k - MPS
... Laplace transform of the electric field II Integrating along a = const and then deforming the contours, whereby we pull a into the negative direction to position a‘ far beyond all poles which become encircled. The integral will be the sum of all residua, ri(k), at the poles, pi(k), and of the contr ...
... Laplace transform of the electric field II Integrating along a = const and then deforming the contours, whereby we pull a into the negative direction to position a‘ far beyond all poles which become encircled. The integral will be the sum of all residua, ri(k), at the poles, pi(k), and of the contr ...
Physics Today
... The drop is an oscillator: When perturbed, it will oscillate at its natural frequency, exchanging surface energy and kinetic energy. When a fluid bath is vibrated vertically, its surface becomes unstable to a field of so-called Faraday waves, such as shown in figure 1a, when the driving acceleration ...
... The drop is an oscillator: When perturbed, it will oscillate at its natural frequency, exchanging surface energy and kinetic energy. When a fluid bath is vibrated vertically, its surface becomes unstable to a field of so-called Faraday waves, such as shown in figure 1a, when the driving acceleration ...
SCI-PS Exam [E-2MGZGB] SOL Practice Questions
... B They combined physically to form a new mixture. C They combined physically to form a new element. D They combined chemically to form carbon and oxygen. ...
... B They combined physically to form a new mixture. C They combined physically to form a new element. D They combined chemically to form carbon and oxygen. ...
Trapping neutral particles endowed with a magnetic moment by an
... B st (r,t) = ⎣B⊥ k cos(kz)[x cos(ωt) + y sin(ωt)]⎦, (2b) Bz where ζ = ωt − kz, k = ω/c is the wave number, B⊥ measures the strength of the vortex wave, and Bz is the constant field. In order to preserve the correct dimension of B⊥ we inserted a factor of k in these formulas. The vortex part can be v ...
... B st (r,t) = ⎣B⊥ k cos(kz)[x cos(ωt) + y sin(ωt)]⎦, (2b) Bz where ζ = ωt − kz, k = ω/c is the wave number, B⊥ measures the strength of the vortex wave, and Bz is the constant field. In order to preserve the correct dimension of B⊥ we inserted a factor of k in these formulas. The vortex part can be v ...
THE BASIC PRINCIPLES OF CLASSICAL ELECTRODYNAMICS
... particle. There is no force, no velocity or acceleration inside the particle. A kinematical state of the material continuum is defined by the field of current density jk. A world line of current jk is not a world line of a material point. That allows us to deny any causal connection between the poin ...
... particle. There is no force, no velocity or acceleration inside the particle. A kinematical state of the material continuum is defined by the field of current density jk. A world line of current jk is not a world line of a material point. That allows us to deny any causal connection between the poin ...
No Slide Title
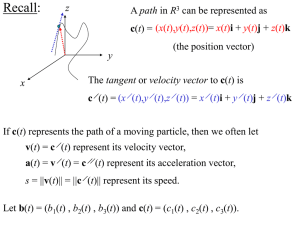
... Newton’s Second Law (page 264 of the text) states that if F(t) is the force at time t acting on a particle with mass m, then F(t) = ma(t) . Let us consider a circular path of a planet of mass m orbiting the sun with Note that t = 2r0/s ...
... Newton’s Second Law (page 264 of the text) states that if F(t) is the force at time t acting on a particle with mass m, then F(t) = ma(t) . Let us consider a circular path of a planet of mass m orbiting the sun with Note that t = 2r0/s ...
No Slide Title - University of Manchester
... An extra term that can give dark energy with negative pressure Expansion of universe may be accelerating! ...
... An extra term that can give dark energy with negative pressure Expansion of universe may be accelerating! ...
Lesson 1 - Faculty Website Listing
... What value would we get if we tried to measure the particle’s energy? The answer is that we can’t know for certain what energy value we would get!! In fact the general interpretation of quantum mechanics (Copenhagen Interpretation) is that the particle has no energy (i.e. energy has no reality) till ...
... What value would we get if we tried to measure the particle’s energy? The answer is that we can’t know for certain what energy value we would get!! In fact the general interpretation of quantum mechanics (Copenhagen Interpretation) is that the particle has no energy (i.e. energy has no reality) till ...
Lecture (2) - MIT OpenCourseWare
... We can plug in the Coulomb force law for F, and solve the equation for a given initial value of r. If rinitial is 10 Å (10-10 m), a typical distance for an H atom, the calculation indicates that r = 0 at t = _______ sec! This predicts that the electron should plummet into the nucleus in ____________ ...
... We can plug in the Coulomb force law for F, and solve the equation for a given initial value of r. If rinitial is 10 Å (10-10 m), a typical distance for an H atom, the calculation indicates that r = 0 at t = _______ sec! This predicts that the electron should plummet into the nucleus in ____________ ...



![SCI-PS Exam [E-2MGZGB] SOL Practice Questions](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016636015_1-c46cd0f3541a3b255b9dbb2d7fe00d05-300x300.png)