Mollusks, Arthropods, and Echinoderms
... 1,000 students aged 10– 19. About how many of these students would you expect to get Lyme disease per year? One or two students ...
... 1,000 students aged 10– 19. About how many of these students would you expect to get Lyme disease per year? One or two students ...
Features of Arthropods
... If a prize were given for sheer numbers, it would go to the arthropods. The total number of arthropod species exceeds that of all other kinds of animals combined. About 900,000 species of arthropods have been recorded, and probably at least as many remain to be classified. There are more species of ...
... If a prize were given for sheer numbers, it would go to the arthropods. The total number of arthropod species exceeds that of all other kinds of animals combined. About 900,000 species of arthropods have been recorded, and probably at least as many remain to be classified. There are more species of ...
Arthropods - walker2013
... as segmented worms In most groups, arthropods are consisted of three segments ...
... as segmented worms In most groups, arthropods are consisted of three segments ...
Collecting and Preserving Insects and Arachnids
... Reference collections are important resources in applied research. Such collections may be generalised or specialised, and can grow very large to contain many thousands of specimens. Museums generally house specimens that represent many or all species that occur in particular geographic regions, as ...
... Reference collections are important resources in applied research. Such collections may be generalised or specialised, and can grow very large to contain many thousands of specimens. Museums generally house specimens that represent many or all species that occur in particular geographic regions, as ...
COMMON TRAIL INSECTS OF BIG BEND NATIONAL PARK by
... thin limestone and shale beds. The seas withdrew during the late Cretaceous, and marine flora and fauna gave way to terrestrial components, including trees, dinosaurs, crocodiles, pteradactyls (such as the giant Quetzalcoatlus), and mammals. Near the end of the Cretaceous and the beginning of the Ce ...
... thin limestone and shale beds. The seas withdrew during the late Cretaceous, and marine flora and fauna gave way to terrestrial components, including trees, dinosaurs, crocodiles, pteradactyls (such as the giant Quetzalcoatlus), and mammals. Near the end of the Cretaceous and the beginning of the Ce ...
Chapter 28: Arthropods
... made of protein and chitin (KI tun). Chitin also is found in the cell walls of fungi and in other animals. In some species, the exoskeleton is a continuous covering over most of the body. In other species, the exoskeleton is made of separate plates held together by hinges. The exoskeleton protects a ...
... made of protein and chitin (KI tun). Chitin also is found in the cell walls of fungi and in other animals. In some species, the exoskeleton is a continuous covering over most of the body. In other species, the exoskeleton is made of separate plates held together by hinges. The exoskeleton protects a ...
Integrated Immune and Cardiovascular Function in Pancrustacea
... Anatomically, this cardiovascular system consists of hemolymph (blood), the hemocoel, and a series of muscular pumps (Fig. 3A) (Pass 2000; Hertel and Pass 2002; Pass et al. 2006). The primary pump is the dorsal vessel, which is a tube-like structure that extends along the dorsal midline of the insec ...
... Anatomically, this cardiovascular system consists of hemolymph (blood), the hemocoel, and a series of muscular pumps (Fig. 3A) (Pass 2000; Hertel and Pass 2002; Pass et al. 2006). The primary pump is the dorsal vessel, which is a tube-like structure that extends along the dorsal midline of the insec ...
click here to file
... • Insects are the only invertebrate animals that can fly. • Flying allows insects to find places to live, food sources, and mates. • Flight also helps them escape from their predators. ...
... • Insects are the only invertebrate animals that can fly. • Flying allows insects to find places to live, food sources, and mates. • Flight also helps them escape from their predators. ...
18.1 Sponges, Cnidarians, Flatworms
... Roundworms reproduce sexually. Sperm and eggs are produced by separate male and female adults. Fertilization takes place inside the female organism. Females lay huge numbers of eggs, sometimes as many as 100,000 per day! The eggs hatch into larvae, which develop into adults. Then the cycle repeats. ...
... Roundworms reproduce sexually. Sperm and eggs are produced by separate male and female adults. Fertilization takes place inside the female organism. Females lay huge numbers of eggs, sometimes as many as 100,000 per day! The eggs hatch into larvae, which develop into adults. Then the cycle repeats. ...
© Study Posters
... Insect heads take many shapes reflecting the characteristic feeding habits of the species concerned. For example, predaceous insects have forward directed mouthparts with a corresponding forward protrusion of the head. The predators in this collage of photos are probably obvious. ...
... Insect heads take many shapes reflecting the characteristic feeding habits of the species concerned. For example, predaceous insects have forward directed mouthparts with a corresponding forward protrusion of the head. The predators in this collage of photos are probably obvious. ...
Arthropods
... numerous animals on earth • More than 1 million different species have been identified • They thrive in almost every habitat • There worldwide population is estimated at a billion billion, or 1018 individuals ...
... numerous animals on earth • More than 1 million different species have been identified • They thrive in almost every habitat • There worldwide population is estimated at a billion billion, or 1018 individuals ...
Atmospheric oxygen level and the evolution of insect body size
... altering the allocation of body materials, energy and space between the respiratory and non-respiratory system. Because HIF and hypoxic regulation of growth are widespread in the animal kingdom (Gorr et al. 2006), it is reasonable to suggest that similar responses would have been present in Palaeozo ...
... altering the allocation of body materials, energy and space between the respiratory and non-respiratory system. Because HIF and hypoxic regulation of growth are widespread in the animal kingdom (Gorr et al. 2006), it is reasonable to suggest that similar responses would have been present in Palaeozo ...
an introduction to insect structure - Biological Sciences
... since all six legs and the wings are found there. The largest muscles are also found in the thorax. The thorax is a box-like structure with extensive internal cuticular cross bracing. It also sports numerous cuticular plates (sclerites) that are intimately involved in locomotion. To conserve mass, s ...
... since all six legs and the wings are found there. The largest muscles are also found in the thorax. The thorax is a box-like structure with extensive internal cuticular cross bracing. It also sports numerous cuticular plates (sclerites) that are intimately involved in locomotion. To conserve mass, s ...
C: Chapter 2: Mollusks, Worms, Arthropods, and Echinoderms
... Between the soft body and the mantle is a space called the mantle cavity. It contains gills—the organs in which carbon dioxide from the mollusk is exchanged for oxygen in the water. The mantle also secretes the shell or protects the body if the mollusk does not have a shell. The shell is made up of ...
... Between the soft body and the mantle is a space called the mantle cavity. It contains gills—the organs in which carbon dioxide from the mollusk is exchanged for oxygen in the water. The mantle also secretes the shell or protects the body if the mollusk does not have a shell. The shell is made up of ...
• Mouthparts 1 • Mouthparts 2 • Thorax and abdomen 1 • Thorax and
... serve the mandibles in chewing insects and the sucking pump in piercing-sucking insects. The hard exoskeleton that is a common feature of arthropods is particularly well illustrated in the head. The lesser appreciated internal cuticular support structures are also well represented by the crossbracin ...
... serve the mandibles in chewing insects and the sucking pump in piercing-sucking insects. The hard exoskeleton that is a common feature of arthropods is particularly well illustrated in the head. The lesser appreciated internal cuticular support structures are also well represented by the crossbracin ...
Iowa Wildlife Series - Iowa Insects, Spiders, and Other Invertebrates
... color but can also have bright spots or stripes. Treehoppers have incredible jumping ability and are known for some of their bizarre shapes and colors which keep them camouflaged among plants. Often, this camouflage is so effective they only are noticed while moving. For example, the buffalo treehop ...
... color but can also have bright spots or stripes. Treehoppers have incredible jumping ability and are known for some of their bizarre shapes and colors which keep them camouflaged among plants. Often, this camouflage is so effective they only are noticed while moving. For example, the buffalo treehop ...
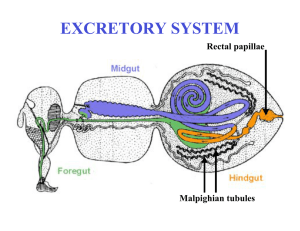
Excretory system - Faculty Support Site
... Among bacterial endosymbionts of insects, the best studied are the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum and its endosymbiont Buchnera sp. APS, and the tsetse fly Glossina morsitans morsitans and its endosymbiont Wigglesworthia glossinidia brevipalpis. As with endosymbiosis in other insects, the symbiosis ...
... Among bacterial endosymbionts of insects, the best studied are the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum and its endosymbiont Buchnera sp. APS, and the tsetse fly Glossina morsitans morsitans and its endosymbiont Wigglesworthia glossinidia brevipalpis. As with endosymbiosis in other insects, the symbiosis ...
A Closer Look at Arthropods
... The entire surface of an arthropod’s body is covered by a protective exoskeleton. An exoskeleton is an external skeleton that supports the animal’s tissues against gravity. Arthropods, such as the rhino beetle in FIGURE 1.1, have exoskeletons made of proteins and chitin. Chitin (KYT-uhn) is a long o ...
... The entire surface of an arthropod’s body is covered by a protective exoskeleton. An exoskeleton is an external skeleton that supports the animal’s tissues against gravity. Arthropods, such as the rhino beetle in FIGURE 1.1, have exoskeletons made of proteins and chitin. Chitin (KYT-uhn) is a long o ...
Basic parts are marked with an A - Illinois Natural History Survey
... These tubes get progressively smaller until each cell is supplied with oxygen. Now, let's look at what we have created. We have a hollow tube, made up of segments grouped into three body regions, head, thorax, and abdomen, in a process called tagmosis—the grouping together of individual segments to ...
... These tubes get progressively smaller until each cell is supplied with oxygen. Now, let's look at what we have created. We have a hollow tube, made up of segments grouped into three body regions, head, thorax, and abdomen, in a process called tagmosis—the grouping together of individual segments to ...
Arthropods
... Insect wings are outgrowths of the body wall. Wings are formed of a thin double membrane of chitin, and they have rigid veins that give the wings strength. ...
... Insect wings are outgrowths of the body wall. Wings are formed of a thin double membrane of chitin, and they have rigid veins that give the wings strength. ...
Chapter 26: Arthropods
... Real-World Reading Link Think about what animal group might have more ...
... Real-World Reading Link Think about what animal group might have more ...
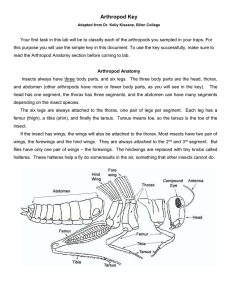
Arthropod key
... large, fully developed wings. But some insects are wingless even as adults. In most cases, an adult will have a hard exoskeleton (the hard shell covering the soft internal organs of an insect). Juveniles will have softer bodies. This will help you determine if the insect is a wingless adult, or a ju ...
... large, fully developed wings. But some insects are wingless even as adults. In most cases, an adult will have a hard exoskeleton (the hard shell covering the soft internal organs of an insect). Juveniles will have softer bodies. This will help you determine if the insect is a wingless adult, or a ju ...
Chapter 28
... You need larger clothes as you grow. Similarly, arthropods must replace their exoskeletons with larger ones in order to allow their bodies to increase in size as they mature. The prob¬ lem is not a simple one, however, because the exoskeleton not only covers all appendages and sense organs, but also ...
... You need larger clothes as you grow. Similarly, arthropods must replace their exoskeletons with larger ones in order to allow their bodies to increase in size as they mature. The prob¬ lem is not a simple one, however, because the exoskeleton not only covers all appendages and sense organs, but also ...
Ch 26 Arthropod Notes
... animal puffs up as a result of increased blood circulation to all parts of its body. • Thus, the new exoskeleton hardens in a larger size, allowing some room for the animal to continue to grow. ...
... animal puffs up as a result of increased blood circulation to all parts of its body. • Thus, the new exoskeleton hardens in a larger size, allowing some room for the animal to continue to grow. ...
Entomophagy
Entomophagy (/ˌɛntəˈmɒfədʒi/, from Greek ἔντομον éntomon, ""insect"", and φᾰγεῖν phagein, ""to eat"") is the human consumption of insects as food: human insectivory. The eggs, larvae, pupae, and adults of certain insect species have been eaten by man since prehistoric times and continue to be an item of the human nutrition in contemporary times.Human insect-eating is common to cultures in most parts of the world, including North, Central, and South America; and Africa, Asia, Australia, and New Zealand. Over 1,000 species of insects are known to be eaten in 80% of the world's nations. The total number of ethnic groups recorded to practice entomophagy is around 3,000. However, in some societies insect-eating is uncommon or even taboo. Today insect eating is rare in the developed world, but insects remain a popular food in many developing regions of Latin America, Africa, Asia, and Oceania. There are some companies that are trying to introduce insects into Western diets.