeating, as its spread will enrich the population for the sex that it determines [8]. That said, some sex-determining alleles do achieve high frequencies. What makes these alleles different? What benefits do they receive that others may not? Two previous theories for the origin of sex chromos ...
Pedigree Charts
... Create a Pedigree Chart for the following scenario: Pedigree 3 This is the story of Grandma and Grandpa Chadwick, and their clan! They were married way back in 1933, and have been just like newlyweds ever since. From their union, 4 individuals were created. Elizabeth, the eldest, was born in 1935. F ...
... Create a Pedigree Chart for the following scenario: Pedigree 3 This is the story of Grandma and Grandpa Chadwick, and their clan! They were married way back in 1933, and have been just like newlyweds ever since. From their union, 4 individuals were created. Elizabeth, the eldest, was born in 1935. F ...
Mitotic recombination counteracts the benefits of
... expend the time and energy to find and court a mate, and they risk disease transmission and predation during mating. Considering the high costs of sex, its ubiquity is one of the most studied and intriguing problems in evolutionary biology (Bell 1982; Barton & Charlesworth 1998; Otto & Lenormand 200 ...
... expend the time and energy to find and court a mate, and they risk disease transmission and predation during mating. Considering the high costs of sex, its ubiquity is one of the most studied and intriguing problems in evolutionary biology (Bell 1982; Barton & Charlesworth 1998; Otto & Lenormand 200 ...