Red Hat Linux System Administration I – Concepts
... Labs are designed specifically for non-Linux administrators wishing to quickly become familiar with the installation, file system concepts, process management, basic scripting, printing, and a host of standard administration commands and utilities. The objective of this class is to help attendees de ...
... Labs are designed specifically for non-Linux administrators wishing to quickly become familiar with the installation, file system concepts, process management, basic scripting, printing, and a host of standard administration commands and utilities. The objective of this class is to help attendees de ...
Chapter 1 Introduction to Operating System Part 1
... - chips containing thousands of transistors on a square centimetre of silicon Powerful personal computer use by business, universities and government are usually called workstations 1980’s – Growth of personal computer running network OS and distributed OS. Network OS – User can log in into remote m ...
... - chips containing thousands of transistors on a square centimetre of silicon Powerful personal computer use by business, universities and government are usually called workstations 1980’s – Growth of personal computer running network OS and distributed OS. Network OS – User can log in into remote m ...
Introduction to Operating Systems - Seneca
... UNIX is an operating system written in the 1970s by AT&T It has become a standard on which many other operating systems are modelled We will be using a command-line interface to communicate with UNIX ...
... UNIX is an operating system written in the 1970s by AT&T It has become a standard on which many other operating systems are modelled We will be using a command-line interface to communicate with UNIX ...
Input/Output
... Software: Device Independence Error handling • Primary handling is by the drivers – It can often react and repair the error before the software layer above notices – Only when, after several tries, repairing fails, the higher layers are informed ...
... Software: Device Independence Error handling • Primary handling is by the drivers – It can often react and repair the error before the software layer above notices – Only when, after several tries, repairing fails, the higher layers are informed ...
Advanced Interactive Executive (AIX) operating system overview
... The UNIX operating system was originally created in the 1970s to provide a test bed for computer science experimentation. 2 This operating system differs from conventional operating systems in several key ways. Essentially, all of the operating system code is written in c to ensure easy portability ...
... The UNIX operating system was originally created in the 1970s to provide a test bed for computer science experimentation. 2 This operating system differs from conventional operating systems in several key ways. Essentially, all of the operating system code is written in c to ensure easy portability ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Interfaces By: Ben Griffin and
... visual prompt by typing in a command on a specified line, receives a response back from the system, and then enters another command, and so forth. The MS-DOS Prompt application in a Windows operating system is an example of the provision of a command line interface. Today, most users prefer the grap ...
... visual prompt by typing in a command on a specified line, receives a response back from the system, and then enters another command, and so forth. The MS-DOS Prompt application in a Windows operating system is an example of the provision of a command line interface. Today, most users prefer the grap ...
[Product Name] Marketing Plan
... – Need the OS to run other applications – Need OS to control hardware – Organises files and directories – Is the ‘front end’ of the computer – The environment the user interacts with – Responds to commands issued by the user Stuart Cunningham - Computer Platforms - 2003 ...
... – Need the OS to run other applications – Need OS to control hardware – Organises files and directories – Is the ‘front end’ of the computer – The environment the user interacts with – Responds to commands issued by the user Stuart Cunningham - Computer Platforms - 2003 ...
Linux Introduction - Personal Web Pages
... ideas to the Linux kernel – At the time, the GNU Project had created many of the components required for a free software operating system, but its own kernel, GNU Hurd, was incomplete and unavailable – BSD operating system had not yet freed itself from ...
... ideas to the Linux kernel – At the time, the GNU Project had created many of the components required for a free software operating system, but its own kernel, GNU Hurd, was incomplete and unavailable – BSD operating system had not yet freed itself from ...
Operating Systems
... loads into memory other operating system programs (called nonresident) from disk storage only as needed. An operating system has three main functions: manage the computer's resources, such as the central processing unit, memory, disk drives, and printers, establish a user interface, and execute and ...
... loads into memory other operating system programs (called nonresident) from disk storage only as needed. An operating system has three main functions: manage the computer's resources, such as the central processing unit, memory, disk drives, and printers, establish a user interface, and execute and ...
Computer Systems - Barefoot Computing
... the software which enables the system to be flexible in meeting a range of user needs. There are different types of software which run on these computer systems: Operating system The operating system enables the various hardware components to communicate and function together and provides the user w ...
... the software which enables the system to be flexible in meeting a range of user needs. There are different types of software which run on these computer systems: Operating system The operating system enables the various hardware components to communicate and function together and provides the user w ...
Embedded Operating Systems Selection Guide
... Internet browser applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 Multimedia applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 Terminal emulation applications . . . . . . . . . . . ...
... Internet browser applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 Multimedia applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 Terminal emulation applications . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Operating Systems Essay Research Paper Operating Systems
... architecture and instruction set, which allowed programs written for one machine to be executed on another. The operating system required to run on this family of computers has to be able to work on all models, be backward compatible and be able to run on both small and large systems. The software w ...
... architecture and instruction set, which allowed programs written for one machine to be executed on another. The operating system required to run on this family of computers has to be able to work on all models, be backward compatible and be able to run on both small and large systems. The software w ...
Modes of Use Presentation
... Have an understanding of a wider range of workrelated IT applications and their effects. ...
... Have an understanding of a wider range of workrelated IT applications and their effects. ...
Operating systems
... It is the most important program that runs on a computer. Every general-purpose computer must have an operating system to run other programs. Operating systems, in general, control the functions of a computer and the running of application programs. They perform basic tasks, such as recognizing inpu ...
... It is the most important program that runs on a computer. Every general-purpose computer must have an operating system to run other programs. Operating systems, in general, control the functions of a computer and the running of application programs. They perform basic tasks, such as recognizing inpu ...
What is Linux? - Longwood Blogs
... http://www.ubuntu.com/download/desktop/create-a-usb-stick-on-windows ...
... http://www.ubuntu.com/download/desktop/create-a-usb-stick-on-windows ...
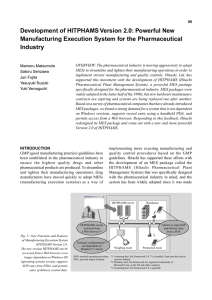
Development of HITPHAMS Version 2.0: Powerful New
... updated interactively as work progresses (see Fig. 3). The ability to input performance and other manufacturing related data in the terminal right at the work site makes the recordkeeping work more efficient and also helps detect and eliminate manufacturing ...
... updated interactively as work progresses (see Fig. 3). The ability to input performance and other manufacturing related data in the terminal right at the work site makes the recordkeeping work more efficient and also helps detect and eliminate manufacturing ...
Online access information sources and services (continued)
... »Unix (and variants such as Linux and Solaris) »Windows NT 4 server; Windows 2000 server; Windows 2003 server;… ...
... »Unix (and variants such as Linux and Solaris) »Windows NT 4 server; Windows 2000 server; Windows 2003 server;… ...
Information flow between computer components In this presentation
... the name of the program in the Start menu. What would we have done if instead of creating a new document, we wanted to go back and modify the old document called WPdoc1? 3. With Windows, user commands are usually entered via a mouse click. How does the user enter a command on a table PC like the iPa ...
... the name of the program in the Start menu. What would we have done if instead of creating a new document, we wanted to go back and modify the old document called WPdoc1? 3. With Windows, user commands are usually entered via a mouse click. How does the user enter a command on a table PC like the iPa ...
xwindows - WordPress.com
... Unix and Linux. The X Window System is the basis for graphical user interfaces. Linux also often confusingly is used to refer to systems like Debian, Ubuntu, Redhat, CentOs, Suse, and many more. These systems are better described as X11+Gnu+Linux. It is largely OS and hardware independent, it is ...
... Unix and Linux. The X Window System is the basis for graphical user interfaces. Linux also often confusingly is used to refer to systems like Debian, Ubuntu, Redhat, CentOs, Suse, and many more. These systems are better described as X11+Gnu+Linux. It is largely OS and hardware independent, it is ...
Operating Systems I Interfaces to Operating Systems MCT260-Operating Systems I
... defines its characteristics • Hardware controls the way you physically manipulate the computer to establish communication ...
... defines its characteristics • Hardware controls the way you physically manipulate the computer to establish communication ...
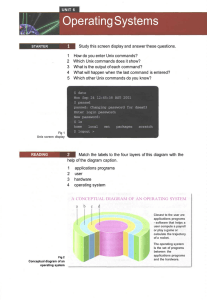
IT ESSENTIALS V. 4.1 Module 5 Fundamental Operating Systems
... driver for that component Information about application, users, hardware, network settings, and file types A block of related data that is given a single name and treated as a single unit CLI – Command Line Interface GUI – Graphical User Interface A set of guidelines used by programmers to ensure th ...
... driver for that component Information about application, users, hardware, network settings, and file types A block of related data that is given a single name and treated as a single unit CLI – Command Line Interface GUI – Graphical User Interface A set of guidelines used by programmers to ensure th ...
Laurence Platt Resume and Technical Summary
... APL, CMS, BASIC, LOTUS 123, EXEC, EXEC2, VISICALC, PL/1, APLDI, AS, STAIRS, ADRS, EDIT1, EDIT2, XEDIT. ...
... APL, CMS, BASIC, LOTUS 123, EXEC, EXEC2, VISICALC, PL/1, APLDI, AS, STAIRS, ADRS, EDIT1, EDIT2, XEDIT. ...
Chapter 1
... PC type of computer, usually used by one person at a time, that may or may not be connected to a network. device driver Computer software designed to provide the operating system and application software access to specific computer hardware. distribution An issuance of UNIX or Linux that is base ...
... PC type of computer, usually used by one person at a time, that may or may not be connected to a network. device driver Computer software designed to provide the operating system and application software access to specific computer hardware. distribution An issuance of UNIX or Linux that is base ...
Introduction to Unix
... Handles communication between the user(s) and the central processor (the computer). Manages the way other programs are stored and run. Common operating systems: Windows95/98, WinNT, Macintosh OS, Linux. ...
... Handles communication between the user(s) and the central processor (the computer). Manages the way other programs are stored and run. Common operating systems: Windows95/98, WinNT, Macintosh OS, Linux. ...
Computer terminal

A computer terminal is an electronic or electromechanical hardware device that is used for entering data into, and displaying data from, a computer or a computing system. Early terminals were inexpensive devices but very slow compared to punched cards or paper tape for input, but as the technology improved and video displays were introduced, terminals pushed these older forms of interaction from the industry. A related development was timesharing systems, which evolved in parallel and made up for any inefficiencies of the user's typing ability with the ability to support multiple users on the same machine, each at their own terminal.The function of a terminal is confined to display and input of data; a device with significant local programmable data processing capability may be called a ""smart terminal"" or fat client. A terminal that depends on the host computer for its processing power is called a ""dumb terminal"" or thin client. A personal computer can run terminal emulator software that replicates the function of a terminal, sometimes allowing concurrent use of local programs and access to a distant terminal host system.





![[Product Name] Marketing Plan](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008423312_1-6ba14a1f3ea5c75f37e0b4b28be854a3-300x300.png)