Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
... Enzymes are proteins that • catalyze nearly all the chemical reactions taking place in the cells of the body • increase the rate of reaction by lowering the energy of activation The enzyme carbonic anhydrase lowers the activation energy needed for the reaction of CO2 and H2O. Chemistry: An Introduct ...
... Enzymes are proteins that • catalyze nearly all the chemical reactions taking place in the cells of the body • increase the rate of reaction by lowering the energy of activation The enzyme carbonic anhydrase lowers the activation energy needed for the reaction of CO2 and H2O. Chemistry: An Introduct ...
1 The diagram below represents a biological process 5
... 9. Which substances are inorganic compounds? 1) water and salts 2) proteins and carbohydrates 3) fats and oils 4) enzymes and hormones 10. Which elements are present in all organic compounds? 1) hydrogen and oxygen 3) nitrogen and carbon 2) nitrogen and oxygen 4) hydrogen and carbon Base your answer ...
... 9. Which substances are inorganic compounds? 1) water and salts 2) proteins and carbohydrates 3) fats and oils 4) enzymes and hormones 10. Which elements are present in all organic compounds? 1) hydrogen and oxygen 3) nitrogen and carbon 2) nitrogen and oxygen 4) hydrogen and carbon Base your answer ...
P6039Datasheet-Lot0041305
... to the serine or threonine. The Enterococcus faecalis O-Glycosidase, also called Endo-α-NAcetylgalactosaminidase, can then remove these core structures with no modification of the serine or threonine residues. Any modification of the core structures, including sialyation, will block the action of th ...
... to the serine or threonine. The Enterococcus faecalis O-Glycosidase, also called Endo-α-NAcetylgalactosaminidase, can then remove these core structures with no modification of the serine or threonine residues. Any modification of the core structures, including sialyation, will block the action of th ...
PP - Columbia University
... Enzymes work as catalysts for two reasons: 1. They bind the substrates putting them in close proximity. 2. They participate in the reaction, weakening the covalent bonds of a substrate by its interaction with their amino acid residue side groups (e.g., by stretching). ...
... Enzymes work as catalysts for two reasons: 1. They bind the substrates putting them in close proximity. 2. They participate in the reaction, weakening the covalent bonds of a substrate by its interaction with their amino acid residue side groups (e.g., by stretching). ...
Biology 2.1 Calendar/Study Guide
... cells, are made of molecules, and perform life functions. Objective 1: Describe the fundamental chemistry of living cells. ...
... cells, are made of molecules, and perform life functions. Objective 1: Describe the fundamental chemistry of living cells. ...
Properties of Amino Acids
... Enzymes fall into classes based on function • There are 6 major classes of enzymes: 1.Oxidoreductases which are involved in oxidation, reduction, and electron or proton transfer reactions; 2.Transferases, catalysing reactions in which groups are transferred; 3.Hydrolases which cleave various covalen ...
... Enzymes fall into classes based on function • There are 6 major classes of enzymes: 1.Oxidoreductases which are involved in oxidation, reduction, and electron or proton transfer reactions; 2.Transferases, catalysing reactions in which groups are transferred; 3.Hydrolases which cleave various covalen ...
Enzyme kineics
... Enzymes fall into classes based on function • There are 6 major classes of enzymes: 1.Oxidoreductases which are involved in oxidation, reduction, and electron or proton transfer reactions; 2.Transferases, catalysing reactions in which groups are transferred; 3.Hydrolases which cleave various covale ...
... Enzymes fall into classes based on function • There are 6 major classes of enzymes: 1.Oxidoreductases which are involved in oxidation, reduction, and electron or proton transfer reactions; 2.Transferases, catalysing reactions in which groups are transferred; 3.Hydrolases which cleave various covale ...
Enzymes - SAVE MY EXAMS!
... In the space below, draw a diagram to show the molecules produced from the complete hydrolysis of the triglyceride. ...
... In the space below, draw a diagram to show the molecules produced from the complete hydrolysis of the triglyceride. ...
Macromolecules_students
... carbohydrates, but it will not affect the breakdown of proteins. The ability of an enzyme molecule to interact with specific molecules is most directly determined by the: A. shapes of the molecules involved B. sequence of bases present in ATP C. number of molecules involved D. amount of glucose pres ...
... carbohydrates, but it will not affect the breakdown of proteins. The ability of an enzyme molecule to interact with specific molecules is most directly determined by the: A. shapes of the molecules involved B. sequence of bases present in ATP C. number of molecules involved D. amount of glucose pres ...
svhs lab bioogy - Sonoma Valley High School
... Explain how carbon bonding with other elements can form different shapes and #’s of bonds. Explain the role of functional groups. Contrast monomers and polymers (macromolecules). Contrast condensation reactions (dehydration synthesis) with hydrolysis. Explain how ATP stores and gives up energy for t ...
... Explain how carbon bonding with other elements can form different shapes and #’s of bonds. Explain the role of functional groups. Contrast monomers and polymers (macromolecules). Contrast condensation reactions (dehydration synthesis) with hydrolysis. Explain how ATP stores and gives up energy for t ...
LABORATORY 2: ENZYME CATALYSIS
... rate is constant. From the third minute through the eighth minute, the rate is changing; it is slowing down. For each successive minute after the first three minutes, the amount of product formed in that interval is less than in the preceding minute. From the seventh minute onward, the reaction rat ...
... rate is constant. From the third minute through the eighth minute, the rate is changing; it is slowing down. For each successive minute after the first three minutes, the amount of product formed in that interval is less than in the preceding minute. From the seventh minute onward, the reaction rat ...
103 final rev worksheet key
... 41. How do heavy metal ions denature proteins? Heavy metal ions form ionic bonds with the sulfur atoms of cysteine atoms, disrupting disulfide bonds. 42. What is a catalyst? A catalyst speeds up a reaction, but is not used up in the reaction. A catalyst usually speeds the reaction up by stabilizing ...
... 41. How do heavy metal ions denature proteins? Heavy metal ions form ionic bonds with the sulfur atoms of cysteine atoms, disrupting disulfide bonds. 42. What is a catalyst? A catalyst speeds up a reaction, but is not used up in the reaction. A catalyst usually speeds the reaction up by stabilizing ...
Describe cell structure and function (90464)
... • Labelled / annotated diagram showing model (either induced fit or lock-key) ...
... • Labelled / annotated diagram showing model (either induced fit or lock-key) ...
Assessment Schedule – 2006
... Labelled / annotated diagram showing model (either induced fit or lock-key) ...
... Labelled / annotated diagram showing model (either induced fit or lock-key) ...
Polymer - Deans Community High School
... These have their polypeptide chains inter woven. The polypeptide chains are held together by hydrogen bonding, between the N-H and the C=O groups. This gives these proteins their properties of toughness, insolubility, and resistance to change in pH and temperature. So they are found in skin,tissue, ...
... These have their polypeptide chains inter woven. The polypeptide chains are held together by hydrogen bonding, between the N-H and the C=O groups. This gives these proteins their properties of toughness, insolubility, and resistance to change in pH and temperature. So they are found in skin,tissue, ...
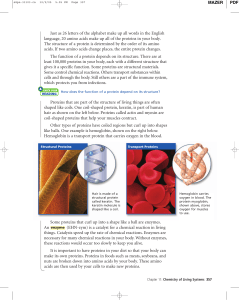
Just as 26 letters of the alphabet make up all words in the English
... language, 20 amino acids make up all of the proteins in your body. The structure of a protein is determined by the order of its amino acids. If two amino acids change places, the entire protein changes. The function of a protein depends on its structure. There are at least 100,000 proteins in your b ...
... language, 20 amino acids make up all of the proteins in your body. The structure of a protein is determined by the order of its amino acids. If two amino acids change places, the entire protein changes. The function of a protein depends on its structure. There are at least 100,000 proteins in your b ...
Enzymes–II
... Coenzymes are thermostable, dialyzable organic compounds. They may be either attached to the protein molecules or may be present in the cytoplasm. The coenzyme accounts for about 1% of the entire enzyme molecule. Sometimes, a distinction is made between coenzymes and cofactors : the former includes ...
... Coenzymes are thermostable, dialyzable organic compounds. They may be either attached to the protein molecules or may be present in the cytoplasm. The coenzyme accounts for about 1% of the entire enzyme molecule. Sometimes, a distinction is made between coenzymes and cofactors : the former includes ...
Restriction Enzymes - Seattle Central College
... • Restriction enzymes are bacterial enzymes that cleave the sugar-phosphate backbone of the DNA at specific nucleotide. • They are member of the class of nucleases. Endonucleases cleave nucleic acid at internal positions, while exonucleases progressively digest from the ends of the nucleic acid mole ...
... • Restriction enzymes are bacterial enzymes that cleave the sugar-phosphate backbone of the DNA at specific nucleotide. • They are member of the class of nucleases. Endonucleases cleave nucleic acid at internal positions, while exonucleases progressively digest from the ends of the nucleic acid mole ...
BIO 101 Exam 2 practice questions Practice questions Ch 8,9 YOU
... 16. Competitive inhibitors stop an enzyme from working by… a. changing the shape of the enzyme b. merging with the substrate instead c. blocking the active site of the enzyme d. combining with the product of the reaction 17. When a molecule binds to an area of an enzyme that is not the active site, ...
... 16. Competitive inhibitors stop an enzyme from working by… a. changing the shape of the enzyme b. merging with the substrate instead c. blocking the active site of the enzyme d. combining with the product of the reaction 17. When a molecule binds to an area of an enzyme that is not the active site, ...
Organic Compounds
... unsaturated fat - a fatty acid that has at least two carbons double bonded to each other instead of to hydrogen atoms - that is, the carbons are NOT bound to the maximum number of hydrogen atoms. causes the fatty acids to bend fatty acids like this cannot pack very tightly together because o ...
... unsaturated fat - a fatty acid that has at least two carbons double bonded to each other instead of to hydrogen atoms - that is, the carbons are NOT bound to the maximum number of hydrogen atoms. causes the fatty acids to bend fatty acids like this cannot pack very tightly together because o ...
Colorimetric End-Point Determination
... Enzyme activity At normal body temperature, cellular chemical reactions, particularly those for the oxidation or transformation of organic compounds would occur very slowly. While raising the temperature would increase the speed of the reaction, living cells cannot be subjected to high temperatures ...
... Enzyme activity At normal body temperature, cellular chemical reactions, particularly those for the oxidation or transformation of organic compounds would occur very slowly. While raising the temperature would increase the speed of the reaction, living cells cannot be subjected to high temperatures ...
Metabolism & Enzymes
... each enzyme works with a specific substrate chemical fit between active site & substrate H bonds & ionic bonds ...
... each enzyme works with a specific substrate chemical fit between active site & substrate H bonds & ionic bonds ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.