synchronous
... EXAMPLE 6.1In a factory a 3cp, 4 kV, 400 kVA synchronous machine is installed along with other induction motors. The following are the loads on the machines:Induction motors: 500 kVA at 0.8 PF lagging.Synchronous motor: 300 kVA at 1.0 PF.(a) Compute the overall power factor of the factory loads.(b) ...
... EXAMPLE 6.1In a factory a 3cp, 4 kV, 400 kVA synchronous machine is installed along with other induction motors. The following are the loads on the machines:Induction motors: 500 kVA at 0.8 PF lagging.Synchronous motor: 300 kVA at 1.0 PF.(a) Compute the overall power factor of the factory loads.(b) ...
Electromagnetic Theory Chapter One: Vector analysis
... Electric field due to a system of discrete charge Electric field due to a continuous distribution of charge Electrostatic force Electric flux and Gauss's law Relation between flux density and electric field intensity The Electric potential Conductors and insulators ...
... Electric field due to a system of discrete charge Electric field due to a continuous distribution of charge Electrostatic force Electric flux and Gauss's law Relation between flux density and electric field intensity The Electric potential Conductors and insulators ...
Chapter 17 & 18
... SIDE BY SIDE, so if part of the circuit stops working the charges still flow. Explain how fused and circuit breakers protect your home against short circuits and circuit overloads. A fuse has a thin strip of metal that expands and contracts in the presence of current. If the current is too high, the ...
... SIDE BY SIDE, so if part of the circuit stops working the charges still flow. Explain how fused and circuit breakers protect your home against short circuits and circuit overloads. A fuse has a thin strip of metal that expands and contracts in the presence of current. If the current is too high, the ...
magnetic - Timber Ridge Elementary
... In our planet we have the North and South Poles. Earth acts like a giant magnet and is surrounded by a magnetic field. Earth’s magnetic field is what causes the needle of a compass to point in different directions and causes the poles of a magnet to point either North or South. ...
... In our planet we have the North and South Poles. Earth acts like a giant magnet and is surrounded by a magnetic field. Earth’s magnetic field is what causes the needle of a compass to point in different directions and causes the poles of a magnet to point either North or South. ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2015 Semester
... • An electric charge changes the properties of the space around it. – It is the source of an “electric field”. – It could be defined as the “force per unit charge”: ...
... • An electric charge changes the properties of the space around it. – It is the source of an “electric field”. – It could be defined as the “force per unit charge”: ...
electrical drives
... braking can be employed. Control gear required speed control, starting and braking is usually simple and easy to operate. 2. They are available in a wide range of torque, speed and power. 3. Electric motors have high efficiency, low no load losses and considerable short time overloading capability. ...
... braking can be employed. Control gear required speed control, starting and braking is usually simple and easy to operate. 2. They are available in a wide range of torque, speed and power. 3. Electric motors have high efficiency, low no load losses and considerable short time overloading capability. ...
Electromagnetic Induction
... voltage. (Technically AC voltage but we will get to that later.) • They have primary and secondary coils linked by an iron core. • Both the coils and the core are insulated to guard against the effects of magnetic fields (we will get to eddy currents later). ...
... voltage. (Technically AC voltage but we will get to that later.) • They have primary and secondary coils linked by an iron core. • Both the coils and the core are insulated to guard against the effects of magnetic fields (we will get to eddy currents later). ...
NOT
... What is Magnetism? _________________________ anything that pulls iron, steel, and certain other metals to it. _________________________ the force around the magnet. _________________________ the space around the magnet where magnetism acts. _________________________ a place on the magnet where the m ...
... What is Magnetism? _________________________ anything that pulls iron, steel, and certain other metals to it. _________________________ the force around the magnet. _________________________ the space around the magnet where magnetism acts. _________________________ a place on the magnet where the m ...
Lecture_IM
... At starting, rotor frequency is high and very little current flows through the lower bars; the effective resistance of the rotor is then the high resistance upper bars. At normal low slip operation, leakage reactances are negligible, and the rotor current flows largely through the low resistance low ...
... At starting, rotor frequency is high and very little current flows through the lower bars; the effective resistance of the rotor is then the high resistance upper bars. At normal low slip operation, leakage reactances are negligible, and the rotor current flows largely through the low resistance low ...
PPT
... Morley looked and looked, and decided it wasn’t there. How do waves travel??? Electricity and magnetism are “relative”: Whether charges move or not depends on which frame we use… This was how Einstein began thinking about his “theory of special relativity”… We’ll leave that theory for later…maybe. ...
... Morley looked and looked, and decided it wasn’t there. How do waves travel??? Electricity and magnetism are “relative”: Whether charges move or not depends on which frame we use… This was how Einstein began thinking about his “theory of special relativity”… We’ll leave that theory for later…maybe. ...
Lecture 5
... the conductor. When currents flow through two parallel conductors in the same direction, the magnetic fields cause the conductors to attract each other; when the flows are in opposite directions, they repel each other. The magnetic field caused by the current in a single loop or wire is such that t ...
... the conductor. When currents flow through two parallel conductors in the same direction, the magnetic fields cause the conductors to attract each other; when the flows are in opposite directions, they repel each other. The magnetic field caused by the current in a single loop or wire is such that t ...
8. Induction motor
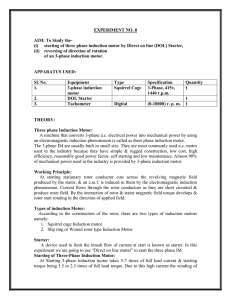
... Three phase Induction Motor: A machine that converts 3-phase a.c. electrical power into mechanical power by using an electromagnetic induction phenomenon is called as three phase induction motor. The 3-phase IM are usually built in small size. They are most commonly used a.c. motor used in the indus ...
... Three phase Induction Motor: A machine that converts 3-phase a.c. electrical power into mechanical power by using an electromagnetic induction phenomenon is called as three phase induction motor. The 3-phase IM are usually built in small size. They are most commonly used a.c. motor used in the indus ...