Other Specified and Unspecified Disorders
... (DSM) A manual produced by the American Psychiatric Association which provides the diagnostic criteria for mental health and substance use disorders, and other problems that may be the focus of clinical attention. Unless otherwise noted, the current edition of the DSM applies. Mental Illness Those m ...
... (DSM) A manual produced by the American Psychiatric Association which provides the diagnostic criteria for mental health and substance use disorders, and other problems that may be the focus of clinical attention. Unless otherwise noted, the current edition of the DSM applies. Mental Illness Those m ...
Anxiety Disorder - West African Rescue Association Ghana
... The form of psychotherapy used for anxiety disorders is cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). The therapy uses cognitive methods (discovering errors in thought, generating rational thoughts, etc) and behavioral methods (relaxation techniques, exposure, and rehearsal) to reduce anxiety and ones reactio ...
... The form of psychotherapy used for anxiety disorders is cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). The therapy uses cognitive methods (discovering errors in thought, generating rational thoughts, etc) and behavioral methods (relaxation techniques, exposure, and rehearsal) to reduce anxiety and ones reactio ...
ODD
... be curbed through different parenting strategies, such as defining boundaries and followingthrough on set consequences. However, sometimes the behaviour may indicate a deeper issue. Oppositional defiant disorder (ODD) is classified as a disruptive, impulse-control and conduct disorder that is charac ...
... be curbed through different parenting strategies, such as defining boundaries and followingthrough on set consequences. However, sometimes the behaviour may indicate a deeper issue. Oppositional defiant disorder (ODD) is classified as a disruptive, impulse-control and conduct disorder that is charac ...
Psych B – Module 28
... another experiencing fearfulness--may result in developing fear. • Fear of an object may be reinforced when by avoiding the feared objects. ...
... another experiencing fearfulness--may result in developing fear. • Fear of an object may be reinforced when by avoiding the feared objects. ...
Pg-CBT-Comparison Effectiveness Presentation
... relationships that underlie these experiences (often from childhood or earlier in life). • it brings together ideas and understanding from different therapies into ...
... relationships that underlie these experiences (often from childhood or earlier in life). • it brings together ideas and understanding from different therapies into ...
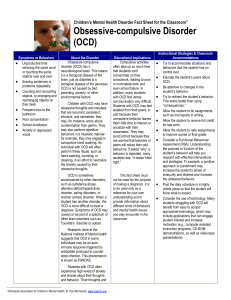
Children`s Mental Health Disorder Fact Sheet for the Classroom
... such as substance abuse, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, eating disorders, or another anxiety disorder. When a student has another disorder, the OCD is more difficult to treat or diagnose. Symptoms of OCD may coexist or be part of a spectrum of other brain disorders such as Tourette’s diso ...
... such as substance abuse, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, eating disorders, or another anxiety disorder. When a student has another disorder, the OCD is more difficult to treat or diagnose. Symptoms of OCD may coexist or be part of a spectrum of other brain disorders such as Tourette’s diso ...
Introduction to Working with the Asian Patient in Primary Care
... P--Psychomotor changes S--thoughts of Suicide ...
... P--Psychomotor changes S--thoughts of Suicide ...
DSM-Ill Diagnoses and Offenses in Committed Female Juvenile
... study was the use of diagnostic instruments not designed for use in children and adolescents, again raising the issue of diagnostic validity. Overall, the vast majority of studies on delinquent youth have neglected the female offender. In this pilot study. we hypothesized that a great diversity and ...
... study was the use of diagnostic instruments not designed for use in children and adolescents, again raising the issue of diagnostic validity. Overall, the vast majority of studies on delinquent youth have neglected the female offender. In this pilot study. we hypothesized that a great diversity and ...
PowerPoint chapter 05
... Pain disorder is characterised by physical pain (such as headache) that causes significant distress and impaired functioning. In addition, psychological factors are believed to have an important role in triggering the pain. ...
... Pain disorder is characterised by physical pain (such as headache) that causes significant distress and impaired functioning. In addition, psychological factors are believed to have an important role in triggering the pain. ...
Understanding borderline personality disorder
... functions that cause behavioural problems. The core symptoms common to most people with BPD are as follows: • Poorly regulated and excessive emotional responses • Harmful impulsive actions • Distorted perceptions and impaired reasoning including problems with real or perceived abandonment • Markedly ...
... functions that cause behavioural problems. The core symptoms common to most people with BPD are as follows: • Poorly regulated and excessive emotional responses • Harmful impulsive actions • Distorted perceptions and impaired reasoning including problems with real or perceived abandonment • Markedly ...
The Bipolar Child - VA Association of Visiting Teachers
... than anyone had conceived. They also strongly supported the hypothesis that the symptoms of bipolar disorder in children are different than those seen in adults. ...
... than anyone had conceived. They also strongly supported the hypothesis that the symptoms of bipolar disorder in children are different than those seen in adults. ...
Behavioral Health
... These competencies and skills sets include, but are not limited to, knowledge of and appropriate training and supervision for: •Caring for residents with mental and psychosocial disorders, as well as residents with a history of trauma and/or post-traumatic stress disorder, that have been identified ...
... These competencies and skills sets include, but are not limited to, knowledge of and appropriate training and supervision for: •Caring for residents with mental and psychosocial disorders, as well as residents with a history of trauma and/or post-traumatic stress disorder, that have been identified ...
Coexisting Disorders in Children
... oppositional defiant disorder or conduct disorder. Children with oppositional defiant disorder often argue with adults and are angry, resentful, and easily annoyed, blaming others when things go wrong. Conduct disorder can include bullying, destructive behaviour, deceitfulness, and rule violat ...
... oppositional defiant disorder or conduct disorder. Children with oppositional defiant disorder often argue with adults and are angry, resentful, and easily annoyed, blaming others when things go wrong. Conduct disorder can include bullying, destructive behaviour, deceitfulness, and rule violat ...
rajiv gandhi university of health sciences
... 6.2 REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE:HISTORY: The Avoidant Personality Disorder has been described in several sources as far as early 1900’s although it was not so named for sometimes. Swiss Psychiatrist ‘EUGENE BLEUR”, described patients who exhibits Signs of Avoidant Personality Disorder in his work in 19 ...
... 6.2 REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE:HISTORY: The Avoidant Personality Disorder has been described in several sources as far as early 1900’s although it was not so named for sometimes. Swiss Psychiatrist ‘EUGENE BLEUR”, described patients who exhibits Signs of Avoidant Personality Disorder in his work in 19 ...
Heredity in comorbid bipolar disorder and obsessive
... this common “comorbidity” represents two diseases, or multiple symptoms of one disease. The clinical question is whether and how to treat the comorbidity since the main treatment for one disease can worsen the other diseases. Serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) for OCD can cause mania and/or more ...
... this common “comorbidity” represents two diseases, or multiple symptoms of one disease. The clinical question is whether and how to treat the comorbidity since the main treatment for one disease can worsen the other diseases. Serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) for OCD can cause mania and/or more ...
Course: Abnormal Psychology - Catholic College of Mandeville
... of stress in the body are called “triggers”. Psychologists have identified that not all individuals who are stressed, or go through stressful life events, develop a psychological disorder. To understand this, theorists and researchers explored other factors that affect the development of a disorder ...
... of stress in the body are called “triggers”. Psychologists have identified that not all individuals who are stressed, or go through stressful life events, develop a psychological disorder. To understand this, theorists and researchers explored other factors that affect the development of a disorder ...
Chapter XII Module 65
... 65-1 Discuss how we draw the line between normality and disorder. 65-2 Discuss the controversy over the diagnosis of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. 65-3 Contrast the Medical Model with the biopsychosocial approach to psychological disorders 65-4 Describe how and why clinicians classify ps ...
... 65-1 Discuss how we draw the line between normality and disorder. 65-2 Discuss the controversy over the diagnosis of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. 65-3 Contrast the Medical Model with the biopsychosocial approach to psychological disorders 65-4 Describe how and why clinicians classify ps ...
Co-Occurring Disorders
... Addictions for 2010, is the director of outpatient for children and adults at NRI Community Services in Woonsocket, RI. An behavioral health educator and trainer, she has presented over 100 trainings throughout New England and is currently a Special Guest Lecturer for the Providence College Social ...
... Addictions for 2010, is the director of outpatient for children and adults at NRI Community Services in Woonsocket, RI. An behavioral health educator and trainer, she has presented over 100 trainings throughout New England and is currently a Special Guest Lecturer for the Providence College Social ...
myers ap – unit 12
... – Unit subsections hyperlinks: Immediately after the unit title slide, a page (slide #3) can be found listing all of the unit’s subsections. While in slide show mode, clicking on any of these hyperlinks will take the user directly to the beginning of that subsection. This allows teachers quick acces ...
... – Unit subsections hyperlinks: Immediately after the unit title slide, a page (slide #3) can be found listing all of the unit’s subsections. While in slide show mode, clicking on any of these hyperlinks will take the user directly to the beginning of that subsection. This allows teachers quick acces ...
Susan Swedo - Conference.ie
... C. Symptoms must be present in the early developmental period (but may not become fully manifest until social demands exceed limited capacities, or may be masked by learned strategies in later life). D. Symptoms cause clinically significant impairment in social, occupational, or other important are ...
... C. Symptoms must be present in the early developmental period (but may not become fully manifest until social demands exceed limited capacities, or may be masked by learned strategies in later life). D. Symptoms cause clinically significant impairment in social, occupational, or other important are ...
Dissociative identity disorder

Dissociative identity disorder (DID), previously known as multiple personality disorder (MPD), is a mental disorder on the dissociative spectrum characterized by the appearance of at least two distinct and relatively enduring identities or dissociated personality states that alternately control a person's behavior, accompanied by memory impairment for important information not explained by ordinary forgetfulness. These symptoms are not accounted for by substance abuse, seizures, other medical conditions, nor by imaginative play in children. Diagnosis is often difficult as there is considerable comorbidity with other mental disorders. Malingering should be considered if there is possible financial or forensic gain, as well as factitious disorder if help-seeking behavior is prominent.DID is one of the most controversial psychiatric disorders, with no clear consensus on diagnostic criteria or treatment. Research on treatment efficacy has been concerned primarily with clinical approaches and case studies. Dissociative symptoms range from common lapses in attention, becoming distracted by something else, and daydreaming, to pathological dissociative disorders. No systematic, empirically-supported definition of ""dissociation"" exists. It is not the same as schizophrenia.Although neither epidemiological surveys nor longitudinal studies have been conducted, it is generally believed that DID rarely resolves spontaneously. Symptoms are said to vary over time. In general, the prognosis is poor, especially for those with comorbid disorders. There are few systematic data on the prevalence of DID. The International Society for the Study of Trauma and Dissociation states that the prevalence is between 1 and 3% in the general population, and between 1 and 5% in inpatient groups in Europe and North America. DID is diagnosed more frequently in North America than in the rest of the world, and is diagnosed three to nine times more often in females than in males. The prevalence of DID diagnoses increased greatly in the latter half of the 20th century, along with the number of identities (often referred to as ""alters"") claimed by patients (increasing from an average of two or three to approximately 16). DID is also controversial within the legal system, where it has been used as a rarely successful form of the insanity defense. The 1990s showed a parallel increase in the number of court cases involving the diagnosis.Dissociative disorders including DID have been attributed to disruptions in memory caused by trauma and other forms of stress, but research on this hypothesis has been characterized by poor methodology. So far, scientific studies, usually focusing on memory, have been few and the results have been inconclusive. An alternative hypothesis for the etiology of DID is as a by-product of techniques employed by some therapists, especially those using hypnosis, and disagreement between the two positions is characterized by intense debate. DID became a popular diagnosis in the 1970s, 80s and 90s, but it is unclear if the actual rate of the disorder increased, if it was more recognized by health care providers, or if sociocultural factors caused an increase in therapy-induced (iatrogenic) presentations. The unusual number of diagnoses after 1980, clustered around a small number of clinicians and the suggestibility characteristic of those with DID, support the hypothesis that DID is therapist-induced. The unusual clustering of diagnoses has also been explained as due to a lack of awareness and training among clinicians to recognize cases of DID.