Astronomy Assignment #1
... On Dec 21 the Sun is at the Winter Solstice on the Ecliptic at -23½ dec. It is thus acting like a southern star. Southern stars rise S of E, reach a low max altitude, rest S of W and spend less than 12 hours above the horizon because most of their diurnal path is below the horizon (See Figure to ri ...
... On Dec 21 the Sun is at the Winter Solstice on the Ecliptic at -23½ dec. It is thus acting like a southern star. Southern stars rise S of E, reach a low max altitude, rest S of W and spend less than 12 hours above the horizon because most of their diurnal path is below the horizon (See Figure to ri ...
ppt - SLAC
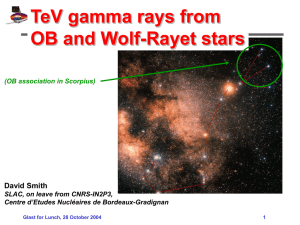
... Wolf-Rayet stars are hot (25-50,000+ degrees K), massive stars (20+ solar mass) with a high rate of mass loss. (This is WR124, at 19h11 +16 ) A few other spectral types don't fit the sequence but instead parallel it. Type W or Wolf-Rayet stars are as hot and blue as the hottest O stars but show stro ...
... Wolf-Rayet stars are hot (25-50,000+ degrees K), massive stars (20+ solar mass) with a high rate of mass loss. (This is WR124, at 19h11 +16 ) A few other spectral types don't fit the sequence but instead parallel it. Type W or Wolf-Rayet stars are as hot and blue as the hottest O stars but show stro ...
Magnitude Scales and Photometric Systems
... magnitudes, measured with these new detectors naturally differ from the visual magnitudes and depend on the color of the star. Initially, there was only the difference between visual magnitudes and ‘blue’ photographic magnitudes to be considered, but several factors resulted in a proliferation of di ...
... magnitudes, measured with these new detectors naturally differ from the visual magnitudes and depend on the color of the star. Initially, there was only the difference between visual magnitudes and ‘blue’ photographic magnitudes to be considered, but several factors resulted in a proliferation of di ...
Andromeda *ruler of men*
... first quadrant of the Northern Hemisphere. Andromeda can be seen at latitudes between +90 degrees and -40 degrees. Using the equatorial coordinate system Andromeda’s right ascension is between 22h and 57.5m and 2h 39.3m and its declination is between 53.19 degrees and 21.68 degrees. The brightest st ...
... first quadrant of the Northern Hemisphere. Andromeda can be seen at latitudes between +90 degrees and -40 degrees. Using the equatorial coordinate system Andromeda’s right ascension is between 22h and 57.5m and 2h 39.3m and its declination is between 53.19 degrees and 21.68 degrees. The brightest st ...
File
... The last and final star is called the Alpheratz. This connects all three stars of Pegasus. It is the most prominent in the sky towards the end of Summer and through Autumn for the northern latitudes. ...
... The last and final star is called the Alpheratz. This connects all three stars of Pegasus. It is the most prominent in the sky towards the end of Summer and through Autumn for the northern latitudes. ...
Emergency Land Navigation
... this outer sphere as a celestial sphere. The stars are fixed upon the sphere in relation to each other and thus are called fixed stars. Out of the many stars found on the sphere, there are only 57 of them, which we consider are bright enough to help us in our navigation. Planets as a class move amon ...
... this outer sphere as a celestial sphere. The stars are fixed upon the sphere in relation to each other and thus are called fixed stars. Out of the many stars found on the sphere, there are only 57 of them, which we consider are bright enough to help us in our navigation. Planets as a class move amon ...
Solutions
... On Dec 21 the Sun is at the Winter Solstice on the Ecliptic at -23½ dec. It is thus acting like a southern star. Southern stars rise S of E, reach a low max altitude, rest S of W and spend less than 12 hours above the horizon because most of their diurnal path is below the horizon (See Figure to ri ...
... On Dec 21 the Sun is at the Winter Solstice on the Ecliptic at -23½ dec. It is thus acting like a southern star. Southern stars rise S of E, reach a low max altitude, rest S of W and spend less than 12 hours above the horizon because most of their diurnal path is below the horizon (See Figure to ri ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... On Dec 21 the Sun is at the Winter Solstice on the Ecliptic at -23½ dec. It is thus acting like a southern star. Southern stars rise S of E, reach a low max altitude, rest S of W and spend less than 12 hours above the horizon because most of their diurnal path is below the horizon (See Figure to ri ...
... On Dec 21 the Sun is at the Winter Solstice on the Ecliptic at -23½ dec. It is thus acting like a southern star. Southern stars rise S of E, reach a low max altitude, rest S of W and spend less than 12 hours above the horizon because most of their diurnal path is below the horizon (See Figure to ri ...
JHK standard stars for large telescopes: the UKIRT Fundamental
... from the equator, became apparent. Consequently a further programme was initiated in 1994, with the intent of strengthening the mutual precision of the magnitudes and colours of the UKIRT Faint Standards and simultaneously of supplementing their number with additional stars, widely distributed both ...
... from the equator, became apparent. Consequently a further programme was initiated in 1994, with the intent of strengthening the mutual precision of the magnitudes and colours of the UKIRT Faint Standards and simultaneously of supplementing their number with additional stars, widely distributed both ...
the UKIRT Fundamental and Extended lists
... from the equator, became apparent. Consequently a further programme was initiated in 1994, with the intent of strengthening the mutual precision of the magnitudes and colours of the UKIRT Faint Standards and simultaneously of supplementing their number with additional stars, widely distributed both ...
... from the equator, became apparent. Consequently a further programme was initiated in 1994, with the intent of strengthening the mutual precision of the magnitudes and colours of the UKIRT Faint Standards and simultaneously of supplementing their number with additional stars, widely distributed both ...
... star, making difficult a precise photometry. For the 2001 season, we could not resolve the pair. In 2000, the sky conditions were better and the star could be separated from the blend in all our images. Although noisy, the light curve phased with a period of about 1.15 days is shown in Figure 3. As ...
WELCOME TO THE MILKY WAY
... 12 h long. Because the rotation axis of Earth is tilted at 23½° in relation to its path around the Sun, we have the seasons. During our summer, the northern side of Earth is pointed towards the Sun. That’s why we have longer days and shorter nights. During winter, the southern side of Earth is point ...
... 12 h long. Because the rotation axis of Earth is tilted at 23½° in relation to its path around the Sun, we have the seasons. During our summer, the northern side of Earth is pointed towards the Sun. That’s why we have longer days and shorter nights. During winter, the southern side of Earth is point ...
identifying seasonal stars in kaurna astronomical traditions
... emu on the celestial plain, while the Mangkamangkaranna (the Pleiades star cluster) represents a group of girls digging roots. The red star Madletaltarni, probably Betelgeuse (Alpha Orionis) or Aldebaran (Alpha Taurii), is the mother of the Tinniinyaranna, and Parnakkoyerli is the father, described ...
... emu on the celestial plain, while the Mangkamangkaranna (the Pleiades star cluster) represents a group of girls digging roots. The red star Madletaltarni, probably Betelgeuse (Alpha Orionis) or Aldebaran (Alpha Taurii), is the mother of the Tinniinyaranna, and Parnakkoyerli is the father, described ...
Variable Stars – II. Pulsating stars
... In this case the star is unstable to pulsation and any small variation, will be reinforced – the pulsation will grow until the energy input by the κ-mechanism reaches a limit. The star will then be pulsating with a stable period and amplitude. Note that the partial ionization zones can be near the s ...
... In this case the star is unstable to pulsation and any small variation, will be reinforced – the pulsation will grow until the energy input by the κ-mechanism reaches a limit. The star will then be pulsating with a stable period and amplitude. Note that the partial ionization zones can be near the s ...
Glencoe Earth Science
... Ursa Minor, and other constellations in the northern sky circle around Polaris. Because of this, they are called circumpolar constellations. The constellations appear to move, as shown in Figure 2, because Earth is in motion. The stars appear to complete one full circle in the sky in about 24 h as E ...
... Ursa Minor, and other constellations in the northern sky circle around Polaris. Because of this, they are called circumpolar constellations. The constellations appear to move, as shown in Figure 2, because Earth is in motion. The stars appear to complete one full circle in the sky in about 24 h as E ...
Automated Detection and Analysis of Meteor Events Using Nightly
... South Pole at -90°. After finding the stars’ coordinates, I compare it to a star catalog and take the closest known bright star compared to the event star. To find the stars the program uses dbfind, which allows the program to set parameters to find the known stars. Each search window was set to a ± ...
... South Pole at -90°. After finding the stars’ coordinates, I compare it to a star catalog and take the closest known bright star compared to the event star. To find the stars the program uses dbfind, which allows the program to set parameters to find the known stars. Each search window was set to a ± ...
THE ABSOLUTE MAGNITUDE OF RR LYRAE - Cosmos
... stars with larger relative errors have brighter luminosities, i.e., have smaller parallaxes, appears clearly when the true parallax is small, compared with error of parallax. Similarly the distant stars have too faint luminosities, i.e., have too large parallaxes, mainly because the true parallax is ...
... stars with larger relative errors have brighter luminosities, i.e., have smaller parallaxes, appears clearly when the true parallax is small, compared with error of parallax. Similarly the distant stars have too faint luminosities, i.e., have too large parallaxes, mainly because the true parallax is ...
Lab PDF - NMSU Astronomy
... to get these lines back. The Sun appears on the line labeled 1.0 R" . All stars of this size, regardless of their luminosity or surface temperature, will lie along this line. In which corner of the diagram (upper right, upper left, lower right, or lower left) would stars with radii 1000 times large ...
... to get these lines back. The Sun appears on the line labeled 1.0 R" . All stars of this size, regardless of their luminosity or surface temperature, will lie along this line. In which corner of the diagram (upper right, upper left, lower right, or lower left) would stars with radii 1000 times large ...
Nazwy gwiazd nieba północnego o etymologii arabskiej
... wyszczególnieniem osób, które wniosły najwięcej. Wykreślone są również etapy transferu nazw arabskich do języków europejskich. Kolejny rozdział to kompilacja nazw gwiazd o etymologii arabskiej z gwiazdozbiorów półkuli północnej. Pogrupowane zostały one alfabetycznie według łacińskich nazw gwiazdozbi ...
... wyszczególnieniem osób, które wniosły najwięcej. Wykreślone są również etapy transferu nazw arabskich do języków europejskich. Kolejny rozdział to kompilacja nazw gwiazd o etymologii arabskiej z gwiazdozbiorów półkuli północnej. Pogrupowane zostały one alfabetycznie według łacińskich nazw gwiazdozbi ...
Stars Stars All Around - Columbus City Schools
... and assign a month to each group. Provide resources for students. (books and websites) ...
... and assign a month to each group. Provide resources for students. (books and websites) ...
Precision age indicators that exploit chemically peculiar stars
... still of great value, blue photometric colors generally indicate galaxies with ongoing star formation, while red colors indicate galaxies that have not formed significant numbers of stars in the last few hundred million years. A technique that often gives higher precision is using Balmer feature str ...
... still of great value, blue photometric colors generally indicate galaxies with ongoing star formation, while red colors indicate galaxies that have not formed significant numbers of stars in the last few hundred million years. A technique that often gives higher precision is using Balmer feature str ...
Small Wonders: Cygnus
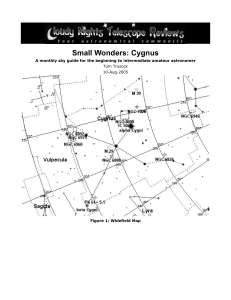
... Three degrees almost directly east of Deneb, we come across one of the most photographed nebulae in the night sky. The North American Nebula is spectacular in long exposure photographs, and unlike many objects in the sky clearly resembles its namesake. Until recently tho, its been considered a chall ...
... Three degrees almost directly east of Deneb, we come across one of the most photographed nebulae in the night sky. The North American Nebula is spectacular in long exposure photographs, and unlike many objects in the sky clearly resembles its namesake. Until recently tho, its been considered a chall ...
Absolute magnitudes and kinematics of barium
... (Jorissen et al. 1996). The obtained groups, given in Table 1, are characterized by different absolute magnitudes and kinematics. These results are analysed in order to assess a possible evolutionary link between the groups. We have used the kinematical results in order to estimate an average sample ...
... (Jorissen et al. 1996). The obtained groups, given in Table 1, are characterized by different absolute magnitudes and kinematics. These results are analysed in order to assess a possible evolutionary link between the groups. We have used the kinematical results in order to estimate an average sample ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... Do you remember the first night that you stood for the very first time under a clear night sky and gazed with bewilderment at its beauty? And did you think something like this as you watched: ‘‘How many stars there are! How can anyone make any sense of this mass of stars?’’ An attentive observer wil ...
... Do you remember the first night that you stood for the very first time under a clear night sky and gazed with bewilderment at its beauty? And did you think something like this as you watched: ‘‘How many stars there are! How can anyone make any sense of this mass of stars?’’ An attentive observer wil ...
Crux

Crux /ˈkrʌks/, located in the deep southern sky, is the smallest yet one of the most distinctive of the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for cross, and it is dominated by a cross-shaped asterism that is commonly known as the Southern Cross. Although visible to the Ancient Greeks, it was seen as part of the constellation Centaurus, and not defined or accurately mapped till the 16th century.Known as Acrux, blue-white Alpha Crucis is the constellation's brightest star and the bottom star of the cross. Nearly as bright are Beta and Gamma, while Delta and Epsilon make up the asterism. Many of the constellation's brighter stars are members of the Scorpius–Centaurus Association, a loose group of hot blue-white stars that appear to share a common origin and motion across the Milky Way. Two star systems have been found to have planets. The constellation also contains four Cepheid variables visible to the naked eye under optimum conditions. Crux also contains the Jewel Box, a bright open cluster, and the Coalsack Nebula, the most prominent dark nebula in the sky.