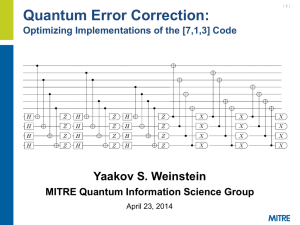
Entanglement and state characterisation from two-photon interference
... existing work. We then describe how we can obtain the temporal wave-function of an unknown two-photon state with a measurement technique common in quantum optics, i.e. the recording of photon pair statistics for different polarisation bases. The trick is to interfere the unknown state with a low-pow ...
... existing work. We then describe how we can obtain the temporal wave-function of an unknown two-photon state with a measurement technique common in quantum optics, i.e. the recording of photon pair statistics for different polarisation bases. The trick is to interfere the unknown state with a low-pow ...
Quantum Techniques for Stochastic Mechanics
... Quantum theory is based, not on probabilities, but on amplitudes. We can use amplitudes to compute probabilities. However, the relation between them is nonlinear: we take the absolute value of an amplitude and square it to get a probability. It thus seems odd to treat amplitudes as directly analogou ...
... Quantum theory is based, not on probabilities, but on amplitudes. We can use amplitudes to compute probabilities. However, the relation between them is nonlinear: we take the absolute value of an amplitude and square it to get a probability. It thus seems odd to treat amplitudes as directly analogou ...
Continuous Variable Quantum Information: Gaussian States and
... (continuous variables), such as those associated to position and momentum of a particle. This second approach has witnessed considerable success due to its versatility, with implementations often encompassing different physical systems, e.g. light quadratures and collective magnetic moments of atomic ...
... (continuous variables), such as those associated to position and momentum of a particle. This second approach has witnessed considerable success due to its versatility, with implementations often encompassing different physical systems, e.g. light quadratures and collective magnetic moments of atomic ...
Quantum Transport in Finite Disordered Electron Systems
... In Part II an atomic-scale quantum point contact was studied with the intention to investigate the effect of the attached leads on its conductance (i.e., the effect of “measuring apparatus” on the “result of measurement”, in the sense of quantum measurement theory). The practical merit of this study i ...
... In Part II an atomic-scale quantum point contact was studied with the intention to investigate the effect of the attached leads on its conductance (i.e., the effect of “measuring apparatus” on the “result of measurement”, in the sense of quantum measurement theory). The practical merit of this study i ...
Quantum Computation, Quantum Theory and AI
... Quantum computers were first envisaged by Nobel Laureate physicist Feynman [47] in 1982. He conceived that no classical computer could simulate certain quantum phenomena without an exponential slowdown, and so realized that quantum mechanical effects should offer something genuinely new to computati ...
... Quantum computers were first envisaged by Nobel Laureate physicist Feynman [47] in 1982. He conceived that no classical computer could simulate certain quantum phenomena without an exponential slowdown, and so realized that quantum mechanical effects should offer something genuinely new to computati ...
Linear and Complex Analysis for Applications John P. D`Angelo
... This book evolved from several of the author’s teaching experiences, his research in complex analysis in several variables, and many conversations with friends and colleagues. It has been also influenced by his attending a meeting (Santa Barbara, 2014) on the revitalization of complex analysis in th ...
... This book evolved from several of the author’s teaching experiences, his research in complex analysis in several variables, and many conversations with friends and colleagues. It has been also influenced by his attending a meeting (Santa Barbara, 2014) on the revitalization of complex analysis in th ...
Atomic Bose-Hubbard Systems with Single-Particle
... states can be quantified in experiments [23]. In few-particle systems, the verification of entanglement can be achieved by witness operators [24] or state tomography [25]. For many-particle systems of interacting, delocalized particles, such as atoms in an optical lattice, a path for the experimenta ...
... states can be quantified in experiments [23]. In few-particle systems, the verification of entanglement can be achieved by witness operators [24] or state tomography [25]. For many-particle systems of interacting, delocalized particles, such as atoms in an optical lattice, a path for the experimenta ...
Ionisation in a strong laser field
... quite early was a depletion of atoms form the enlightened volume due to ionisation. Thus, there exists a saturation intensity, Is , above which number of ions changes more slowly than expected from eq. (1.16) [31, 32, 33]. The next step in the consideration of MPI is quite natural and concerns multi ...
... quite early was a depletion of atoms form the enlightened volume due to ionisation. Thus, there exists a saturation intensity, Is , above which number of ions changes more slowly than expected from eq. (1.16) [31, 32, 33]. The next step in the consideration of MPI is quite natural and concerns multi ...
Manifestations of Berry`s phase in molecules and condensed matter
... As in the discrete case outlined above, γ is a gauge-invariant quantity and therefore is potentially observable. The main discovery of Berry’s milestone paper can in fact be spelled out as follows: there exist a whole class of observables which cannot be cast as the expectation values of any operato ...
... As in the discrete case outlined above, γ is a gauge-invariant quantity and therefore is potentially observable. The main discovery of Berry’s milestone paper can in fact be spelled out as follows: there exist a whole class of observables which cannot be cast as the expectation values of any operato ...
HBNI Th65 - The Institute of Mathematical Sciences
... and quantum types) manifest themselves, and also studies the interplay between these two aspects in various physical settings. Quantum channels represent all possible evolutions of states, including measurements, allowed by quantum mechanics, while correlations are intrinsic (nonlocal) properties of ...
... and quantum types) manifest themselves, and also studies the interplay between these two aspects in various physical settings. Quantum channels represent all possible evolutions of states, including measurements, allowed by quantum mechanics, while correlations are intrinsic (nonlocal) properties of ...
Two-resonator circuit quantum electrodynamics: Dissipative theory
... part of the impedances Re关Z共兲兴. In general, internal loss mechanisms are also relevant in superconducting resonators at low powers and low temperatures. They often originate from fluctuators on the resonator surface, which are usually modeled as two-level systems. Thus, we interpret the J共兲 in a ...
... part of the impedances Re关Z共兲兴. In general, internal loss mechanisms are also relevant in superconducting resonators at low powers and low temperatures. They often originate from fluctuators on the resonator surface, which are usually modeled as two-level systems. Thus, we interpret the J共兲 in a ...
Clustered states in the fractional quantum Hall effect
... samples. It was in that same paper that the authors demonstrated an unorthodox procedure to obtain a new series of quantum Hall states. Although that series was proposed as an academic example, it included a description of the 21 state. What makes the Moore-Read state so special is its prediction of ...
... samples. It was in that same paper that the authors demonstrated an unorthodox procedure to obtain a new series of quantum Hall states. Although that series was proposed as an academic example, it included a description of the 21 state. What makes the Moore-Read state so special is its prediction of ...
silicon in the quantum limit: quantum computing
... The pursuit of spin and quantum entanglement-based devices in solid-state systems has become a global endeavor. The approach of the quantum size limit in computer electronics, the many recent advances in nanofabrication, and the rediscovery that information is physical (and thus based on quantum phy ...
... The pursuit of spin and quantum entanglement-based devices in solid-state systems has become a global endeavor. The approach of the quantum size limit in computer electronics, the many recent advances in nanofabrication, and the rediscovery that information is physical (and thus based on quantum phy ...
Relativistic quantum information theory and quantum reference frames
... quantum information theory of localised qubits in curved spacetimes. This part of the thesis details how to obtain from field theory a description of a localised qubit in curved spacetime that traverses a classical trajectory. The particles to provide the physical realisations of a localised qubit a ...
... quantum information theory of localised qubits in curved spacetimes. This part of the thesis details how to obtain from field theory a description of a localised qubit in curved spacetime that traverses a classical trajectory. The particles to provide the physical realisations of a localised qubit a ...
Probability amplitude

In quantum mechanics, a probability amplitude is a complex number used in describing the behaviour of systems. The modulus squared of this quantity represents a probability or probability density.Probability amplitudes provide a relationship between the wave function (or, more generally, of a quantum state vector) of a system and the results of observations of that system, a link first proposed by Max Born. Interpretation of values of a wave function as the probability amplitude is a pillar of the Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics. In fact, the properties of the space of wave functions were being used to make physical predictions (such as emissions from atoms being at certain discrete energies) before any physical interpretation of a particular function was offered. Born was awarded half of the 1954 Nobel Prize in Physics for this understanding (see #References), and the probability thus calculated is sometimes called the ""Born probability"". These probabilistic concepts, namely the probability density and quantum measurements, were vigorously contested at the time by the original physicists working on the theory, such as Schrödinger and Einstein. It is the source of the mysterious consequences and philosophical difficulties in the interpretations of quantum mechanics—topics that continue to be debated even today.