Lesson 10 Printable Lessons - First Presbyterian Church of
... opposing this persecution. During this time Constantine proved to be an able general and beloved leader. In 305 Galerius became Emperor and after a long night of drinking agreed to send Constantine to serve with his father. A year later, when his father died, the Army in Britannia (where Constantine ...
... opposing this persecution. During this time Constantine proved to be an able general and beloved leader. In 305 Galerius became Emperor and after a long night of drinking agreed to send Constantine to serve with his father. A year later, when his father died, the Army in Britannia (where Constantine ...
pax romana - Western Civilization HomePage
... Lepidus, sanctioned civilian slaughter and property theft. Peace is a relative term, when looking at the Pax Romana. ...
... Lepidus, sanctioned civilian slaughter and property theft. Peace is a relative term, when looking at the Pax Romana. ...
HIST 2311 Topic Seven: Roman Empire On the morning of March 15
... tempted to meddle in civic affairs. He also created the Praetorian Guard, an elite corps of 9000 men charged with defending him. Stationed at Rome, the members of the Guard were from Italy only, and received higher pay than soldiers in the Roman legions. The Guard served as the personal bodyguard to ...
... tempted to meddle in civic affairs. He also created the Praetorian Guard, an elite corps of 9000 men charged with defending him. Stationed at Rome, the members of the Guard were from Italy only, and received higher pay than soldiers in the Roman legions. The Guard served as the personal bodyguard to ...
How did Rome become an empire?
... Cleopatra, Antony committed suicide; Octavian controlled Rome; republic ended ...
... Cleopatra, Antony committed suicide; Octavian controlled Rome; republic ended ...
The Long Decline of the Roman Empire
... The final phase (f.y.i.) There were more periods of revolt and chaos. Barbarian invasions kept occurring. Much of the time no single emperor controlled both East and West. Increasingly the army was German (hired mercenaries loyal only to $). Theodosius (379-395) was last to control both East and ...
... The final phase (f.y.i.) There were more periods of revolt and chaos. Barbarian invasions kept occurring. Much of the time no single emperor controlled both East and West. Increasingly the army was German (hired mercenaries loyal only to $). Theodosius (379-395) was last to control both East and ...
The Rise and Fall of Rome (Lecture Notes)
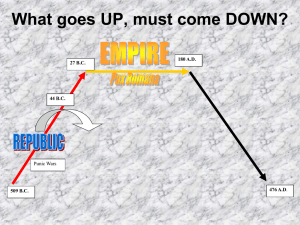
... confided to individuals, called dictators, who were expected to relinquish control when the emergency was over. In the second half of the first century B.C.E., this system finally broke down in a series of struggles between rival contenders for sole power. In 27 B.C.E., all parties accepted Augustus ...
... confided to individuals, called dictators, who were expected to relinquish control when the emergency was over. In the second half of the first century B.C.E., this system finally broke down in a series of struggles between rival contenders for sole power. In 27 B.C.E., all parties accepted Augustus ...
Chapter 9 Section 3 PowerPoint
... • The Romans called them barbarians. • In the past Roman army had been able to defeat them, now however, they could not stop them. • In the 400’s the Germanic tribes overran the empire. • The Visigoths and the Vandals captured and looted Rome. ...
... • The Romans called them barbarians. • In the past Roman army had been able to defeat them, now however, they could not stop them. • In the 400’s the Germanic tribes overran the empire. • The Visigoths and the Vandals captured and looted Rome. ...
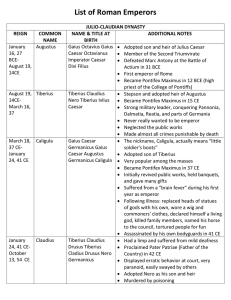
Day 15 emperor readings
... Augustus was the founder of the Roman Empire and its first Emperor, ruling from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He was born Gaius Octavius into an old and wealthy equestrian branch of the plebeian Octavii family. His maternal great-uncle Julius Caesar was assassinated in 44 BC, and Octavius was name ...
... Augustus was the founder of the Roman Empire and its first Emperor, ruling from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He was born Gaius Octavius into an old and wealthy equestrian branch of the plebeian Octavii family. His maternal great-uncle Julius Caesar was assassinated in 44 BC, and Octavius was name ...
Constantine the Great
... the creation of a new city which would become Constantinople, now Istanbul. The Roman emperor, Flavius Valerius Aurelius Constantinus, or Constantine I, was born at Naissus, in Upper Moesia. He was the eldest son of Constantinus Chlorus and Helena, and first distinguished himself as a soldier in Dio ...
... the creation of a new city which would become Constantinople, now Istanbul. The Roman emperor, Flavius Valerius Aurelius Constantinus, or Constantine I, was born at Naissus, in Upper Moesia. He was the eldest son of Constantinus Chlorus and Helena, and first distinguished himself as a soldier in Dio ...
The end of the Empire
... from other provinces to protect Rome. These soldiers did not care about Rome. Powerful generals kept fighting among themselves about who should be the next emperor. This fighting caused Rome to have at least 23 emperors in 73 years. All but one were assassinated. ...
... from other provinces to protect Rome. These soldiers did not care about Rome. Powerful generals kept fighting among themselves about who should be the next emperor. This fighting caused Rome to have at least 23 emperors in 73 years. All but one were assassinated. ...
The End of the Empire Rome`s Greatness
... from other provinces to protect Rome. These soldiers did not care about Rome. Powerful generals kept fighting among themselves about who should be the next emperor. This fighting caused Rome to have at least 23 emperors in 73 years. All but one were assassinated. ...
... from other provinces to protect Rome. These soldiers did not care about Rome. Powerful generals kept fighting among themselves about who should be the next emperor. This fighting caused Rome to have at least 23 emperors in 73 years. All but one were assassinated. ...
Constantine the Great
... the creation of a new city which would become Constantinople, now Istanbul. The Roman emperor, Flavius Valerius Aurelius Constantinus, or Constantine I, was born at Naissus, in Upper Moesia. He was the eldest son of Constantinus Chlorus and Helena, and first distinguished himself as a soldier in Dio ...
... the creation of a new city which would become Constantinople, now Istanbul. The Roman emperor, Flavius Valerius Aurelius Constantinus, or Constantine I, was born at Naissus, in Upper Moesia. He was the eldest son of Constantinus Chlorus and Helena, and first distinguished himself as a soldier in Dio ...
The Fall of Rome - White Plains Public Schools
... lacked new sources of gold and silver. Desperate for revenue, the government raised taxes. It also started minting coins that contained less and less silver. It hoped to create more money with the same amount of precious metal. However, the economy soon suffered from inflation, a drastic drop in the ...
... lacked new sources of gold and silver. Desperate for revenue, the government raised taxes. It also started minting coins that contained less and less silver. It hoped to create more money with the same amount of precious metal. However, the economy soon suffered from inflation, a drastic drop in the ...
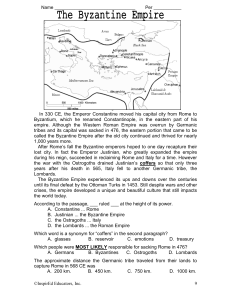
In 330 CE, the Emperor Constantine moved his capital city from
... The point at which to begin, as it should be, is with the august ruler’s rise to power. Flavius Julianus Justinianus was nephew to the last Roman emperor, Justin, and advanced to consul of the Eastern Empire during his uncle’s reign. Upon Justin’s death in April of 527 the year of our Lord, Justinia ...
... The point at which to begin, as it should be, is with the august ruler’s rise to power. Flavius Julianus Justinianus was nephew to the last Roman emperor, Justin, and advanced to consul of the Eastern Empire during his uncle’s reign. Upon Justin’s death in April of 527 the year of our Lord, Justinia ...
Classical Themes in Popular Entertainment
... the Republic. His reign was the last one in the golden era of Roman Emperors that began after the assassination of Domitian in 96 A.D. Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius and himself. Marcus had twice appointed an Imperial colleague and successor. He associated with Lucius Verus from the beginnin ...
... the Republic. His reign was the last one in the golden era of Roman Emperors that began after the assassination of Domitian in 96 A.D. Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius and himself. Marcus had twice appointed an Imperial colleague and successor. He associated with Lucius Verus from the beginnin ...
Reasons for the Decline of the Western Roman Empire
... One of the most difficult problems was choosing a new emperor. Unlike Greece where transition may not have been smooth but was at least consistent, the Romans never created an effective system to determine how new emperors would be selected. The choice was always open to debate between the old emper ...
... One of the most difficult problems was choosing a new emperor. Unlike Greece where transition may not have been smooth but was at least consistent, the Romans never created an effective system to determine how new emperors would be selected. The choice was always open to debate between the old emper ...
Era of Good Emperors - World History with Ms. Byrne
... Marcus Saluius Otho Murdered Galba and his successor to claim the throne of emperor Quickly realized it was very difficult to rule in Rome Committed suicide Aulus Vitellius Served as a co-emperor with Otho (without the credit) His claim to the throne was challeneged by legions stationed in ...
... Marcus Saluius Otho Murdered Galba and his successor to claim the throne of emperor Quickly realized it was very difficult to rule in Rome Committed suicide Aulus Vitellius Served as a co-emperor with Otho (without the credit) His claim to the throne was challeneged by legions stationed in ...
This list begins with the founding of the village of Rome around
... Several barbarian groups included the Vandals, Alans, Suevi and Burgundians overran Gaul Roman forces withdrew from Britain, led by Constantine, the troops' choice for emperor A new Eastern Emperor, Theodosius II, took office at age 7. Honorius ordered the assassination of Stilicho Alaric's Visigoth ...
... Several barbarian groups included the Vandals, Alans, Suevi and Burgundians overran Gaul Roman forces withdrew from Britain, led by Constantine, the troops' choice for emperor A new Eastern Emperor, Theodosius II, took office at age 7. Honorius ordered the assassination of Stilicho Alaric's Visigoth ...
8 Reasons Why Rome Fell
... military upkeep of the empire, technological advancement slowed and Rome’s civil infrastructure fell into disrepair. ...
... military upkeep of the empire, technological advancement slowed and Rome’s civil infrastructure fell into disrepair. ...
8 Reasons Why Rome Fell - westerncivilizationwhs
... funds were funneled into the military upkeep of the empire, technological advancement slowed and Rome’s civil infrastructure fell into disrepair. 5. Government corruption and political instability If Rome’s sheer size made it difficult to govern, ineffective and inconsistent leadership only served t ...
... funds were funneled into the military upkeep of the empire, technological advancement slowed and Rome’s civil infrastructure fell into disrepair. 5. Government corruption and political instability If Rome’s sheer size made it difficult to govern, ineffective and inconsistent leadership only served t ...
Chapter 5
... Primarily responsible guarding the frontiers & maintain domestic order in the provinces The standing army was 28 legions – A legion consisted of 5400 soldiers (150,000 total troops) – Not large by modern terms or for the size of the empire (50 million total pop.) ...
... Primarily responsible guarding the frontiers & maintain domestic order in the provinces The standing army was 28 legions – A legion consisted of 5400 soldiers (150,000 total troops) – Not large by modern terms or for the size of the empire (50 million total pop.) ...
Sofia City Tour - ISSE 2017 Official Website
... Sofia. Many archeologists and historians believe that at this time or during the Hellenistic period (4th-1st centuries BC) on the latest this settlement grew into a city, landscaped following the architectural standards of the ancient Greek polis. After the Roman conquest in the present-day Bulgaria ...
... Sofia. Many archeologists and historians believe that at this time or during the Hellenistic period (4th-1st centuries BC) on the latest this settlement grew into a city, landscaped following the architectural standards of the ancient Greek polis. After the Roman conquest in the present-day Bulgaria ...