Document
... j. How is it possible that Canopus is more luminous than Achernar, given their respective spectral types? Canopus is cooler than Achernar; therefore, the only way Canopus can be more luminous is because it is LARGER. 2. List the evolutionary stages of the Sun’s life cycle & describe how its size (Ra ...
... j. How is it possible that Canopus is more luminous than Achernar, given their respective spectral types? Canopus is cooler than Achernar; therefore, the only way Canopus can be more luminous is because it is LARGER. 2. List the evolutionary stages of the Sun’s life cycle & describe how its size (Ra ...
PDF version (two pages, including the full text)
... Southern Cross and the Pointers (Alpha and Beta Centauri). Alpha Centauri is a triple system, with two sun like stars orbiting each other every 80 years and a dim red dwarf tagging along at a much larger distance. This star was discovered by Robert Innes at the Union Observatory in Johannesburg in 1 ...
... Southern Cross and the Pointers (Alpha and Beta Centauri). Alpha Centauri is a triple system, with two sun like stars orbiting each other every 80 years and a dim red dwarf tagging along at a much larger distance. This star was discovered by Robert Innes at the Union Observatory in Johannesburg in 1 ...
Astronomy Test Review
... 11. The temperature of a star can be determined by its color. 13. Parallax is the apparent displacement (movement) of an object due to the change in position of the observer. 14. Apparent magnitude is how bright a star is as seen from Earth where as absolute magnitude is the brightness of a star fro ...
... 11. The temperature of a star can be determined by its color. 13. Parallax is the apparent displacement (movement) of an object due to the change in position of the observer. 14. Apparent magnitude is how bright a star is as seen from Earth where as absolute magnitude is the brightness of a star fro ...
properties of stars 2012
... So… if apparent brightness is determined (by using a light meter) and d is known (perhaps by parallax), luminosity can be determined. Apparent Magnitude: Hipparchus, in 150 B.C. classified stars by magnitude, with 1 being the brightest, and six being the dimmest. With the advent of technology, brigh ...
... So… if apparent brightness is determined (by using a light meter) and d is known (perhaps by parallax), luminosity can be determined. Apparent Magnitude: Hipparchus, in 150 B.C. classified stars by magnitude, with 1 being the brightest, and six being the dimmest. With the advent of technology, brigh ...
ASTR 300 Stars and Stellar Systems Spring 2011
... (a) Which star has the greatest luminosity ? Look at Figure 9-9 of your text. The only supergiant (class I) is Antares, M1 I. It is the most luminous. (b) Which star has the highest surface temperature ? Spica. B1 spectral type is hotter than Regulus which is B7. (c) Which star has the lowest surfac ...
... (a) Which star has the greatest luminosity ? Look at Figure 9-9 of your text. The only supergiant (class I) is Antares, M1 I. It is the most luminous. (b) Which star has the highest surface temperature ? Spica. B1 spectral type is hotter than Regulus which is B7. (c) Which star has the lowest surfac ...
May - RASC St. John`s Centre
... very bright stars about 60º away. One is Vega in Lyra, The Lyre, which Appolo, the god of music as well as the Sun, gave his son Orpheus with which he played the most enchanting music. Arcing slightly in the direction of Polaris along this line finds Deneb in Cygnus, The Swan, also known as the Nort ...
... very bright stars about 60º away. One is Vega in Lyra, The Lyre, which Appolo, the god of music as well as the Sun, gave his son Orpheus with which he played the most enchanting music. Arcing slightly in the direction of Polaris along this line finds Deneb in Cygnus, The Swan, also known as the Nort ...
Astronomy Part 2 - Malvern Troop 7
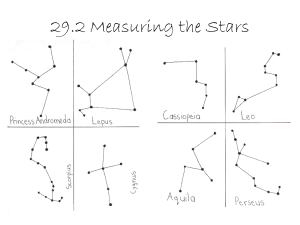
... runs a distinctive line of three stars comprising Orion’s Belt. To the top right of Orion lies another prominent star, Alderbaran, which represents the eye of Taurus. Continue the line from Orion through Aldebaran brings you to the Pleiades, a star cluster. ...
... runs a distinctive line of three stars comprising Orion’s Belt. To the top right of Orion lies another prominent star, Alderbaran, which represents the eye of Taurus. Continue the line from Orion through Aldebaran brings you to the Pleiades, a star cluster. ...
Reading Preview
... A star’s ________ gives clues about the star’s temperature. The coolest stars appear ________. The hottest stars appear ________. Very large stars are called ________ stars or ____________ stars. Our sun is a medium sized ________. Most stars are ________ than the sun. White dwarf stars are abou ...
... A star’s ________ gives clues about the star’s temperature. The coolest stars appear ________. The hottest stars appear ________. Very large stars are called ________ stars or ____________ stars. Our sun is a medium sized ________. Most stars are ________ than the sun. White dwarf stars are abou ...
ď - Google Sites
... 2. What is the general relationship between temperature and star brightness? ...
... 2. What is the general relationship between temperature and star brightness? ...
Solutions 5
... In high-mass stars everything takes place more rapidly. Greater mass means greater gravity and the protostar process is accelerated. Greater mass leads to greater core pressures and temperatures, thus, a hotter more luminous star. The greater mass star consumes the available hydrogen at a much highe ...
... In high-mass stars everything takes place more rapidly. Greater mass means greater gravity and the protostar process is accelerated. Greater mass leads to greater core pressures and temperatures, thus, a hotter more luminous star. The greater mass star consumes the available hydrogen at a much highe ...
HR DIAGRAM REPORT FORM
... A. Plot an H-R diagram for the brightest stars from table 10.1. B. Plot an H-R diagram for the closest stars from table 10.2. 1. Which type of star is most common on each diagram? Choices are: Main Sequence (V), Giants (combine all I,II,III,IV types), White Dwarfs. Do not count Sun. Go to the tables ...
... A. Plot an H-R diagram for the brightest stars from table 10.1. B. Plot an H-R diagram for the closest stars from table 10.2. 1. Which type of star is most common on each diagram? Choices are: Main Sequence (V), Giants (combine all I,II,III,IV types), White Dwarfs. Do not count Sun. Go to the tables ...
1 Sep: 6.13am BST 15 Sep: 6.43am BST 30 Sep: 7.14am BST
... and Aquila (the Eagle) whose brightest stars of Deneb, Vega and Altair respectively make up the Summer Triangle. The Swan’s beak is marked by Albireo and halfway between Albireo and Altair is Sagitta (the Arrow) a small but lovely constellation representing an arrow sailing harmlessly between the tw ...
... and Aquila (the Eagle) whose brightest stars of Deneb, Vega and Altair respectively make up the Summer Triangle. The Swan’s beak is marked by Albireo and halfway between Albireo and Altair is Sagitta (the Arrow) a small but lovely constellation representing an arrow sailing harmlessly between the tw ...
Redshift - Old Age and Red Giants
... Canopus, Rigel, Betelgeuse, Antares are type I supergiants. Q2. (only answer question portion) Rigel, Betelgeuse, Antares, Deneb are type II bright giants. Q3. (only answer question portion) Arcturus, Capella, Agena, Aldebaran, Pollux are type III giants Q4. Canopus, Arcturus, Capella, Rigel, Betelg ...
... Canopus, Rigel, Betelgeuse, Antares are type I supergiants. Q2. (only answer question portion) Rigel, Betelgeuse, Antares, Deneb are type II bright giants. Q3. (only answer question portion) Arcturus, Capella, Agena, Aldebaran, Pollux are type III giants Q4. Canopus, Arcturus, Capella, Rigel, Betelg ...
a. Recognize the physical attributes of stars in the night sky such as
... This is not meant to be printed off and given as a test…this document is to give you ideas of how this standard might be assessed. Please use these as an example when you are developing your own formative assessments. Remember formative assessment is to be given throughout the teaching of a standard ...
... This is not meant to be printed off and given as a test…this document is to give you ideas of how this standard might be assessed. Please use these as an example when you are developing your own formative assessments. Remember formative assessment is to be given throughout the teaching of a standard ...
File
... OBJECTIVE: Compare a stars color, temperature, brightness, and size to its spectral class. PURPOSE: Plot stars according to brightness and temperature to create an HR diagram. PROCEDURES: 1. Study the star data table on the back. 2. The sun, used as a standard brightness, is given a value of 1. The ...
... OBJECTIVE: Compare a stars color, temperature, brightness, and size to its spectral class. PURPOSE: Plot stars according to brightness and temperature to create an HR diagram. PROCEDURES: 1. Study the star data table on the back. 2. The sun, used as a standard brightness, is given a value of 1. The ...
Winter constellations
... supergiant star about twenty times the mass of the sun. The bottom ‘star’ of Orion’s sword appears slightly fuzzy to the naked eye and is the Orion Nebula, number 42 in Charles Messier’s famous list of nebulae of 1759, part of a cloud of gas and dust where new stars are forming. Following the line o ...
... supergiant star about twenty times the mass of the sun. The bottom ‘star’ of Orion’s sword appears slightly fuzzy to the naked eye and is the Orion Nebula, number 42 in Charles Messier’s famous list of nebulae of 1759, part of a cloud of gas and dust where new stars are forming. Following the line o ...
Finding Constellations From Orion
... From Orion Orion, the Hunter, is probably the most easily recognized constellation of winter and spring (or at least his belt is). But by using his belt and the other stars, you can locate several other constellations as well. Capella ...
... From Orion Orion, the Hunter, is probably the most easily recognized constellation of winter and spring (or at least his belt is). But by using his belt and the other stars, you can locate several other constellations as well. Capella ...
Sun and Stars
... The Big and Little Dippers are very well-known to humans. They are part of other constellations in our universe, and are easily found. The Big Dipper makes up part of the constellation of the ursa Major, or the Big Bear. The Little Dipper is part of the constellation Ursa Minor, the Little Bear. ...
... The Big and Little Dippers are very well-known to humans. They are part of other constellations in our universe, and are easily found. The Big Dipper makes up part of the constellation of the ursa Major, or the Big Bear. The Little Dipper is part of the constellation Ursa Minor, the Little Bear. ...
THE HERTZSPRUNG-RUSSELL DIAGRAM (H
... Hypothesis: If a star has a (circle one: greater / lesser) mass, then its life will be longer. Independent Variable: ___________________________ (what variable will you be changing?) Dependent Variable: ____________________________ (What variable will you be measuring?) Procedure: A. Using the “Mass ...
... Hypothesis: If a star has a (circle one: greater / lesser) mass, then its life will be longer. Independent Variable: ___________________________ (what variable will you be changing?) Dependent Variable: ____________________________ (What variable will you be measuring?) Procedure: A. Using the “Mass ...
Binary Star Systems Discussion Points 1. What characteristic of a
... 13. Which light curve shows a system where the two stars are the most different from one another? 14. Which light curve shows a system where the two stars are the most similar to one another? 15. Label the primary and secondary minimums on the V809 Cygnii curve. 16. For the V809 Cygnii light curve, ...
... 13. Which light curve shows a system where the two stars are the most different from one another? 14. Which light curve shows a system where the two stars are the most similar to one another? 15. Label the primary and secondary minimums on the V809 Cygnii curve. 16. For the V809 Cygnii light curve, ...
Document
... • When two stars are gravitationally bound to each other, they orbit a common center of mass • Often appear bound to each other, even with a telescope ...
... • When two stars are gravitationally bound to each other, they orbit a common center of mass • Often appear bound to each other, even with a telescope ...
Capella

Capella is the brightest star in the constellation Auriga, the sixth brightest in the night sky and the third brightest in the northern celestial hemisphere, after Arcturus and Vega. Its name is derived from the diminutive of the Latin capra ""goat"", hence ""little goat"". Capella also bears the Bayer designation Alpha Aurigae (often abbreviated to α Aurigae, α Aur or Alpha Aur). Although it appears to be a single star to the naked eye, it is actually a star system of four stars in two binary pairs. The first pair consists of two bright, large type-G giant stars, both with a radius around 10 times that of the Sun and two and a half times its mass, in close orbit around each other. Designated Capella Aa and Capella Ab, these two stars have both exhausted their core hydrogen fuel and become giant stars, though it is unclear exactly what stage they are on the stellar evolutionary pathway. The second pair, around 10,000 astronomical units from the first, consists of two faint, small and relatively cool red dwarfs. They are designated Capella H and Capella L. The stars labelled Capella C through to G and I through to K are actually unrelated stars in the same visual field. The Capella system is relatively close, at only 42.8 light-years (13.1 pc) from Earth.