what are enzymes
... chemical reactions in living things. Without enzymes, our guts would take weeks and weeks to digest our food, and our muscles, nerves, and bones would not work properly. Essentially, we would not be living! ...
... chemical reactions in living things. Without enzymes, our guts would take weeks and weeks to digest our food, and our muscles, nerves, and bones would not work properly. Essentially, we would not be living! ...
Global Properties of the Metabolic Map of
... competing with its substrates—is defined as a modulator, in the absence of any biological term for this concept.) The information lists all compounds that are known to activate or inhibit an enzyme from in vitro enzymological studies. The database also identifies, for each enzyme, that subset of its ...
... competing with its substrates—is defined as a modulator, in the absence of any biological term for this concept.) The information lists all compounds that are known to activate or inhibit an enzyme from in vitro enzymological studies. The database also identifies, for each enzyme, that subset of its ...
Electron Transport Chain, Oxidative phosphorylation and Pentose
... 2. How many Co-enzyme Q10 molecules will be needed to oxidize one molecule of NADH, or one molecule of FADH2. One molecule of CoQ10 3. Fe++/Fe+++ plays major role in the transfer electron s from one molecule to other during mitochondrial ETC and many complexes and proteins have either Fe-S centres o ...
... 2. How many Co-enzyme Q10 molecules will be needed to oxidize one molecule of NADH, or one molecule of FADH2. One molecule of CoQ10 3. Fe++/Fe+++ plays major role in the transfer electron s from one molecule to other during mitochondrial ETC and many complexes and proteins have either Fe-S centres o ...
Enzyme Lab
... bases are frequently used catalysts in organic chemistry and can accelerate reactions thousands of times. The biological catalysts known as enzymes catalyze the great majority of chemical reactions in the cell. Enzymes can accelerate reactions 1014 to 1020 times, amounts that are far greater than an ...
... bases are frequently used catalysts in organic chemistry and can accelerate reactions thousands of times. The biological catalysts known as enzymes catalyze the great majority of chemical reactions in the cell. Enzymes can accelerate reactions 1014 to 1020 times, amounts that are far greater than an ...
1 Unit 11-12: Equilibrium and Acid/Bases Notes Colligative
... Increase surface area of reactants ‐ the more sites exposed to react, the more collisions can occur ‐ a large piece of copper will react slower in acid than many small pieces Increase concentration of reactants ‐ more moles (therefore particles) available to react in a 6.0M solution vs. a 0 ...
... Increase surface area of reactants ‐ the more sites exposed to react, the more collisions can occur ‐ a large piece of copper will react slower in acid than many small pieces Increase concentration of reactants ‐ more moles (therefore particles) available to react in a 6.0M solution vs. a 0 ...
Enzyme Kinetics
... Activation energy and Transition State • All chemical reactions have an energy barrier, the activation energy barrier (∆G‡) that must be overcome for reaction to occur. The energy barrier can be overcome by increasing the temperature, an option not possible for living organisms. Enzymes employ other ...
... Activation energy and Transition State • All chemical reactions have an energy barrier, the activation energy barrier (∆G‡) that must be overcome for reaction to occur. The energy barrier can be overcome by increasing the temperature, an option not possible for living organisms. Enzymes employ other ...
Nugget
... Photoremovable Protecting Groups and Cage Compounds The project develops new “cage compounds” for practical applications in biochemistry, cellular biology, and physiology. Cage compounds provide the means for quickly introducing biological agents into cells. Once released, such biological agents or ...
... Photoremovable Protecting Groups and Cage Compounds The project develops new “cage compounds” for practical applications in biochemistry, cellular biology, and physiology. Cage compounds provide the means for quickly introducing biological agents into cells. Once released, such biological agents or ...
Optimization and Control of Agent
... specified, this understanding can then lead to a possibly much simpler equation-based model that is faithful for the specific control objective, but possibly few or none of the other features. Secondly, the need for optimization and control might be an ongoing process, e.g., for models that are used ...
... specified, this understanding can then lead to a possibly much simpler equation-based model that is faithful for the specific control objective, but possibly few or none of the other features. Secondly, the need for optimization and control might be an ongoing process, e.g., for models that are used ...
1 enzyme catalysis lab protocol
... back to your desk and keep it on ice! (This is very important—catalase disintegrates quickly.) Get a 1 mL syringe and reserve it for catalase. 4. Get approximately 90 mL of H2O2 in a plastic cup, and then put 10mL in each of the labeled plastic cups except the baseline cup. 5. Get a stopwatch and fi ...
... back to your desk and keep it on ice! (This is very important—catalase disintegrates quickly.) Get a 1 mL syringe and reserve it for catalase. 4. Get approximately 90 mL of H2O2 in a plastic cup, and then put 10mL in each of the labeled plastic cups except the baseline cup. 5. Get a stopwatch and fi ...
Unit 13, Lesson 1
... changes color. In the presence of large amounts of reducing agent, the color of the indicator is characteristic of its reduced form. The indicator assumes the color of its oxidized form when it is present in an oxidizing medium. At or near the equivalence point, a sharp change in the indicator’s col ...
... changes color. In the presence of large amounts of reducing agent, the color of the indicator is characteristic of its reduced form. The indicator assumes the color of its oxidized form when it is present in an oxidizing medium. At or near the equivalence point, a sharp change in the indicator’s col ...
Exploration of the Dynamic Properties of Protein Complexes
... Protein complexes are not static, but rather highly dynamic with subunits that undergo 1-dimensional diffusion with respect to each other. Interactions within protein complexes are modulated through regulatory inputs that alter interactions and introduce new components and deplete existing component ...
... Protein complexes are not static, but rather highly dynamic with subunits that undergo 1-dimensional diffusion with respect to each other. Interactions within protein complexes are modulated through regulatory inputs that alter interactions and introduce new components and deplete existing component ...
Defined megadalton hyaluronan polymer standards. Anal
... The biotin–HA chains in the range of approximately 0.5– 2.0 MDa were very monodisperse based on their migration on gels as tight bands as in Fig. 3. The SEC–MALLS profiles yielded polydispersity values ranging from 1.02 to 1.06; for reference, the value for an ideal polymer is 1. Monodisperse biotiny ...
... The biotin–HA chains in the range of approximately 0.5– 2.0 MDa were very monodisperse based on their migration on gels as tight bands as in Fig. 3. The SEC–MALLS profiles yielded polydispersity values ranging from 1.02 to 1.06; for reference, the value for an ideal polymer is 1. Monodisperse biotiny ...
24.t Glycolysis
... phosphorylation of fructgse G-phosphate to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate is called the committed step of glycolysis. Fruct6se 1,6-bisphosphateis now cleavedto give a pair of three-carbon compounds, dihydroxyacetone phosphate and. glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. ...
... phosphorylation of fructgse G-phosphate to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate is called the committed step of glycolysis. Fruct6se 1,6-bisphosphateis now cleavedto give a pair of three-carbon compounds, dihydroxyacetone phosphate and. glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. ...
Critical Considerations for Analytical Similarity Assessment
... Visual profile comparison could be subjective. An objective comparison for spectrum similarity would require complex mathematical algorithm ...
... Visual profile comparison could be subjective. An objective comparison for spectrum similarity would require complex mathematical algorithm ...
Macromolecules Biological Molecules Macromolecules
... General points about biological macromolecules 2- Isomers have different arrangements of the same atoms 3- The structures of macromolecules reflect their functions 4- Most macromolecules are formed by condensation and broken down by hydrolysis ...
... General points about biological macromolecules 2- Isomers have different arrangements of the same atoms 3- The structures of macromolecules reflect their functions 4- Most macromolecules are formed by condensation and broken down by hydrolysis ...
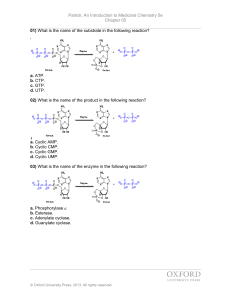
499 Med Chem Chap 5 problems
... 14) Which of the following molecules is bound to a G-protein in the inactivated state? a. GMP b. GDP c. GTP d. None of these. 15) Which of the following molecules binds to the G-protein when the G-protein binds to the G-protein coupled receptor and is activated? a. GMP b. GDP c. GTP d. None of these ...
... 14) Which of the following molecules is bound to a G-protein in the inactivated state? a. GMP b. GDP c. GTP d. None of these. 15) Which of the following molecules binds to the G-protein when the G-protein binds to the G-protein coupled receptor and is activated? a. GMP b. GDP c. GTP d. None of these ...
Chapter 5 Chemical Equilibrium 1 State whether each of the
... (c) You should have found that Hvap is smaller at the higher temperature. Why is this so? This is because at higher temperature, the water molecules already have higher energy, so less is required to vaporize them from the liquid into the gas phase. ...
... (c) You should have found that Hvap is smaller at the higher temperature. Why is this so? This is because at higher temperature, the water molecules already have higher energy, so less is required to vaporize them from the liquid into the gas phase. ...
Relaxation and Molecular Dynamics
... • Expand position, velocity and acceleration as a Taylor series in t • Based on an initial set of positions, velocities and accelerations extrapolate to the next timestep e.g. v t t v t a.t (true for constant acceleration) ...
... • Expand position, velocity and acceleration as a Taylor series in t • Based on an initial set of positions, velocities and accelerations extrapolate to the next timestep e.g. v t t v t a.t (true for constant acceleration) ...
Kinetic analysis of cooperativity of phosphorylated L
... Data processing All data were analysed by non-linear least-squares regression analysis using the GraphPad Prism version 4.0 (GraphPad Software Inc., USA), SigmaPlot 9.0 (Systat Software Inc., USA), and Microsoft Excel XP (Microsoft Corporation, USA). The values reported are given with standard erro ...
... Data processing All data were analysed by non-linear least-squares regression analysis using the GraphPad Prism version 4.0 (GraphPad Software Inc., USA), SigmaPlot 9.0 (Systat Software Inc., USA), and Microsoft Excel XP (Microsoft Corporation, USA). The values reported are given with standard erro ...
Chapter 10 Chemical Reactions
... 1) Make sure the formulas are correct if you wrote the reaction. If you put a metal and nonmetal together you must CHECK that the CHARGES add to zero charge! 2) Count the # of atoms for each element on both sides of the equation 3) Change coefficients NOT subscripts. 4) Balance polyatomic ions as a ...
... 1) Make sure the formulas are correct if you wrote the reaction. If you put a metal and nonmetal together you must CHECK that the CHARGES add to zero charge! 2) Count the # of atoms for each element on both sides of the equation 3) Change coefficients NOT subscripts. 4) Balance polyatomic ions as a ...
GENERAL CHEMISTRY SECTION IV: THERMODYNAMICS
... Here’s another way to think of state functions: any information about what happened to a state function during the reaction is irrelevant – like how quickly it reacted, or the phases it went through. Take temperature, for example: if you’re given the starting (T1) and final (T2) temperatures, then r ...
... Here’s another way to think of state functions: any information about what happened to a state function during the reaction is irrelevant – like how quickly it reacted, or the phases it went through. Take temperature, for example: if you’re given the starting (T1) and final (T2) temperatures, then r ...
Unit 6: Reactions and Stoichiometry
... At the most fundamental level, the chemist needs a unit that describes a very large quantity. One of the most well-known numbers in the study of chemistry is number of units in a mole. The number of units in a mole is called Avogadro’s number (named after the Italian physicist). The mole is defined ...
... At the most fundamental level, the chemist needs a unit that describes a very large quantity. One of the most well-known numbers in the study of chemistry is number of units in a mole. The number of units in a mole is called Avogadro’s number (named after the Italian physicist). The mole is defined ...
THERMODYNAMICS OF REACTING SYSTEMS
... This chapter explains the basics of thermodynamic calculations for reacting systems. Reaction ...
... This chapter explains the basics of thermodynamic calculations for reacting systems. Reaction ...
do not - wwphs
... How do enzymes work? 1) Enzymes act upon a substance called a substrate 2) The enzyme has an indent in it called the active site where the substrate can fit into, kind of like a lock and a key ...
... How do enzymes work? 1) Enzymes act upon a substance called a substrate 2) The enzyme has an indent in it called the active site where the substrate can fit into, kind of like a lock and a key ...
Ch. 3 Sections 3.9-3.10 Notes
... number of moles of product that could form? Note the coefficients tell us that 1 mol of N2 consumes 3 mol of H2. 1 mol N2 ↔ 3 mol H2 But 5 mol of H2 was used, not 3, so there will be 2 mol of H2 left over. Once the 1 mol of N2 taken is consumed, no additional NH3 can form. Therefore, the reactant th ...
... number of moles of product that could form? Note the coefficients tell us that 1 mol of N2 consumes 3 mol of H2. 1 mol N2 ↔ 3 mol H2 But 5 mol of H2 was used, not 3, so there will be 2 mol of H2 left over. Once the 1 mol of N2 taken is consumed, no additional NH3 can form. Therefore, the reactant th ...