Child and Adolescent Psychopathology
... disorders did not emerge until the late 1970s. Before the 1970s depression was thought to be rare in children and clinicians believed that depression was expressed in behavioral disturbances such as behavior problems, enuresis, and somatic concerns. During the late 1970s, investigators demonstra ...
... disorders did not emerge until the late 1970s. Before the 1970s depression was thought to be rare in children and clinicians believed that depression was expressed in behavioral disturbances such as behavior problems, enuresis, and somatic concerns. During the late 1970s, investigators demonstra ...
Chapter 7: Self & Moral Development
... Separation Anxiety Disorder • The most common anxiety disorder for children (2 – 41%); may have other anxiety-based disorders • Characterized by unrealistic fears, oversensitivity, selfconsciousness, nightmares, chronic anxiety, low self-confidence, apprehensive in new situations • Described as shy ...
... Separation Anxiety Disorder • The most common anxiety disorder for children (2 – 41%); may have other anxiety-based disorders • Characterized by unrealistic fears, oversensitivity, selfconsciousness, nightmares, chronic anxiety, low self-confidence, apprehensive in new situations • Described as shy ...
Don’t let depression haunt your holidays
... there is a flip side to that coin. For many people, the holidays can bring stress, anxiety and mood changes. What’s more, about one person in 10 is at risk for a serious medical illness known as Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) or clinical depression. It differs from expected, mild mood changes such ...
... there is a flip side to that coin. For many people, the holidays can bring stress, anxiety and mood changes. What’s more, about one person in 10 is at risk for a serious medical illness known as Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) or clinical depression. It differs from expected, mild mood changes such ...
8-AFFECTIVE DISORDERS
... (Tyramine dietary restrictions). c. SSRIs: - Fluvoxamine, fluoxetine, “Rx. For 6/12. if recurrent lithium as an adjunct appears to be affective “ Physical :- ElecrtoConvulsiveTherapy (ECT). ...
... (Tyramine dietary restrictions). c. SSRIs: - Fluvoxamine, fluoxetine, “Rx. For 6/12. if recurrent lithium as an adjunct appears to be affective “ Physical :- ElecrtoConvulsiveTherapy (ECT). ...
Bipolar Disorder and Substance Use Disorders
... more days than not, as indicated either by subjective account or observation by others, for at least 2 years, but without a major depressive episode occurring. ...
... more days than not, as indicated either by subjective account or observation by others, for at least 2 years, but without a major depressive episode occurring. ...
Chapter 5
... Signs should be taken seriously. The more signs exhibited, the more likely it is that the person is thinking about suicide Recognizing these signs may help prevent `````````````````````a SUICIDE``````````````````````` Direct statements “I wish I were dead” Deterioration of schoolwork Indirect ...
... Signs should be taken seriously. The more signs exhibited, the more likely it is that the person is thinking about suicide Recognizing these signs may help prevent `````````````````````a SUICIDE``````````````````````` Direct statements “I wish I were dead” Deterioration of schoolwork Indirect ...
Geriatric Depression
... Persons 65 years or older 39.6 million in 2009 (the latest year for which data is available) or 12.9% of the U.S. population 72.1 million or 19% of the population estimated in ...
... Persons 65 years or older 39.6 million in 2009 (the latest year for which data is available) or 12.9% of the U.S. population 72.1 million or 19% of the population estimated in ...
Key terms - Ms. Paras
... Exam (combined with Abnormal Behavior): Wednesday, March 8th This section of the course provides students with an understanding of empirically based treatments of psychological disorders. The topic emphasizes descriptions of treatment modalities based on various orientations in psychology. Learning ...
... Exam (combined with Abnormal Behavior): Wednesday, March 8th This section of the course provides students with an understanding of empirically based treatments of psychological disorders. The topic emphasizes descriptions of treatment modalities based on various orientations in psychology. Learning ...
Unmasking Male Depression: Understanding and Treating
... of a Major Depressive Episode in addition to the normal response to a significant loss. ...
... of a Major Depressive Episode in addition to the normal response to a significant loss. ...
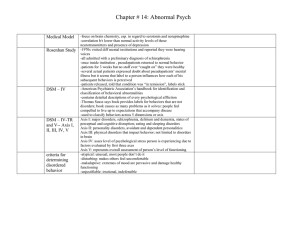
Abnormal Psych
... Maladaptive- destructive to oneself or others (exaggeration of normal, acceptable behavior). Unjustifiable- without a rational basis Disturbing- troublesome to other people Atypical- so different that they violate a norm (what is acceptable in their culture). ...
... Maladaptive- destructive to oneself or others (exaggeration of normal, acceptable behavior). Unjustifiable- without a rational basis Disturbing- troublesome to other people Atypical- so different that they violate a norm (what is acceptable in their culture). ...
Personality disorder
... MPD is a socially acceptable way for some troubled people to make sense of their problems. Therapists looking for MPD may reward patients with attention and praise for revealing more and more personalities. ...
... MPD is a socially acceptable way for some troubled people to make sense of their problems. Therapists looking for MPD may reward patients with attention and praise for revealing more and more personalities. ...
Schizophrenia & Depr..
... For a significant portion of the time since the onset of the disturbance, one or more major areas of functioning such as work, interpersonal relations, or self-care are markedly below the level achieved prior to the onset (or when the onset is in childhood or adolescence, failure to achieve expect ...
... For a significant portion of the time since the onset of the disturbance, one or more major areas of functioning such as work, interpersonal relations, or self-care are markedly below the level achieved prior to the onset (or when the onset is in childhood or adolescence, failure to achieve expect ...
Depression
... - clear, distinct boundaries between the 2 categories hard to find - John Feighner at Washington University (“Feighner criteria” 1972) 3 criteria ...
... - clear, distinct boundaries between the 2 categories hard to find - John Feighner at Washington University (“Feighner criteria” 1972) 3 criteria ...
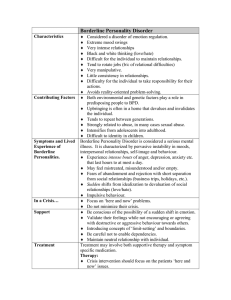
Borderline Personality Disorder
... Difficulty for the individual to take responsibility for their actions. ♦ Avoids reality-oriented problem-solving. ♦ Both environmental and genetic factors play a role in predisposing people to BPD. ♦ Upbringing is often in a home that devalues and invalidates the individual. ♦ Tends to repeat betwe ...
... Difficulty for the individual to take responsibility for their actions. ♦ Avoids reality-oriented problem-solving. ♦ Both environmental and genetic factors play a role in predisposing people to BPD. ♦ Upbringing is often in a home that devalues and invalidates the individual. ♦ Tends to repeat betwe ...
Update on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Juvenile Mood
... Continuation therapy recommended for all patients for at least 6 to 12 months Maintenance treatment may be indicated for some patients with > 2 or 3 discrete episodes of depression Combined meds +psychotherapy therapy likely will lead to best outcomes ...
... Continuation therapy recommended for all patients for at least 6 to 12 months Maintenance treatment may be indicated for some patients with > 2 or 3 discrete episodes of depression Combined meds +psychotherapy therapy likely will lead to best outcomes ...
Medical Model - Biloxi Public Schools
... -all admitted with a preliminary diagnosis of schizophrenia -once inside institution , pseudopatients returned to normal behavior -patients for 3 weeks but no staff ever “caught on” they were healthy -several actual patients expressed doubt about pseudopatients’ mental illness but it seems that labe ...
... -all admitted with a preliminary diagnosis of schizophrenia -once inside institution , pseudopatients returned to normal behavior -patients for 3 weeks but no staff ever “caught on” they were healthy -several actual patients expressed doubt about pseudopatients’ mental illness but it seems that labe ...
Mood Disorders Depression and Bipolar
... A. Depressed mood most of the day, more days than not, for at least 2 years B. Presence, while depressed, of 2 (or more) of the following: 1. Poor appetite or overeating 2. Insomnia or hypersomnia 3. Low energy or fatigue 4. Low self-esteem 5. Poor concentration or difficulty making decisions 6. Fee ...
... A. Depressed mood most of the day, more days than not, for at least 2 years B. Presence, while depressed, of 2 (or more) of the following: 1. Poor appetite or overeating 2. Insomnia or hypersomnia 3. Low energy or fatigue 4. Low self-esteem 5. Poor concentration or difficulty making decisions 6. Fee ...
melatonin Mood disorders
... -Studies show that families of individuals who later develop Schizophrenia are often on the verge of falling apart. Diathesis-stress hypothesis: a person may inherit a predisposition toward Schizophrenia and from there environmental factors play a role. ...
... -Studies show that families of individuals who later develop Schizophrenia are often on the verge of falling apart. Diathesis-stress hypothesis: a person may inherit a predisposition toward Schizophrenia and from there environmental factors play a role. ...
Chapter 14, Mood Disorders
... Major depression is diagnosed when symptoms are present for at least two weeks, have a sudden onset and are significant enough to impact daily functioning. ...
... Major depression is diagnosed when symptoms are present for at least two weeks, have a sudden onset and are significant enough to impact daily functioning. ...
Name__________________________Date_______________Period
... Chapter 16 – Psychological Disorders 1. Why is it difficult to draw a line between normal and abnormal behavior? 2. What are some problems with defining abnormality as any deviation from the majority? 3. According to the adjustment definition of normal, what type of person would be “abnormal”? 4. Ho ...
... Chapter 16 – Psychological Disorders 1. Why is it difficult to draw a line between normal and abnormal behavior? 2. What are some problems with defining abnormality as any deviation from the majority? 3. According to the adjustment definition of normal, what type of person would be “abnormal”? 4. Ho ...
Mental Health Nursing: Anxiety Disorders
... behavior Increase the pt’s self-esteem Modify negative thinking patterns ...
... behavior Increase the pt’s self-esteem Modify negative thinking patterns ...
Dr Darton Presentation
... • Metabolic syndrome – weight gain, increased blood fats, diabetes • Blood disorders • Antimuscarinic effects • Constipation • Life-limiting • ‘not worth the candle’? ...
... • Metabolic syndrome – weight gain, increased blood fats, diabetes • Blood disorders • Antimuscarinic effects • Constipation • Life-limiting • ‘not worth the candle’? ...
Adjustment and Breakdown
... needs an increased amount in order to produce the same effect Dissociative Identity Disorder- a dissociative disorder in which a person exhibits two or more personality states How to treat panic disorders- Well you could always just use some drugs of the antidepressant category, yeah that will be en ...
... needs an increased amount in order to produce the same effect Dissociative Identity Disorder- a dissociative disorder in which a person exhibits two or more personality states How to treat panic disorders- Well you could always just use some drugs of the antidepressant category, yeah that will be en ...
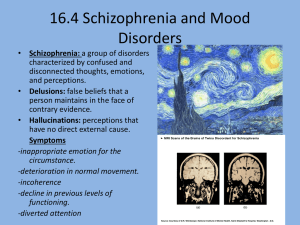
Psychotic Disorders
... ◦ Psychotic symptoms: distort a person’s thinking. They include hallucinations, delusions, trouble organizing thoughts and abnormal movements. ◦ “Negative” symptoms: make it difficult to show emotions and function normally. An individual may seem depressed and withdrawn. ◦ Cognitive symptoms: affect ...
... ◦ Psychotic symptoms: distort a person’s thinking. They include hallucinations, delusions, trouble organizing thoughts and abnormal movements. ◦ “Negative” symptoms: make it difficult to show emotions and function normally. An individual may seem depressed and withdrawn. ◦ Cognitive symptoms: affect ...