Enzymes - WordPress.com
... site for binding substrates. It provides a threedimensional environment that both shields substrates from solvent and facilitates catalysis. It also binds any cofactors and prosthetic groups that may be required for catalysis. Organisation of enzyme structure (ex lysozyme ). Binding sites in blue, c ...
... site for binding substrates. It provides a threedimensional environment that both shields substrates from solvent and facilitates catalysis. It also binds any cofactors and prosthetic groups that may be required for catalysis. Organisation of enzyme structure (ex lysozyme ). Binding sites in blue, c ...
Slides
... Review-level Model-Organism Database for E. coli Tracks evolving annotation of the E. coli genome and ...
... Review-level Model-Organism Database for E. coli Tracks evolving annotation of the E. coli genome and ...
Net Ionic Prep Session NMSI INSTRUCTOR
... Answer Question 4 below. The Section II score weighting for this question is 10 percent. 4. For each of the following three reactions, in part (i) write a balanced equation for the reaction and in part (ii) answer the question about the reaction. In part (i), coefficients should be in terms of lowes ...
... Answer Question 4 below. The Section II score weighting for this question is 10 percent. 4. For each of the following three reactions, in part (i) write a balanced equation for the reaction and in part (ii) answer the question about the reaction. In part (i), coefficients should be in terms of lowes ...
Hexokinase
... • Consists of two phases: 1. First phase converts glucose to two Glyceraldehyde-3-P – Energy investment phase – Consumes 2 molecules of ATP 2. Second phase produces two pyruvates – Energy generation phase – Produces 4 molecules of ATP • Products are 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP and 2 NADH • Essentially all cel ...
... • Consists of two phases: 1. First phase converts glucose to two Glyceraldehyde-3-P – Energy investment phase – Consumes 2 molecules of ATP 2. Second phase produces two pyruvates – Energy generation phase – Produces 4 molecules of ATP • Products are 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP and 2 NADH • Essentially all cel ...
AP Chemistry
... In the SO2 molecule, both of the bonds between sulfur and oxygen have the same length. Explain this observation, supporting your explanation by drawing in the box below a Lewis electron-dot diagram (or diagrams) for the SO2 molecule ...
... In the SO2 molecule, both of the bonds between sulfur and oxygen have the same length. Explain this observation, supporting your explanation by drawing in the box below a Lewis electron-dot diagram (or diagrams) for the SO2 molecule ...
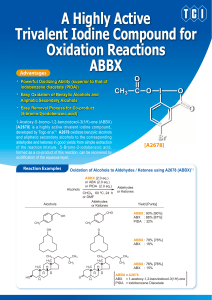
A Highly Active Trivalent Iodine Compound for
... Oxidation of Alcohols to Aldehydes / Ketones using A2678 (ABBX)1) ...
... Oxidation of Alcohols to Aldehydes / Ketones using A2678 (ABBX)1) ...
to an allosteric site
... enzyme's three-dimensional shape. Substrate = The substance an enzyme acts on and makes more reactive. • An enzyme binds to its substrate and catalyzes its conversion to product. The enzyme is released in original form. Substrate + enzyme enzyme-substrate complex product + enzyme • The substrate bin ...
... enzyme's three-dimensional shape. Substrate = The substance an enzyme acts on and makes more reactive. • An enzyme binds to its substrate and catalyzes its conversion to product. The enzyme is released in original form. Substrate + enzyme enzyme-substrate complex product + enzyme • The substrate bin ...
Homo-coupling of terminal alkynes on a noble metal surface
... data in Fig. 2d evidence a drastic transformation of the dimerdominated sample (Fig. 2b) upon tempering at 370 K for 10 min. Although the observed structures are rather irregular, they definitely must comprise multiple interconnections between the original TEB constituents, which can hardly be identi ...
... data in Fig. 2d evidence a drastic transformation of the dimerdominated sample (Fig. 2b) upon tempering at 370 K for 10 min. Although the observed structures are rather irregular, they definitely must comprise multiple interconnections between the original TEB constituents, which can hardly be identi ...
Enzyme Reading - BizierDiemHonorsBiology
... As with any other protein, an enzyme's structure and shape are essential to its function. And like other proteins, an enzyme's shape is sensitive to changes in its surrounding environment. Therefore, factors such as pH and temperature can greatly affect how well an enzyme works or if it can work at ...
... As with any other protein, an enzyme's structure and shape are essential to its function. And like other proteins, an enzyme's shape is sensitive to changes in its surrounding environment. Therefore, factors such as pH and temperature can greatly affect how well an enzyme works or if it can work at ...
8872 Chemistry H1 syllabus for 2016
... 10. bring together knowledge, principles and concepts from different areas of chemistry, and apply them in a particular context 11. use chemical skills in contexts which bring together different areas of the subject. These assessment objectives cannot be precisely specified in the Syllabus content b ...
... 10. bring together knowledge, principles and concepts from different areas of chemistry, and apply them in a particular context 11. use chemical skills in contexts which bring together different areas of the subject. These assessment objectives cannot be precisely specified in the Syllabus content b ...
Chapter 8
... If the subscripts are changed then the identity of the reactants and products is also changed. Equations must be balanced using the actual reactants and products. 7. A combustion reaction is an exothermic process (usually burning) done in the presence of oxygen. 8. The activity series given in Table ...
... If the subscripts are changed then the identity of the reactants and products is also changed. Equations must be balanced using the actual reactants and products. 7. A combustion reaction is an exothermic process (usually burning) done in the presence of oxygen. 8. The activity series given in Table ...
PDF 2/page
... They control the rate of the respective pathway and whether it is turned on or shut off. ...
... They control the rate of the respective pathway and whether it is turned on or shut off. ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules TEKS 9A
... The student is expected to: 9A compare the structures and functions of different types of biomolecules, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids ...
... The student is expected to: 9A compare the structures and functions of different types of biomolecules, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids ...
The Depth of Chemical Time and the Power of Enzymes as Catalysts
... According to a “rule of thumb”, traceable to some early experiments by Harcourt, reaction rates tend to double with a 10 °C rise of temperature12 so that “Q10 ) 2”. One would then expect a 65-fold increase in rate if the temperature rose from 25 to 100 °C. However, reactions can be conducted at high ...
... According to a “rule of thumb”, traceable to some early experiments by Harcourt, reaction rates tend to double with a 10 °C rise of temperature12 so that “Q10 ) 2”. One would then expect a 65-fold increase in rate if the temperature rose from 25 to 100 °C. However, reactions can be conducted at high ...
The Depth of Chemical Time and the Power of Enzymes
... According to a “rule of thumb”, traceable to some early experiments by Harcourt, reaction rates tend to double with a 10 °C rise of temperature12 so that “Q10 ) 2”. One would then expect a 65-fold increase in rate if the temperature rose from 25 to 100 °C. However, reactions can be conducted at high ...
... According to a “rule of thumb”, traceable to some early experiments by Harcourt, reaction rates tend to double with a 10 °C rise of temperature12 so that “Q10 ) 2”. One would then expect a 65-fold increase in rate if the temperature rose from 25 to 100 °C. However, reactions can be conducted at high ...
Intermolecular forces and molecules
... Use the Three Atoms screen of the Molecule Polarity sim to manipulate the electronegativity of, and angle between, the three atoms. ...
... Use the Three Atoms screen of the Molecule Polarity sim to manipulate the electronegativity of, and angle between, the three atoms. ...
biomolecular_STRUCTURES
... before use by the body Organs and cells communicate through molecules circulating in the blood stream—hormones ...
... before use by the body Organs and cells communicate through molecules circulating in the blood stream—hormones ...
The active site
... Enzymes are substrate specific (cont.,) The rate that a specific number of enzymes converts substrates to products depends in part on substrate concentrations At low substrate concentrations, an increase in substrate speeds binding to available active sites – However, there is a limit to how ...
... Enzymes are substrate specific (cont.,) The rate that a specific number of enzymes converts substrates to products depends in part on substrate concentrations At low substrate concentrations, an increase in substrate speeds binding to available active sites – However, there is a limit to how ...
Nonlinear Self-organization Dynamics of a Metabolic Process of the
... performed with the help of the theory of nonlinear differential equations [20, 21] and the methods of mathematical modeling of biochemical systems applied and developed by the authors. in [22-38]. ...
... performed with the help of the theory of nonlinear differential equations [20, 21] and the methods of mathematical modeling of biochemical systems applied and developed by the authors. in [22-38]. ...
Physiology Lecture Outline: Enzymes
... enzymes are involved) and they are transformed into products. All enzymes are proteins with specific 3-D shapes and they contain small regions where substrates bind to the enzyme called the active site. Enzymes carry out catalysis by binding to substrate molecules and bringing them close together an ...
... enzymes are involved) and they are transformed into products. All enzymes are proteins with specific 3-D shapes and they contain small regions where substrates bind to the enzyme called the active site. Enzymes carry out catalysis by binding to substrate molecules and bringing them close together an ...
Unit 2 Chemical Reactions
... Acetylene gas is a fuel used in welding torches, and it combines with oxygen to produce a very hot flame. Because it is an organic compound, it contains carbon. When it burns in pure oxygen, it should produce carbon dioxide. This gas is the product of complete combustion. If there is not enough oxyg ...
... Acetylene gas is a fuel used in welding torches, and it combines with oxygen to produce a very hot flame. Because it is an organic compound, it contains carbon. When it burns in pure oxygen, it should produce carbon dioxide. This gas is the product of complete combustion. If there is not enough oxyg ...
Structural Biochemistry/Enzyme
... biological reactions in the absence of enzymes may be as much as a million times slower. Virtually all enzymes are proteins, though the converse is not true and other molecules such as RNA can also catalyze reactions. The most remarkable characteristics of enzymes are their ability to accelerate che ...
... biological reactions in the absence of enzymes may be as much as a million times slower. Virtually all enzymes are proteins, though the converse is not true and other molecules such as RNA can also catalyze reactions. The most remarkable characteristics of enzymes are their ability to accelerate che ...