Psychiatric illnesses in Children and Adolescents: types and treatment
... Panic disorder, an anxiety disorder with episodes of panic attacks: periods of intense fear that last 10 minutes, or longer, usually brief and very intense, with four of the following: ...
... Panic disorder, an anxiety disorder with episodes of panic attacks: periods of intense fear that last 10 minutes, or longer, usually brief and very intense, with four of the following: ...
Strategies to deal with depression in epilepsy
... They tend to respond to changes in antiepileptic or antidepressive medications These patients tend to be more irritable and emotional Many have dysthymia between seizures ...
... They tend to respond to changes in antiepileptic or antidepressive medications These patients tend to be more irritable and emotional Many have dysthymia between seizures ...
Understanding Students with Emotional or Behavioral Disorders
... • Inability to learn (cannot be explained by intellectual, sensory, or health factors) • Inability to develop or maintain interpersonal relationships • Inappropriate types of behaviors or feelings • Pervasive mood of unhappiness or depression • Physical symptoms or fears associated with personal or ...
... • Inability to learn (cannot be explained by intellectual, sensory, or health factors) • Inability to develop or maintain interpersonal relationships • Inappropriate types of behaviors or feelings • Pervasive mood of unhappiness or depression • Physical symptoms or fears associated with personal or ...
Document
... Symptoms of Major Depression The onset of the first episode of major depression is gradual or mild. The symptoms represent a significant change from how a person functioned before the illness: persistently sad, or irritable mood pronounced changes in sleep, appetite, and energy difficulty t ...
... Symptoms of Major Depression The onset of the first episode of major depression is gradual or mild. The symptoms represent a significant change from how a person functioned before the illness: persistently sad, or irritable mood pronounced changes in sleep, appetite, and energy difficulty t ...
meaning of treatment
... their memories are what give them the need for other hands. And the desolation of lovers is the same: that enormous emptiness carved out of such tiny beings as we are asks to be filled; the need for the new love is faithfulness to the old. ...
... their memories are what give them the need for other hands. And the desolation of lovers is the same: that enormous emptiness carved out of such tiny beings as we are asks to be filled; the need for the new love is faithfulness to the old. ...
Depressive Disorders in Women
... Hypomania: Diagnostic Criteria • All the criteria of a Manic episode except without marked impairment ...
... Hypomania: Diagnostic Criteria • All the criteria of a Manic episode except without marked impairment ...
MENTAL DISORDERS
... THOUGHTS, FEELINGS, AND BEHAVIORS OF A PERSON, PREVENTING HIM OR HER FROM LEADING A HAPPY, HEALTHFUL, AND PRODUCTIVE LIFE REQUIRE MEDICAL ATTENTION JUST LIKE PHYSICAL ILLNESSES ...
... THOUGHTS, FEELINGS, AND BEHAVIORS OF A PERSON, PREVENTING HIM OR HER FROM LEADING A HAPPY, HEALTHFUL, AND PRODUCTIVE LIFE REQUIRE MEDICAL ATTENTION JUST LIKE PHYSICAL ILLNESSES ...
16 DEVELOPMENTAL PSYCHOPATHOLOGY LEARNING
... C. Depression 1. Chronic feelings of worthlessness, hopelessness, self-blame 2. Masked depression-- depression expressed in atypical symptoms like aggression 3. Depression rare in childhood and more common in adolescence 4. Suicide attempts in children rare but do occur 5. Multiple types of therapie ...
... C. Depression 1. Chronic feelings of worthlessness, hopelessness, self-blame 2. Masked depression-- depression expressed in atypical symptoms like aggression 3. Depression rare in childhood and more common in adolescence 4. Suicide attempts in children rare but do occur 5. Multiple types of therapie ...
General classes of disorders
... They are very effective for depression Side effects include orthostatic hypotension, weight gain, dry mouth, sedation, sexual dysfunction and sleep disturbance Hypertensive crisis can develop when MAOI’s are taken with tyramine-rich foods or ...
... They are very effective for depression Side effects include orthostatic hypotension, weight gain, dry mouth, sedation, sexual dysfunction and sleep disturbance Hypertensive crisis can develop when MAOI’s are taken with tyramine-rich foods or ...
Psychological Disorders-Mood
... * Feelings of pessimism, despair or hopelessness * Generalized loss of interest or pleasure * Social withdrawal * Chronic fatigue or tiredness * Feelings of guilt or brooding about the past * Subjective feelings of irritability or excessive anger * Decreased activity, effectiveness or productivity * ...
... * Feelings of pessimism, despair or hopelessness * Generalized loss of interest or pleasure * Social withdrawal * Chronic fatigue or tiredness * Feelings of guilt or brooding about the past * Subjective feelings of irritability or excessive anger * Decreased activity, effectiveness or productivity * ...
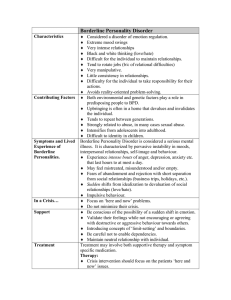
Borderline Personality Disorder
... Difficulty for the individual to take responsibility for their actions. ♦ Avoids reality-oriented problem-solving. ♦ Both environmental and genetic factors play a role in predisposing people to BPD. ♦ Upbringing is often in a home that devalues and invalidates the individual. ♦ Tends to repeat betwe ...
... Difficulty for the individual to take responsibility for their actions. ♦ Avoids reality-oriented problem-solving. ♦ Both environmental and genetic factors play a role in predisposing people to BPD. ♦ Upbringing is often in a home that devalues and invalidates the individual. ♦ Tends to repeat betwe ...
Psychopathology - HomePage Server for UT Psychology
... Ea. May have own voice, speech pattern, habits, memories, sexual orientation, clothing, handwriting, brain-wave, BP, eyeglass prescription, rxns… ...
... Ea. May have own voice, speech pattern, habits, memories, sexual orientation, clothing, handwriting, brain-wave, BP, eyeglass prescription, rxns… ...
Ten Leading Causes of Disability in the World
... Episodes and numerous periods with depressed mood or loss of interest or pleasure that did not meet criterion A of a Major Depressive Episode During a two year period (one year in children and adolescents) of the disturbance, never without hypomanic or depressive symptoms for more than a two month ...
... Episodes and numerous periods with depressed mood or loss of interest or pleasure that did not meet criterion A of a Major Depressive Episode During a two year period (one year in children and adolescents) of the disturbance, never without hypomanic or depressive symptoms for more than a two month ...
Does Depression Affect Women more than it Affects Men?
... annoyance towards the clinician rather than sadness. Because of these emotions towards the clinician, the patient usually develops a sense of guilt. ...
... annoyance towards the clinician rather than sadness. Because of these emotions towards the clinician, the patient usually develops a sense of guilt. ...
Exploring Depression in Older Adults, Barriers to Diagnosis and Treatment
... often goes undiagnosed and untreated, perhaps due to a misconception that depression is a normal response to aging or its symptoms can be mistaken as signs of other health conditions. Stigma may also affect how likely older adults, compared to younger adults, are to seek mental health treatment. Thi ...
... often goes undiagnosed and untreated, perhaps due to a misconception that depression is a normal response to aging or its symptoms can be mistaken as signs of other health conditions. Stigma may also affect how likely older adults, compared to younger adults, are to seek mental health treatment. Thi ...
River deaths in Northern Ireland
... Bipolar affective disorder This disease is when people have major mood swings. Those affected by the illness may have 'normal' mood for months or even years. The mood-swings of bipolar disorder should not be confused with the mood changes that we all experience from time to time. They are much mor ...
... Bipolar affective disorder This disease is when people have major mood swings. Those affected by the illness may have 'normal' mood for months or even years. The mood-swings of bipolar disorder should not be confused with the mood changes that we all experience from time to time. They are much mor ...
Major Depressive Disorder
... • Diminished ability to think or concentrate, or indecisiveness. • Recurrent thoughts of death, recurrent suicidal ideation, suicide attempts, or suicide plans. ...
... • Diminished ability to think or concentrate, or indecisiveness. • Recurrent thoughts of death, recurrent suicidal ideation, suicide attempts, or suicide plans. ...
Kinds of Anxiety Issues I Work With Generalized Anxiety Disorder
... humiliation (social phobia). Feeling socially clumsy, having trouble with small talk in social situations, and letting fear of embarrassment or humiliation cause avoidance of triggering situations. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder - Can manifest from mild to severe including obsessive thoughts and repe ...
... humiliation (social phobia). Feeling socially clumsy, having trouble with small talk in social situations, and letting fear of embarrassment or humiliation cause avoidance of triggering situations. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder - Can manifest from mild to severe including obsessive thoughts and repe ...
Depression in Late Life
... • Somatic delusions common, but few hallucinations • Nihilistic beliefs, hopelessness • Often have suicidal ideations ...
... • Somatic delusions common, but few hallucinations • Nihilistic beliefs, hopelessness • Often have suicidal ideations ...
Tips for Living - Understanding Mood Disorders
... Some people with depression also experience mania, and the combination of the two is known as bipolar disorder. When a person experiences symptoms of mania, he or she has feelings of extreme irritability, inflated self-esteem, racing thoughts, poor judgment, and the urge to engage in extremely risky ...
... Some people with depression also experience mania, and the combination of the two is known as bipolar disorder. When a person experiences symptoms of mania, he or she has feelings of extreme irritability, inflated self-esteem, racing thoughts, poor judgment, and the urge to engage in extremely risky ...
NS330 Quiz 3 - WordPress.com
... depressive syndrome usually present most of day, more days than not, for at least 2 yrs, often cannot be distinguished from person’s usual pattern of functioning Biological Theories: -genetic factors- inc’d heritability is assoc’d w/ earlier age of onset, greater rate of comorbidity & inc’d risk of ...
... depressive syndrome usually present most of day, more days than not, for at least 2 yrs, often cannot be distinguished from person’s usual pattern of functioning Biological Theories: -genetic factors- inc’d heritability is assoc’d w/ earlier age of onset, greater rate of comorbidity & inc’d risk of ...
Lecture 5
... No Major Depressive Episode has been present during the first 2 years of the disturbance (1 year for children and adolescents); i.e., the disturbance is not better accounted for by chronic Major Depressive Disorder, or Major Depressive Disorder, In Partial Remission. Note: There may have been previo ...
... No Major Depressive Episode has been present during the first 2 years of the disturbance (1 year for children and adolescents); i.e., the disturbance is not better accounted for by chronic Major Depressive Disorder, or Major Depressive Disorder, In Partial Remission. Note: There may have been previo ...
Mood Disorders and Schizophrenia
... • Often called “treatment of last resort” • Involves placing electrodes on the skull and administering a mild electric current that passes through the brain and causes a seizure • Usual treatments consists of a series of 10-12 ECT sessions, at the rate of about three per ...
... • Often called “treatment of last resort” • Involves placing electrodes on the skull and administering a mild electric current that passes through the brain and causes a seizure • Usual treatments consists of a series of 10-12 ECT sessions, at the rate of about three per ...
bipolar disorder: at-a-glance
... there are periods of well-being, it is unfortunately the case that many individuals affected by this disorder have serious residual symptoms (often of depression) between full relapses. DIAGNOSIS Bipolar disorder often emerges between the late teens and early thirties. Although the illness can occur ...
... there are periods of well-being, it is unfortunately the case that many individuals affected by this disorder have serious residual symptoms (often of depression) between full relapses. DIAGNOSIS Bipolar disorder often emerges between the late teens and early thirties. Although the illness can occur ...
Major depressive disorder

Major depressive disorder (MDD) (also known as clinical depression, major depression, unipolar depression, or unipolar disorder; or as recurrent depression in the case of repeated episodes) is a mental disorder characterized by a pervasive and persistent low mood that is accompanied by low self-esteem and by a loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. The term ""depression"" is used in a number of different ways. It is often used to mean this syndrome but may refer to other mood disorders or simply to a low mood. Major depressive disorder is a disabling condition that adversely affects a person's family, work or school life, sleeping and eating habits, and general health. In the United States, around 3.4% of people with major depression commit suicide, and up to 60% of people who commit suicide had depression or another mood disorder.The diagnosis of major depressive disorder is based on the patient's self-reported experiences, behavior reported by relatives or friends, and a mental status examination. There is no laboratory test for major depression, although physicians generally request tests for physical conditions that may cause similar symptoms. The most common time of onset is between the ages of 20 and 30 years, with a later peak between 30 and 40 years.Typically, people are treated with antidepressant medication and, in many cases, also receive counseling, particularly cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). Medication appears to be effective, but the effect may only be significant in the most severely depressed. Hospitalization may be necessary in cases with associated self-neglect or a significant risk of harm to self or others. A minority are treated with electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). The course of the disorder varies widely, from one episode lasting weeks to a lifelong disorder with recurrent major depressive episodes. Depressed individuals have shorter life expectancies than those without depression, in part because of greater susceptibility to medical illnesses and suicide. It is unclear whether medications affect the risk of suicide. Current and former patients may be stigmatized.The understanding of the nature and causes of depression has evolved over the centuries, though this understanding is incomplete and has left many aspects of depression as the subject of discussion and research. Proposed causes include psychological, psycho-social, hereditary, evolutionary and biological factors. Long-term substance abuse may cause or worsen depressive symptoms. Psychological treatments are based on theories of personality, interpersonal communication, and learning. Most biological theories focus on the monoamine chemicals serotonin, norepinephrine and dopamine, which are naturally present in the brain and assist communication between nerve cells. This cluster of symptoms (syndrome) was named, described and classified as one of the mood disorders in the 1980 edition of the American Psychiatric Association's diagnostic manual.