(1)
... (1) Consider a system with single particle density of states g(ε) = A ε Θ(ε) Θ(W −ε), which is linear on the interval [0, W ] and vanishes outside this interval. Find the second virial coefficient for both bosons and fermions. Plot your results as a function of dimensionless temperature t = kB T /W ...
... (1) Consider a system with single particle density of states g(ε) = A ε Θ(ε) Θ(W −ε), which is linear on the interval [0, W ] and vanishes outside this interval. Find the second virial coefficient for both bosons and fermions. Plot your results as a function of dimensionless temperature t = kB T /W ...
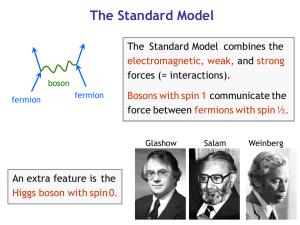
chapterS4BuildingBlo..
... have enough energy to get close enough to other protons for fusion (electromagnetic repulsion is too strong). ...
... have enough energy to get close enough to other protons for fusion (electromagnetic repulsion is too strong). ...
Formulae and constants sheet - SCSA
... Gravitational field strength Moment of a force (force at angle θ to lever arm) ...
... Gravitational field strength Moment of a force (force at angle θ to lever arm) ...
AP Chapter 5
... molecular orbitals which greatly complicates the ability to predict the pairing of electrons. ...
... molecular orbitals which greatly complicates the ability to predict the pairing of electrons. ...
photoelectric-effect-qrg
... 5. The limit voltage U0 is much bigger for violet than for yellow light. 6. The intensity of the light does not influence the limit voltage. With classical wave theory of light we would expect that the emission of electrons does not depend on the wavelength of the light. The photoelectric effect (an ...
... 5. The limit voltage U0 is much bigger for violet than for yellow light. 6. The intensity of the light does not influence the limit voltage. With classical wave theory of light we would expect that the emission of electrons does not depend on the wavelength of the light. The photoelectric effect (an ...
Transport Characteristics of Gated Core
... Recent development of nanotechnology enables to fabricate the semiconductor nanowires (NW) with the coremultishell structure (CMS) for which the outer diameter is less than 30 nm [1]. Such nanostructures find an application in the quantum electronics because of their transport properties which are d ...
... Recent development of nanotechnology enables to fabricate the semiconductor nanowires (NW) with the coremultishell structure (CMS) for which the outer diameter is less than 30 nm [1]. Such nanostructures find an application in the quantum electronics because of their transport properties which are d ...
One-dimensional Schrödinger equation
... predetermined accuracy – with an eigenvalue. The first code presented at the end of this chapter implements such a strategy. ...
... predetermined accuracy – with an eigenvalue. The first code presented at the end of this chapter implements such a strategy. ...
The relation between the ( hypothetical) intrinsic vibrational motion
... number of Φ0= hc/e, otherwise the wavefunction will not be kept singlevalued. Such point is discussed in detail for a particle in confined motion in the book by Frenkel[8], and in its simpler form this results in the BohrSommerfeld-Wilson quantization rules. Although no special attention was given t ...
... number of Φ0= hc/e, otherwise the wavefunction will not be kept singlevalued. Such point is discussed in detail for a particle in confined motion in the book by Frenkel[8], and in its simpler form this results in the BohrSommerfeld-Wilson quantization rules. Although no special attention was given t ...
Grade 12 Unit 9 - Amazon Web Services
... you have seen an argument that light behaves like a series of packets of energy, called photons, or quanta, each photon small enough to interact with a single electron. The wave theory cannot explain the photoelectric effect and the quantum theory cannot explain interference and diffraction. Which i ...
... you have seen an argument that light behaves like a series of packets of energy, called photons, or quanta, each photon small enough to interact with a single electron. The wave theory cannot explain the photoelectric effect and the quantum theory cannot explain interference and diffraction. Which i ...
Gravitational Cat State and Stochastic Semiclassical Gravity*
... Newtonian gravity. In a quantum description of matter a single motionless massive particle can in principle be in a superposition state of two spatially-separated locations. This superposition state in gravity, or gravitational cat state, would lead to fluctuations in the Newtonian force exerted on ...
... Newtonian gravity. In a quantum description of matter a single motionless massive particle can in principle be in a superposition state of two spatially-separated locations. This superposition state in gravity, or gravitational cat state, would lead to fluctuations in the Newtonian force exerted on ...
hdwsmp2011 - FSU High Energy Physics
... Colliding bunches of protons and anti-protons; bunches meet each other every 396 ns in the center of two detectors (DØ and CDF) (steered apart at other places) Each particle has ~ 980 GeV of energy, so the total energy in the center of mass ...
... Colliding bunches of protons and anti-protons; bunches meet each other every 396 ns in the center of two detectors (DØ and CDF) (steered apart at other places) Each particle has ~ 980 GeV of energy, so the total energy in the center of mass ...
chapter 5
... the matter waves - will be a valid description of how “small” things move – and the square of which Ψ(x,t)2 will give us the probability of finding the particle of the matter wave there (x) and then (t) Ψ(x,t) contains everything that is and can be know about the particle, to get the probability of ...
... the matter waves - will be a valid description of how “small” things move – and the square of which Ψ(x,t)2 will give us the probability of finding the particle of the matter wave there (x) and then (t) Ψ(x,t) contains everything that is and can be know about the particle, to get the probability of ...