Animal Behavior
... • Different species have heightened senses which are used for communication. – Visual – Auditory – Tactile ...
... • Different species have heightened senses which are used for communication. – Visual – Auditory – Tactile ...
Chapter 6 – Survey of Animals ()
... are specialized for specific functions. These systems include: - Circulatory - Lymphatic - Integumentary (skin) - Digestive - Respiratory - Excretory - Muscular - Endocrine - Reproductive - Nervous - Skeletal ...
... are specialized for specific functions. These systems include: - Circulatory - Lymphatic - Integumentary (skin) - Digestive - Respiratory - Excretory - Muscular - Endocrine - Reproductive - Nervous - Skeletal ...
Chapter 6 – Survey of Animals
... and are specialized for specific functions. These systems include: - Circulatory - Lymphatic - Integumentary (skin) - Digestive Digesti e - Respiratory - Excretory - Muscular - Endocrine - Reproductive - Nervous - Skeletal ...
... and are specialized for specific functions. These systems include: - Circulatory - Lymphatic - Integumentary (skin) - Digestive Digesti e - Respiratory - Excretory - Muscular - Endocrine - Reproductive - Nervous - Skeletal ...
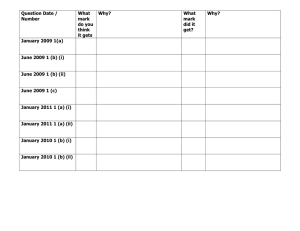
1 (a) What do behaviourists mean by the term operant conditioning
... Likely answers: testosterone; aggression as an evolutionary trait, genetics; heritability, etc. Behaviourist: One mark for brief or muddled explanation. Two marks for an accurate and detailed explanation. Likely answers: learning by association; principles of operant conditioning; reinforcement. Cre ...
... Likely answers: testosterone; aggression as an evolutionary trait, genetics; heritability, etc. Behaviourist: One mark for brief or muddled explanation. Two marks for an accurate and detailed explanation. Likely answers: learning by association; principles of operant conditioning; reinforcement. Cre ...
Chapter 35: Animal Behavior
... • Many instinctive behaviors consist of actions that always continue in a certain order once they have begun ...
... • Many instinctive behaviors consist of actions that always continue in a certain order once they have begun ...
Relationships in the Ecosystem
... Competition …when 2 organisms or species have the same niche they will compete for resources. The “loser” will either have to leave, get another niche or die. ...
... Competition …when 2 organisms or species have the same niche they will compete for resources. The “loser” will either have to leave, get another niche or die. ...
Animal Behavior
... • Occurs during a ‘sensitive’ or ‘critical’ development period • Imprinting of baby geese on mother was studied by Konrad Lorenz ...
... • Occurs during a ‘sensitive’ or ‘critical’ development period • Imprinting of baby geese on mother was studied by Konrad Lorenz ...
Adapt Your Own Animal
... protection from larger fish that prey on it. Its major food source is dying off and new food sources live in deeper, colder waters. Other small fish at this water level tend to swim faster than this clown fish can swim. Animal B: A small mammal living in the forest has trouble finding food at night. ...
... protection from larger fish that prey on it. Its major food source is dying off and new food sources live in deeper, colder waters. Other small fish at this water level tend to swim faster than this clown fish can swim. Animal B: A small mammal living in the forest has trouble finding food at night. ...
$doc.title
... 1. Trained personnel who are familiar with the species must check all animals daily for signs of disease, illness or unsafe environment (includes feed, litter, water, temperature, humidity, etc.) 2. The re ...
... 1. Trained personnel who are familiar with the species must check all animals daily for signs of disease, illness or unsafe environment (includes feed, litter, water, temperature, humidity, etc.) 2. The re ...
Ch 17 (30 MCQ questions)
... a) Attitudes and attributions summarize vast amounts of information from our complex social world. b) Many of the concepts and experimental methods central to the field of attitude research have been borrowed from work in cognitive psychology. c) Social cognition focuses on the perception and proces ...
... a) Attitudes and attributions summarize vast amounts of information from our complex social world. b) Many of the concepts and experimental methods central to the field of attitude research have been borrowed from work in cognitive psychology. c) Social cognition focuses on the perception and proces ...
final exam study guide intro to animal kingdom first semester
... Which of these scientists is credited with developing the system of grouping organisms that is still used today? What model is sometimes used to identify a group’s derived traits? The placing of information or objects into groups based on certain similarities is called ____________. When using binom ...
... Which of these scientists is credited with developing the system of grouping organisms that is still used today? What model is sometimes used to identify a group’s derived traits? The placing of information or objects into groups based on certain similarities is called ____________. When using binom ...
Social_life
... We err in the direction of paying too little attention to external causes of behaviour when evaluating other people (Fundamental Attribution Error) Why do we err like this? If someone is always influenced by the situation, it is difficult to predict how they are going to behave in other situat ...
... We err in the direction of paying too little attention to external causes of behaviour when evaluating other people (Fundamental Attribution Error) Why do we err like this? If someone is always influenced by the situation, it is difficult to predict how they are going to behave in other situat ...
Relationships in the Ecosystem
... for food. Prey = animal that is eaten by another. Predator / Prey populations will change in response to each other’s population. ...
... for food. Prey = animal that is eaten by another. Predator / Prey populations will change in response to each other’s population. ...
Faculty Research Support Grants 2012 First Round successful
... James Neill, Lynne Magor-Blatch, Daniel Bowen, Ben Hopkins, Lee-Anne Gassner, Pepita Marsh Groups Total ...
... James Neill, Lynne Magor-Blatch, Daniel Bowen, Ben Hopkins, Lee-Anne Gassner, Pepita Marsh Groups Total ...
Animal Behavior
... behavior with a good or bad response (trial and error) • Pups or cubs with porcupines ...
... behavior with a good or bad response (trial and error) • Pups or cubs with porcupines ...
Learning theories Classical conditioning • Automatic responses with
... Learning theories Classical conditioning Automatic responses with new stimuli Ivan Pavlov Russian physiologist 1920’s Unconditioned response/stimuli – Naturally occurring with normal response Conditioned response/stimuli – Stimuli which evokes an emotional response. E.g. Pavlov’s dog’s tun ...
... Learning theories Classical conditioning Automatic responses with new stimuli Ivan Pavlov Russian physiologist 1920’s Unconditioned response/stimuli – Naturally occurring with normal response Conditioned response/stimuli – Stimuli which evokes an emotional response. E.g. Pavlov’s dog’s tun ...
Animal Behavior 09
... Social behavior is often used to help the survival of that species & to make the organisms more efficient. Often, there is a division-oflabor setup & most, if not all, of the organisms are related to one another. Therefore, by sticking together, it increases the chances that those genes of the indi ...
... Social behavior is often used to help the survival of that species & to make the organisms more efficient. Often, there is a division-oflabor setup & most, if not all, of the organisms are related to one another. Therefore, by sticking together, it increases the chances that those genes of the indi ...
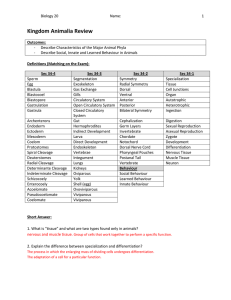
Kingdom Animalia Review Answer Key
... Short Answer: 1. What is “tissue” and what are two types found only in animals? nervous and muscle tissue. Group of cells that work together to perform a specific function. 2. Explain the difference between specialization and differentiation? The process in which the enlarging mass of dividing cells ...
... Short Answer: 1. What is “tissue” and what are two types found only in animals? nervous and muscle tissue. Group of cells that work together to perform a specific function. 2. Explain the difference between specialization and differentiation? The process in which the enlarging mass of dividing cells ...
Animal Behavior - Phillips Scientific Methods
... dinner causes the dog to salivate without food being present ...
... dinner causes the dog to salivate without food being present ...
Animal Behavior
... • Animal learns to repeat behaviors that result in reward and avoid behaviors that result in punishment. • Also known as trial and error • Example: Good grades and performing well in school ...
... • Animal learns to repeat behaviors that result in reward and avoid behaviors that result in punishment. • Also known as trial and error • Example: Good grades and performing well in school ...
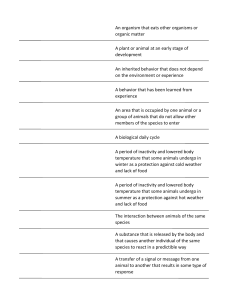
An organism that eats other organisms or organic matter A plant or
... An organism that eats other organisms or organic matter A plant or animal at an early stage of development An inherited behavior that does not depend on the environment or experience A behavior that has been learned from experience An area that is occupied by one animal or a group of animals that do ...
... An organism that eats other organisms or organic matter A plant or animal at an early stage of development An inherited behavior that does not depend on the environment or experience A behavior that has been learned from experience An area that is occupied by one animal or a group of animals that do ...
RESEARCH INTEREST The frame work It is well known that within
... as on sexual differentiation. The embryonic exposure to maternal hormones is, at least partly, a function of the hormonal status of the mother, which is in turn depending on environmental conditions. This opens the fascinating possibility that mothers translate the environmental conditions to their ...
... as on sexual differentiation. The embryonic exposure to maternal hormones is, at least partly, a function of the hormonal status of the mother, which is in turn depending on environmental conditions. This opens the fascinating possibility that mothers translate the environmental conditions to their ...
Ethology

Ethology is the scientific and objective study of animal behaviour, usually with a focus on behaviour under natural conditions, and viewing behaviour as an evolutionarily adaptive trait. Behaviourism is a term that also describes the scientific and objective study of animal behaviour, but it usually refers to the study of trained behavioural responses in a laboratory context, and without a particular emphasis on evolutionary adaptivity.Many naturalists have studied aspects of animal behaviour throughout history. Ethology has its scientific roots in the work of Charles Darwin and of American and German ornithologists of the late 19th and early 20th century, including Charles O. Whitman, Oskar Heinroth, and Wallace Craig. The modern discipline of ethology is generally considered to have begun during the 1930s with the work of Dutch biologist Nikolaas Tinbergen and by Austrian biologists Konrad Lorenz and Karl von Frisch, joint awardees of the 1973 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Ethology is a combination of laboratory and field science, with a strong relation to some other disciplines such as neuroanatomy, ecology, and evolution. Ethologists are typically interested in a behavioural process rather than in a particular animal group, and often study one type of behaviour, such as aggression, in a number of unrelated animals.Ethology is a rapidly growing field. Since the dawn of the 21st century, many aspects of animal communication, emotions, culture, learning and sexuality that the scientific community long thought it understood have been re-examined, and new conclusions reached. New fields, such as neuroethology, have developed.Understanding ethology or animal behaviour can be important in animal training. Considering the natural behaviours of different species or breeds enables the trainer to select the individuals best suited to perform the required task. It also enables the trainer to encourage the performance of naturally occurring behaviours and also the discontinuance of undesirable behaviours.