Glencoe World History: Modern Times
... D. The Germans did not think that the United States would enter the war before the British were starved. However, in April 1917, the United States responded to unrestricted submarine warfare by declaring war on Germany. Though large numbers of American troops did not arrive until 1918, the Allies we ...
... D. The Germans did not think that the United States would enter the war before the British were starved. However, in April 1917, the United States responded to unrestricted submarine warfare by declaring war on Germany. Though large numbers of American troops did not arrive until 1918, the Allies we ...
Revolution, Civil War, and the `Long` First World War in Russia
... Most observers sketch this out as the defeat at Tannenberg, the more damaging ‘Great Retreat’ in Poland in 1915 following the German Gorlice-Tarnów breakthtrough, and finally the limited success of the wide-front counter-offensive in western Ukraine carried out under General A. A. Brusilov in the su ...
... Most observers sketch this out as the defeat at Tannenberg, the more damaging ‘Great Retreat’ in Poland in 1915 following the German Gorlice-Tarnów breakthtrough, and finally the limited success of the wide-front counter-offensive in western Ukraine carried out under General A. A. Brusilov in the su ...
Slide 1 - Lepley
... • August 1,1914 Germany declares war on Russia • August 2, 1914 Germany demands Belgium declare access to German troops ...
... • August 1,1914 Germany declares war on Russia • August 2, 1914 Germany demands Belgium declare access to German troops ...
Reading Essentials and Study Guide World War I and the Russian
... Before 1914 many political leaders thought war was not a real possibility because it involved so many political and economic risks. Others thought diplomats could easily prevent war. Both ideas were proven wrong in August 1914. However, the new illusions, or false beliefs, that replaced them were ju ...
... Before 1914 many political leaders thought war was not a real possibility because it involved so many political and economic risks. Others thought diplomats could easily prevent war. Both ideas were proven wrong in August 1914. However, the new illusions, or false beliefs, that replaced them were ju ...
World War I and the Russian Revolution
... – At the First Battle of the Marne, German forces advanced to within 30 miles of Paris, when the French counterattacked, and forced the Germans to retreat, and try to outflank the English and French forces, which then tried to flank the Germans, and this went on until they reached the North Sea. Ger ...
... – At the First Battle of the Marne, German forces advanced to within 30 miles of Paris, when the French counterattacked, and forced the Germans to retreat, and try to outflank the English and French forces, which then tried to flank the Germans, and this went on until they reached the North Sea. Ger ...
CHAPTER 26 War and Revolution, 1914–1920
... Trench lines established along the Marne to Ypres in Belgium remained little changed until the end of the war. With the failure of the Schlieffen Plan, Germany was committed to a two-front war. ...
... Trench lines established along the Marne to Ypres in Belgium remained little changed until the end of the war. With the failure of the Schlieffen Plan, Germany was committed to a two-front war. ...
Chapter 23 War and Revolution, 1914-1919
... • On the Western Front, Germany swept through Belgium into northern France and was stopped a short distance from Paris at the First Battle of the Marne. • The Western Front turned into a stalemate, with neither side able to push the other out of the system of trench warfare they had begun. • The tre ...
... • On the Western Front, Germany swept through Belgium into northern France and was stopped a short distance from Paris at the First Battle of the Marne. • The Western Front turned into a stalemate, with neither side able to push the other out of the system of trench warfare they had begun. • The tre ...
Europe Plunges into War - History With Mr. Green
... Alfred Graf von Schlieffen (SHLEE•fuhn). The plan called for attacking and defeating France in the west and then rushing east to fight Russia. The Germans felt they could carry out such a plan because Russia lagged behind the rest of Europe in its railroad system and thus would take longer to supply ...
... Alfred Graf von Schlieffen (SHLEE•fuhn). The plan called for attacking and defeating France in the west and then rushing east to fight Russia. The Germans felt they could carry out such a plan because Russia lagged behind the rest of Europe in its railroad system and thus would take longer to supply ...
WH2 13.2 File - Columbus Academy Intranet
... gas, armored tanks, larger artillery—had not delivered the fast-moving war they had expected. All this new technology did was kill greater numbers of people ...
... gas, armored tanks, larger artillery—had not delivered the fast-moving war they had expected. All this new technology did was kill greater numbers of people ...
powerpoint slides
... 2. Free navigation of all seas. 3. An end to all economic barriers between countries. 4. Countries to reduce weapon numbers. 5. All decisions regarding the colonies should be impartial 6. The German Army is to be removed from Russia. Russia should be left to develop her own political set-up. 7. Belg ...
... 2. Free navigation of all seas. 3. An end to all economic barriers between countries. 4. Countries to reduce weapon numbers. 5. All decisions regarding the colonies should be impartial 6. The German Army is to be removed from Russia. Russia should be left to develop her own political set-up. 7. Belg ...
Alliances and Fronts of the War
... Treaty signed with revolutionary government (Lenin – 1917) lost ¼ of the country. The Balkan Front The Allies abandoned attempts to land in the Balkans after ...
... Treaty signed with revolutionary government (Lenin – 1917) lost ¼ of the country. The Balkan Front The Allies abandoned attempts to land in the Balkans after ...
The Russian Army
... • In 1914 Russia possessed only 68,200 km of railway and that was largely concentrated in Poland and western Russia. • This gave rise to enormous difficulties in transporting troops and supplies to the front, especially after some 4,800 km of track were lost after the German advance into Poland. • ...
... • In 1914 Russia possessed only 68,200 km of railway and that was largely concentrated in Poland and western Russia. • This gave rise to enormous difficulties in transporting troops and supplies to the front, especially after some 4,800 km of track were lost after the German advance into Poland. • ...
World War I - aum.edu.mm
... • On 28 July, the Austro-Hungarians declared war on Serbia and subsequently invaded • Russia mobilized in support of Serbia, Germany invaded neutral Belgium and Luxembourg before moving towards France, leading the United Kingdom to declare war on Germany • After the German march on Paris was halted, ...
... • On 28 July, the Austro-Hungarians declared war on Serbia and subsequently invaded • Russia mobilized in support of Serbia, Germany invaded neutral Belgium and Luxembourg before moving towards France, leading the United Kingdom to declare war on Germany • After the German march on Paris was halted, ...
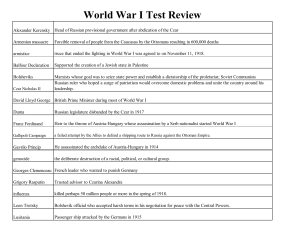
World War I Test Review
... Marxists whose goal was to seize state power and establish a dictatorship of the proletariat; Soviet Communists Russian ruler who hoped a surge of patriotism would overcome domestic problems and unite the country around his ...
... Marxists whose goal was to seize state power and establish a dictatorship of the proletariat; Soviet Communists Russian ruler who hoped a surge of patriotism would overcome domestic problems and unite the country around his ...
World War/Russian Revolution/Stalin Test /55
... Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy. This alliance system kept the peace until June 28, 1914, when Archduke Ferdinand of _________________________was assassinated in Sarajevo by a_______________ nationalist. Austria-Hungary then declared war on _____________. This was the match that lit the fuse of ...
... Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy. This alliance system kept the peace until June 28, 1914, when Archduke Ferdinand of _________________________was assassinated in Sarajevo by a_______________ nationalist. Austria-Hungary then declared war on _____________. This was the match that lit the fuse of ...
World War One
... The heir to the Hapsburg throne of Austria- Hungary, assassinated by Gavrilo Princip on June 28th 1914. His assassination started World War One. ...
... The heir to the Hapsburg throne of Austria- Hungary, assassinated by Gavrilo Princip on June 28th 1914. His assassination started World War One. ...
AP IMAGES OF WORLD WAR I
... in World War I? Which leader did the Bolsheviks follow? How did Russian troops respond to the uprising in the ‘Revolution’ of 1905? How did Russian troops respond to the uprising in the ‘Revolution’ of 1917 ...
... in World War I? Which leader did the Bolsheviks follow? How did Russian troops respond to the uprising in the ‘Revolution’ of 1905? How did Russian troops respond to the uprising in the ‘Revolution’ of 1917 ...
workbook - anglické gymnázium brno
... World War I (WWI), which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939 (World War II), and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918. It involved all the world ...
... World War I (WWI), which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939 (World War II), and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918. It involved all the world ...
Eastern Front (World War I)
.jpg?width=300)
During World War I, the Eastern Front (Russian: Восточный фронт, sometimes called the ""Second Fatherland War"" or ""Second Patriotic War"" (Russian: Вторая Отечественная война) in Russian sources) was a theatre of operations that encompassed at its greatest extent the entire frontier between the Russian Empire and Romania on one side and the Austro-Hungarian Empire, Bulgaria, the Ottoman Empire and Germany on the other. It stretched from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Black Sea in the south, included most of Eastern Europe and stretched deep into Central Europe as well. The term contrasts with ""Western Front"", which was being fought in Belgium and France.In the opening months of the war, the Imperial Russian Army attempted an invasion of eastern Prussia in the northwestern theater, only to be beaten back by the Germans after some initial success. At the same time, in the south, they successfully invaded Galicia, defeating the Austro-Hungarian forces there. In Russian Poland, the Germans failed to take Warsaw. But by 1915, the German and Austro-Hungarian armies were on the advance, dealing the Russians heavy casualties in Galicia and in Poland, forcing it to retreat. Grand Duke Nicholas was sacked from his position as the commander-in-chief and replaced by the Tsar himself. Several offensives against the Germans in 1916 failed, including Lake Naroch Offensive and the Baranovichi Offensive. However, General Aleksei Brusilov oversaw a highly successful operation against Austria-Hungary that became known as the Brusilov Offensive, which saw the Russian army make large gains.The Kingdom of Romania entered the war in August 1916. The Entente promised the region of Transylvania (which was part of Austria-Hungary) in return for Romanian support. The Romanian Army invaded Transylvania and had initial successes, but was forced to stop and was pushed back by the Austro-Hungarians when Bulgaria attacked them in the south. Meanwhile, a revolution occurred in Russia in February 1917 (one of the several causes being the hardships of the war). Tsar Nicholas II was forced to abdicate and a Russian Provisional Government was founded, with Georgy Lvov as its first leader, who was eventually replaced by Alexander Kerensky.The newly formed Russian Republic continued to fight the war along side Romania and the rest of the Entente until it was overthrown by the Bolsheviks in October 1917. Kerensky oversaw the July Offensive, which was largely a failure and caused a collapse in the Russian army. The new government established by the Bolsheviks signed the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk with the Central Powers, taking it out of the war and making large territorial concessions. Romania was forced to surrender and signed a similar treaty, though both of the treaties were nullified with the surrender of the Central Powers in November 1918.