Short- and long-range functions of Goosecoid in
... Secreted ventralizing factors of the BMP, Wnt and Nodal families function in gradients in the early embryo and organizer-derived molecules attenuate the activity of these factors (Niehrs, 2004). Ventrally expressed Wnt8 restricts the size of the zebrafish organizer in the late blastula/early gastrul ...
... Secreted ventralizing factors of the BMP, Wnt and Nodal families function in gradients in the early embryo and organizer-derived molecules attenuate the activity of these factors (Niehrs, 2004). Ventrally expressed Wnt8 restricts the size of the zebrafish organizer in the late blastula/early gastrul ...
Malaysian Guidelines for Stem Cell Research and Therapy
... cells is the ease of growth in a culture. It is relatively easy for researchers to grow a large number of embryonic stem cells in culture compared to adult stem cells which are relatively rare and have no methods for greatly expanding the number in cultures. Finally, if a patient’s own cells are use ...
... cells is the ease of growth in a culture. It is relatively easy for researchers to grow a large number of embryonic stem cells in culture compared to adult stem cells which are relatively rare and have no methods for greatly expanding the number in cultures. Finally, if a patient’s own cells are use ...
Using food and controlling growth - Delivery guide
... that ‘ventilation’ is breathing and oxygen is not all that is breathed in/not only carbon dioxide is breathed out. Learners often believe that plants photosynthesise in the day and only respire at night whilst others believe that leaves photosynthesise and roots respire. It could be valuable to star ...
... that ‘ventilation’ is breathing and oxygen is not all that is breathed in/not only carbon dioxide is breathed out. Learners often believe that plants photosynthesise in the day and only respire at night whilst others believe that leaves photosynthesise and roots respire. It could be valuable to star ...
Leukaemia Section Chronic myelogenous leukaemia (CML) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Interestingly, the outcome on IM therapy has been shown to be correlated with the Sokal score at diagnosis. The most recent update of this trial has shown for the first time, a reduction of secondary events (accelerated phase, blast crisis) over time, with no patients progressing towards blast crisi ...
... Interestingly, the outcome on IM therapy has been shown to be correlated with the Sokal score at diagnosis. The most recent update of this trial has shown for the first time, a reduction of secondary events (accelerated phase, blast crisis) over time, with no patients progressing towards blast crisi ...
Question paper - Unit B731/02 - Modules B1, B2, B3 - Higher
... and the numbers of lemmings. Describe this pattern and explain how it affects the populations of snowy owls and lemmings. ...
... and the numbers of lemmings. Describe this pattern and explain how it affects the populations of snowy owls and lemmings. ...
Scaling up Delivery Guide
... understand the electrical and ‘mechanical’ activity of the heart. With the increasing size of the population, the need for food production is vital. Food production depends greatly on the environmental conditions the water levels and nutrient ability. The transport systems in plants are important fo ...
... understand the electrical and ‘mechanical’ activity of the heart. With the increasing size of the population, the need for food production is vital. Food production depends greatly on the environmental conditions the water levels and nutrient ability. The transport systems in plants are important fo ...
10-4
... Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent cells found in the early embryo. In 1998, researchers at the University of Wisconsin found a way to grow these embryonic stem cells in culture. Their experiments confirmed that such cells did indeed have the capacity to produce just about any cell type in the huma ...
... Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent cells found in the early embryo. In 1998, researchers at the University of Wisconsin found a way to grow these embryonic stem cells in culture. Their experiments confirmed that such cells did indeed have the capacity to produce just about any cell type in the huma ...
[PDF]
... In Drosophila ovary, germline stem cells (GSC) provide an attractive system for investigating the regulatory mechanisms that determine stem cell fate (Lin, 2002; Spradling et al., 2001). Studies from several laboratories have identified the genes that are essential for GSC fate determination. Both t ...
... In Drosophila ovary, germline stem cells (GSC) provide an attractive system for investigating the regulatory mechanisms that determine stem cell fate (Lin, 2002; Spradling et al., 2001). Studies from several laboratories have identified the genes that are essential for GSC fate determination. Both t ...
Cell Differentiation
... Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent cells found in the early embryo. In 1998, researchers at the University of Wisconsin found a way to grow these embryonic stem cells in culture. Their experiments confirmed that such cells did indeed have the capacity to produce just about any cell type in the huma ...
... Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent cells found in the early embryo. In 1998, researchers at the University of Wisconsin found a way to grow these embryonic stem cells in culture. Their experiments confirmed that such cells did indeed have the capacity to produce just about any cell type in the huma ...
C - Aptagen
... Pseudoknot (ligand for HIV-1 reverse transcriptase) G-quartet (ligand for thrombin) Hairpin (ligand for bacteriophage for T4 polymerase) Stem loop/bulge (ligand for ATP) ...
... Pseudoknot (ligand for HIV-1 reverse transcriptase) G-quartet (ligand for thrombin) Hairpin (ligand for bacteriophage for T4 polymerase) Stem loop/bulge (ligand for ATP) ...
Cloning and Stem Cells
... Treatment for disease Scientists believe that stem cells may, at some point in the future, become the basis for treatment of diseases caused by irreversibly damaged and injured tissue, such as occurs in diabetes, heart disease and Parkinson’s disease. They are particularly optimistic in cases where ...
... Treatment for disease Scientists believe that stem cells may, at some point in the future, become the basis for treatment of diseases caused by irreversibly damaged and injured tissue, such as occurs in diabetes, heart disease and Parkinson’s disease. They are particularly optimistic in cases where ...
Germline stem cell niches
... Therefore, the knowledge gained from studies on GSCs is important for applying human GSCs to treat infertility and degenerative diseases. In addition, because stem cells from different systems share many similarities such as self-renewal and the supporting niche, the knowledge of molecular mechanism ...
... Therefore, the knowledge gained from studies on GSCs is important for applying human GSCs to treat infertility and degenerative diseases. In addition, because stem cells from different systems share many similarities such as self-renewal and the supporting niche, the knowledge of molecular mechanism ...
human embryonic stem cell therapy
... used has been shown to be inadequate. In my view, the same needs to be said of some of the philosophical categories used to evaluate the moral standing of the embryo. The traditional Aristotelian categories appropriated by Aquinas and other Scholastics come from a static worldview that understood, f ...
... used has been shown to be inadequate. In my view, the same needs to be said of some of the philosophical categories used to evaluate the moral standing of the embryo. The traditional Aristotelian categories appropriated by Aquinas and other Scholastics come from a static worldview that understood, f ...
8.2 Cells and Energy
... plants. An organism that is not fully developed is called an embryo. In animal embryos, stem cells can develop into different types of cells. Your body has over 200,000 different types of cells. It has blood cells, muscle cells, skin cells, and stomach cells just to name a few. Each type of cell has ...
... plants. An organism that is not fully developed is called an embryo. In animal embryos, stem cells can develop into different types of cells. Your body has over 200,000 different types of cells. It has blood cells, muscle cells, skin cells, and stomach cells just to name a few. Each type of cell has ...
14 Stem Cell Differentiation
... A stem cell produces daughter cells that might remain as stem cells or begin a pathway of differentiation into one of a variety of specialized cell types. Stem cells are classified into three groups, depending on where they are on the pathway toward differentiation. Totipotent stem cells can produce ...
... A stem cell produces daughter cells that might remain as stem cells or begin a pathway of differentiation into one of a variety of specialized cell types. Stem cells are classified into three groups, depending on where they are on the pathway toward differentiation. Totipotent stem cells can produce ...
Yaron Fuchs, Ph.D. - Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine
... apoptosis through the TNF-pathway. eLife 2013, 2, e01004. (Impact factor 8.3) - Fuchs Y., Brunwasser M., Haif S., Hadad J., Shneyer B., Goldshmidt-Tran O., Korsensky L., Abed M., Zisman-Rosen S., Koren L., Carmi Y., Apte R., Yang B.R., Orian A., Bejar J., and Ron D., (2012): Sef is a novel inhibitor ...
... apoptosis through the TNF-pathway. eLife 2013, 2, e01004. (Impact factor 8.3) - Fuchs Y., Brunwasser M., Haif S., Hadad J., Shneyer B., Goldshmidt-Tran O., Korsensky L., Abed M., Zisman-Rosen S., Koren L., Carmi Y., Apte R., Yang B.R., Orian A., Bejar J., and Ron D., (2012): Sef is a novel inhibitor ...
Regulation of germ line stem cell homeostasis
... (SSCs) develop to ultimately form spermatozoa. In the seminiferous epithelium, SSCs self-renew to maintain the pool of stem cells throughout life, or they differentiate to generate a large number of germ cells. A balance between SSC self-renewal and differentiation is therefore essential to maintain ...
... (SSCs) develop to ultimately form spermatozoa. In the seminiferous epithelium, SSCs self-renew to maintain the pool of stem cells throughout life, or they differentiate to generate a large number of germ cells. A balance between SSC self-renewal and differentiation is therefore essential to maintain ...
Winter 2016 USC Stem Cell Newsletter
... “I love what I do, and I want to keep being a scientist as long as I can. It’s a privilege to get to do this.” ...
... “I love what I do, and I want to keep being a scientist as long as I can. It’s a privilege to get to do this.” ...
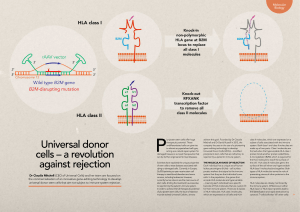
Universal donor cells – a revolution against rejection
... cells that are universally compatible. First, a single-chain, non-polymorphic HLA class I transgene composed of the HLA-E molecule fused to the beta 2-microglobulin HLA class I common subunit is knockedin to the beta 2-microglobulin locus. This transgene acts as a decoy preventing lysis of the modif ...
... cells that are universally compatible. First, a single-chain, non-polymorphic HLA class I transgene composed of the HLA-E molecule fused to the beta 2-microglobulin HLA class I common subunit is knockedin to the beta 2-microglobulin locus. This transgene acts as a decoy preventing lysis of the modif ...
Five years of successful stem cell research at HI-STEM
... In addition, the HI-STEM team discovered metastasis-inducing stem cells in the blood of breast cancer patients. Since the number of such cells correlates with a patient’s chance of survival, the ability to detect them may enhance diagnostic methods. The scientists are now trying to inhibit the cells ...
... In addition, the HI-STEM team discovered metastasis-inducing stem cells in the blood of breast cancer patients. Since the number of such cells correlates with a patient’s chance of survival, the ability to detect them may enhance diagnostic methods. The scientists are now trying to inhibit the cells ...
LAB 16 - Stuyvesant High School
... through the process of GASEOUS DIFFUSION. In addition, the lower epidermis of leaves contain openings called STOMATES. The size of the stoma (stoma is singular, stomates is plural) opening is regulated by the chloroplast containing GUARD CELLS which surround it. Gas exchange through the stomates is ...
... through the process of GASEOUS DIFFUSION. In addition, the lower epidermis of leaves contain openings called STOMATES. The size of the stoma (stoma is singular, stomates is plural) opening is regulated by the chloroplast containing GUARD CELLS which surround it. Gas exchange through the stomates is ...
PDF
... January 2011. As many of you will already know, Gordon is a world renowned specialist in the field of human and mouse embryonic stem cell differentiation. Neurodevelopment is another key and expanding area of developmental biology for Development, and to strengthen our handling of both neurodevelopm ...
... January 2011. As many of you will already know, Gordon is a world renowned specialist in the field of human and mouse embryonic stem cell differentiation. Neurodevelopment is another key and expanding area of developmental biology for Development, and to strengthen our handling of both neurodevelopm ...
UC Davis Stem Cell Program
... epilepsy, traumatic brain injury, cerebral palsy and spinal cord injury. TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY – ...
... epilepsy, traumatic brain injury, cerebral palsy and spinal cord injury. TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY – ...
Independent Essay * Stem Cell Niches
... showed that β-catenin was strongly expressed at high levels in the ventricular zone at all ages during cortical neurogenesis. The lateral ventricles appeared to have grown in size and lined up with neural progenitor cells, indicating a substantial increase in the precursor population. In order to fu ...
... showed that β-catenin was strongly expressed at high levels in the ventricular zone at all ages during cortical neurogenesis. The lateral ventricles appeared to have grown in size and lined up with neural progenitor cells, indicating a substantial increase in the precursor population. In order to fu ...





![[PDF]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008788908_1-bd555ffa380d32685e53d16c74ff36d7-300x300.png)