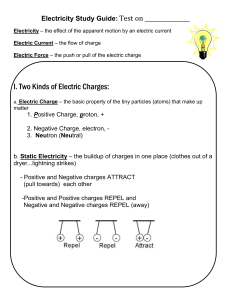
Electric Charge
... Permanent magnets are usually made of steel. All magnets have a north pole and a south pole. b. Electromagnet – a temporary magnet made by wrapping a coil carrying a current around an iron core. Created by wrapping a wire around an iron core (nail) and connecting both ends of the wire to a bat ...
... Permanent magnets are usually made of steel. All magnets have a north pole and a south pole. b. Electromagnet – a temporary magnet made by wrapping a coil carrying a current around an iron core. Created by wrapping a wire around an iron core (nail) and connecting both ends of the wire to a bat ...
Basic Electrical Circuits
... Current is a flow of electricity that is not constant. In fact the direction of current flow periodically switches direction. Examples of AC are: ...
... Current is a flow of electricity that is not constant. In fact the direction of current flow periodically switches direction. Examples of AC are: ...
Условие - Reshaem
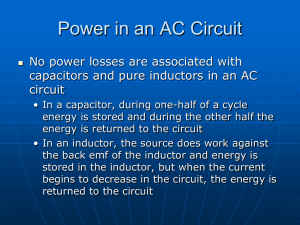
... in one direction only. It flows provided a direct voltage source is applied to the circuit. An alternating current is a current that changes its direction of flow through a circuit. It flows provided an alternating voltage source is applied to the circuit. Alternating current flows in cycles. The nu ...
... in one direction only. It flows provided a direct voltage source is applied to the circuit. An alternating current is a current that changes its direction of flow through a circuit. It flows provided an alternating voltage source is applied to the circuit. Alternating current flows in cycles. The nu ...
COURSE TITLE BASICS OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING I Code
... magnetism, applicable to other study courses and practical work. Physical properties of all materials used in electrical engineering devices and systems, as well as their components, are thoroughly studied. Particular attention will be Learning outcomes paid to the application of aquired knowledge a ...
... magnetism, applicable to other study courses and practical work. Physical properties of all materials used in electrical engineering devices and systems, as well as their components, are thoroughly studied. Particular attention will be Learning outcomes paid to the application of aquired knowledge a ...
Topics to study for electrostatics and electricity test
... Understand the difference between parallel and series circuits and advantages of the parallel circuit Know the difference between a circuit breaker and a fuse ...
... Understand the difference between parallel and series circuits and advantages of the parallel circuit Know the difference between a circuit breaker and a fuse ...
E f
... generate 60 Hz, they are usually rotating at 3600 rpm and turn 2-pole generators. •Water turbines are most efficient when rotating at low speeds (200-300 rpm); therefore, they usually turn generators with many poles. ...
... generate 60 Hz, they are usually rotating at 3600 rpm and turn 2-pole generators. •Water turbines are most efficient when rotating at low speeds (200-300 rpm); therefore, they usually turn generators with many poles. ...
the big picture
... In a phono cartridge, when the stylus passes through the grooves of a record it will vibrate. This causes the magnet inside the coil to also vibrate. Since there is now a rapidly changing magnetic field inside the coil, electromagnetic induction occurs. ...
... In a phono cartridge, when the stylus passes through the grooves of a record it will vibrate. This causes the magnet inside the coil to also vibrate. Since there is now a rapidly changing magnetic field inside the coil, electromagnetic induction occurs. ...
Basic electrical engineering
... Magnetic circuits – mmf, field strength, flux density, reluctance, permeability – comparison of electric and magnetic circuits – force on current carrying conductor in magnetic filed. Module II (12 hours) Electromagnetic Induction – Faraday’s laws – lenz’s law – statically and dynamically induced em ...
... Magnetic circuits – mmf, field strength, flux density, reluctance, permeability – comparison of electric and magnetic circuits – force on current carrying conductor in magnetic filed. Module II (12 hours) Electromagnetic Induction – Faraday’s laws – lenz’s law – statically and dynamically induced em ...
Magnetism
... the gravitational forces acting between the atoms. At the atomic level, electric forces between oppositely charged electrons and protons hold atoms and molecules together and thus are involved in all chemical reactions. On a larger scale, these forces hold solid and liquid materials together and act ...
... the gravitational forces acting between the atoms. At the atomic level, electric forces between oppositely charged electrons and protons hold atoms and molecules together and thus are involved in all chemical reactions. On a larger scale, these forces hold solid and liquid materials together and act ...
Maxwell`s Equations (4)
... whether induction can occur in the opposite sense; that is, can a changing electric flux induce a magnetic field? The answer is that it can; furthermore, the equation governing the induction of a magnetic field is almost symmetric with the above equation. We often call it Maxwell's law of induction ...
... whether induction can occur in the opposite sense; that is, can a changing electric flux induce a magnetic field? The answer is that it can; furthermore, the equation governing the induction of a magnetic field is almost symmetric with the above equation. We often call it Maxwell's law of induction ...