A Magnet is an object with a magnetic force or field that attracts or
... A Magnet is an object with a magnetic force or field that attracts or repels objects. A magnet’s property of attracting material is called magnetism. Magnetism is a force that acts on moving electric charges and magnetic material. Iron and steel are attracted to a magnet. Not all metals are attracte ...
... A Magnet is an object with a magnetic force or field that attracts or repels objects. A magnet’s property of attracting material is called magnetism. Magnetism is a force that acts on moving electric charges and magnetic material. Iron and steel are attracted to a magnet. Not all metals are attracte ...
Guided Reading Chapter 10: Electric Charges
... 4. A device that uses an electromagnet to measure small amounts of current is called a(n) _______________. 5. What is used to turn the pointer of a galvanometer? 6. In a galvanometer, what does the amount of rotation of the loops of wire and the pointer depend on? ...
... 4. A device that uses an electromagnet to measure small amounts of current is called a(n) _______________. 5. What is used to turn the pointer of a galvanometer? 6. In a galvanometer, what does the amount of rotation of the loops of wire and the pointer depend on? ...
Magnetic field of magnets Interaction between magnetic poles: like
... (ii) Electric motors An electric motor contains a rectangular coil which is free to rotate between the pales of a magnet. Current flows into the coil via carbon brushes and a commutator (or split ring). ...
... (ii) Electric motors An electric motor contains a rectangular coil which is free to rotate between the pales of a magnet. Current flows into the coil via carbon brushes and a commutator (or split ring). ...
PHYS 222 Exam 1 Study Guide
... differences across each, while the voltage difference across each resistor which is in parallel with each other is the same. - Setting up equivalent resistors - Power output of resistors and emfs - Generating equations for a circuit using Kirchoff’s Loop rule and the junction rule Exam 2: - Magnetic ...
... differences across each, while the voltage difference across each resistor which is in parallel with each other is the same. - Setting up equivalent resistors - Power output of resistors and emfs - Generating equations for a circuit using Kirchoff’s Loop rule and the junction rule Exam 2: - Magnetic ...
Resistance is the opposition that a substance offers to the flow of
... Basic Theory of Transformer Say you have one winding which is supplied by an alternating electrical source. The alternating current through the winding produces a continually changing flux or alternating flux that surrounds the winding. If any other winding is brought nearer to the previous one, obv ...
... Basic Theory of Transformer Say you have one winding which is supplied by an alternating electrical source. The alternating current through the winding produces a continually changing flux or alternating flux that surrounds the winding. If any other winding is brought nearer to the previous one, obv ...
2011 Efficient Multiphysics Analysis of Drum Rollers Mircea Popescu INDUCTICA TECHNICAL CONFERENCE
... It is obvious that electromagnetic, thermal and mechanic aspects, all of them coupled by the electric motor model, have to be considered. The necessary complexity of the sub-models differs. While the mechanic load could be described by relatively simple equations, the electro-magnetic motor model i ...
... It is obvious that electromagnetic, thermal and mechanic aspects, all of them coupled by the electric motor model, have to be considered. The necessary complexity of the sub-models differs. While the mechanic load could be described by relatively simple equations, the electro-magnetic motor model i ...
Lecture 16
... generator The major difference is the contacts to the rotating loop are made by a split ring, ...
... generator The major difference is the contacts to the rotating loop are made by a split ring, ...
EM worksheet
... Electromagnets can be made stronger by adding coils or turns of wire or by adding more electricity. Permanent magnets can actually lose some of their magnetism overtime as a result of being dropped repeatedly. Similar to regular magnets, electromagnets also attract to magnetic metals such as iron, n ...
... Electromagnets can be made stronger by adding coils or turns of wire or by adding more electricity. Permanent magnets can actually lose some of their magnetism overtime as a result of being dropped repeatedly. Similar to regular magnets, electromagnets also attract to magnetic metals such as iron, n ...
Magnetism and Electromagnetism
... Electricity can make a magnetic field Magnets can make electricity A current can generate a magnetic field, which makes the iron shavings move ...
... Electricity can make a magnetic field Magnets can make electricity A current can generate a magnetic field, which makes the iron shavings move ...
here
... Large high-speed electrical generators use a rotating magnetic field produced by a cylindrical rotor in the form of a electromagnet having either 2 or 4 magnetic poles. The rotor body is a solid steel forging containing radial slots for the coils which make up the electromagnets (rotor windings). T ...
... Large high-speed electrical generators use a rotating magnetic field produced by a cylindrical rotor in the form of a electromagnet having either 2 or 4 magnetic poles. The rotor body is a solid steel forging containing radial slots for the coils which make up the electromagnets (rotor windings). T ...
Key Words:
... insulation system deterioration mechanisms in utility generators. Since 1951, the on-line measurement of PD has been used to assess the need for motor and generator maintenance in stator windings [1]. More particularly, online PD measurement has been able to determine whether the electrical insulati ...
... insulation system deterioration mechanisms in utility generators. Since 1951, the on-line measurement of PD has been used to assess the need for motor and generator maintenance in stator windings [1]. More particularly, online PD measurement has been able to determine whether the electrical insulati ...
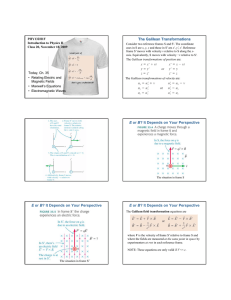
Maxwell`s Equations 1.The concept of displacement current was a
... floor, the current induced in the wire will flow Ans:B A) clockwise B) counterclockwise 4. If the South pole of a bar magnet is moved up away from a wire loop on the floor, the current induced in the wire will flow Ans:B A) clockwise B) counterclockwise 5. Displacement current (ID) is proportional t ...
... floor, the current induced in the wire will flow Ans:B A) clockwise B) counterclockwise 4. If the South pole of a bar magnet is moved up away from a wire loop on the floor, the current induced in the wire will flow Ans:B A) clockwise B) counterclockwise 5. Displacement current (ID) is proportional t ...
Chapter 12 Test Study Guide: Simple Machines WORK A force
... *In order for work to be done, a force must be exerted over a certain distance. (The direction of the force and motion must be the same for maximum work to be done.) Ex: Opening a door to enter a room is an example of work being done on an object. Work is measured in units called joules. Much of the ...
... *In order for work to be done, a force must be exerted over a certain distance. (The direction of the force and motion must be the same for maximum work to be done.) Ex: Opening a door to enter a room is an example of work being done on an object. Work is measured in units called joules. Much of the ...
... What is Stator Endwinding Vibration Monitoring? • Abnormal operating events such as short Generator stator windings outside of the circuits resulting in stress and deflection stator core are referred to as the endwinding of components beyond their mechanical (EW). The EW is at high-voltage and requ ...
Oct - Directorate General of Shipping
... (a) reduce the voltage applied to the motor during the starting period (b) increase the volt age for "across-the-line starting" (c) provide a backup means of voltage regulation for emergency starting (d) allow the voltage to be either stepped up or down, depending on the application, to ensure full ...
... (a) reduce the voltage applied to the motor during the starting period (b) increase the volt age for "across-the-line starting" (c) provide a backup means of voltage regulation for emergency starting (d) allow the voltage to be either stepped up or down, depending on the application, to ensure full ...