Salicylate (Aspirin) Ingestion
... 3. Adult patients who are acutely poisoned usually present with a mixed respiratory alkalosis and metabolic acidosis 4. Respiratory alkalosis may be transient in children so that metabolic acidosis may occur early in the course 5. Patients with mixed acid-base disturbances have been found to have no ...
... 3. Adult patients who are acutely poisoned usually present with a mixed respiratory alkalosis and metabolic acidosis 4. Respiratory alkalosis may be transient in children so that metabolic acidosis may occur early in the course 5. Patients with mixed acid-base disturbances have been found to have no ...
Biochemistry The Citric Acid Cycle Chapter 17:
... • Lipoamide swings to pyruvate dehydrogenase to accept acetyl group • Swings to transacetylase to transfer it to CoA-SH • Swings to dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase to regenerate ...
... • Lipoamide swings to pyruvate dehydrogenase to accept acetyl group • Swings to transacetylase to transfer it to CoA-SH • Swings to dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase to regenerate ...
biochemistry of proteins and nucleic acids
... Clinical and diagnostic value. At various diseases of stomach acidity can be increased, dropped and zero. At peptic ulcer of stomach or hyperacid gastritis the hyperacidity – augmentation of the maintenance of free hydrochloric acid and whole acid is observed. At hypoacid gastritis or carcinoma of t ...
... Clinical and diagnostic value. At various diseases of stomach acidity can be increased, dropped and zero. At peptic ulcer of stomach or hyperacid gastritis the hyperacidity – augmentation of the maintenance of free hydrochloric acid and whole acid is observed. At hypoacid gastritis or carcinoma of t ...
ANTIDIABETICS AND HYPOGLYCEMICS
... bind to K+ channels on pancreatic cells, resulting in increased insulin secretion. Compared to the sulfonylureas, the hypoglycemic effects of the meglitinides are shorter in duration. ...
... bind to K+ channels on pancreatic cells, resulting in increased insulin secretion. Compared to the sulfonylureas, the hypoglycemic effects of the meglitinides are shorter in duration. ...
Design and analysis of metabolic pathways supporting
... Several natural alternative carbon fixation pathways can support autotrophic growth when the cells are supplied with an electron source. These are reviewed and compared extensively elsewhere [49,65–67]. Notably, to the best of our knowledge, the reductive pentose phosphate pathway is the only carbon ...
... Several natural alternative carbon fixation pathways can support autotrophic growth when the cells are supplied with an electron source. These are reviewed and compared extensively elsewhere [49,65–67]. Notably, to the best of our knowledge, the reductive pentose phosphate pathway is the only carbon ...
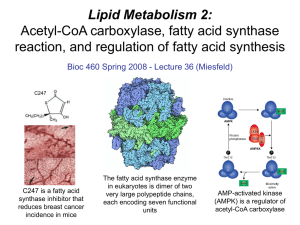
Lecture 36 - Lipid Metabolism 2
... • Fatty acid synthesis takes place in the cytosol, uses NADPH as coenzyme in redox reactions, and the building block is malonyl-CoA. • Acetyl-CoA carboxylase is the key regulated enzyme in fatty acid synthesis and is responsible for generating malonyl-CoA in a carboxylation reaction using acetyl-CoA ...
... • Fatty acid synthesis takes place in the cytosol, uses NADPH as coenzyme in redox reactions, and the building block is malonyl-CoA. • Acetyl-CoA carboxylase is the key regulated enzyme in fatty acid synthesis and is responsible for generating malonyl-CoA in a carboxylation reaction using acetyl-CoA ...
Modelling glycolysis with Cellware
... notable for three reasons: 1) Hexokinase is one of the regulated enzymes in the pathway, 2) phosphorylation traps glucose in the cell because of two negative charges in glucose 6-phosphate and 3) Phosphorylation destabilizes glucose making way for further catalysis. Third reaction in glycolysis is a ...
... notable for three reasons: 1) Hexokinase is one of the regulated enzymes in the pathway, 2) phosphorylation traps glucose in the cell because of two negative charges in glucose 6-phosphate and 3) Phosphorylation destabilizes glucose making way for further catalysis. Third reaction in glycolysis is a ...
Functional genomics analysis of foliar condensed tannin and
... SCOTT A. HARDING,1 HONGYING JIANG,1,2 MIJEONG LEE JEONG,1,3 FANNY L. CASADO,1,4 HAN-WEI LIN1 and CHUNG-JUI TSAI1,5 ...
... SCOTT A. HARDING,1 HONGYING JIANG,1,2 MIJEONG LEE JEONG,1,3 FANNY L. CASADO,1,4 HAN-WEI LIN1 and CHUNG-JUI TSAI1,5 ...
View/Open - Oregon State University
... 1995; Porter & Feig, 2005; Kogure et al, 1979; Ferguson et al, 1984). Clearly, there is a need to attempt to cultivate the uncultivated marine species by new techniques and characterize them by genomic studies. The abundance of these microorganisms suggests their importance and their physiology may ...
... 1995; Porter & Feig, 2005; Kogure et al, 1979; Ferguson et al, 1984). Clearly, there is a need to attempt to cultivate the uncultivated marine species by new techniques and characterize them by genomic studies. The abundance of these microorganisms suggests their importance and their physiology may ...
answer key - chem.uwec.edu
... • Describe the factors that contribute to a high negative free energy for phosphoryl transfer. (Question 2) • Discuss the relationship between oxidation and metabolism. (Question 1) • Describe the structures of the nucleotides that are used in oxidation/reduction reactions. • Describe some of the ac ...
... • Describe the factors that contribute to a high negative free energy for phosphoryl transfer. (Question 2) • Discuss the relationship between oxidation and metabolism. (Question 1) • Describe the structures of the nucleotides that are used in oxidation/reduction reactions. • Describe some of the ac ...
ACID – BASE, FLUIDS, AND ELECTROLYTES EXTRA NOTES
... systems to function optimally in the body.4 Normal blood pH ranges from 7.3-7.4.3 Decreased pH is termed acidemia and is caused by an increase in the concentration of hydrogen ions ([H+]). Increased blood pH is termed alkalemia and is caused by a decrease in the [H+]. The buffer systems that maintai ...
... systems to function optimally in the body.4 Normal blood pH ranges from 7.3-7.4.3 Decreased pH is termed acidemia and is caused by an increase in the concentration of hydrogen ions ([H+]). Increased blood pH is termed alkalemia and is caused by a decrease in the [H+]. The buffer systems that maintai ...
PPT - Med Study Group
... food eaten Generally they are autosomal recessive traits Food not broken down properly may produce chemicals that build up in various parts of the body causing medical problems and learning disorders. ...
... food eaten Generally they are autosomal recessive traits Food not broken down properly may produce chemicals that build up in various parts of the body causing medical problems and learning disorders. ...
slides#8 - DENTISTRY 2012
... food eaten Generally they are autosomal recessive traits Food not broken down properly may produce chemicals that build up in various parts of the body causing medical problems and learning disorders. ...
... food eaten Generally they are autosomal recessive traits Food not broken down properly may produce chemicals that build up in various parts of the body causing medical problems and learning disorders. ...
Metabolic Acidosis
... Type B Lactic Acidosis • Low rate of acid production, otherwise acidosis would have killed the patient • Normal ECF volume rules out DKA and AKA • No history of GI problem rules out D-lactic acidosis • L-Lactic acid level was higher than 30 mmol/L and the patient was taking metformin for the treatm ...
... Type B Lactic Acidosis • Low rate of acid production, otherwise acidosis would have killed the patient • Normal ECF volume rules out DKA and AKA • No history of GI problem rules out D-lactic acidosis • L-Lactic acid level was higher than 30 mmol/L and the patient was taking metformin for the treatm ...
Approach to Metabolic Alkalosis
... Metabolic alkalosis in the setting of excess or apparent excess of mineralocorticoids occurs as a result of stimulation of the collecting duct ion transport. Aldosterone stimulates sodium reabsorption in the collecting duct of the kidney by activating the mineralocorticoid receptor of sodium-potassi ...
... Metabolic alkalosis in the setting of excess or apparent excess of mineralocorticoids occurs as a result of stimulation of the collecting duct ion transport. Aldosterone stimulates sodium reabsorption in the collecting duct of the kidney by activating the mineralocorticoid receptor of sodium-potassi ...
October 15 AP Biology - John D. O`Bryant School of Math & Science
... B) high temperatures make catalysis unnecessary. C) their enzymes have high optimal temperatures. D) their enzymes are completely insensitive to temperature. E) they use molecules other than proteins or RNAs as their main catalysts. ...
... B) high temperatures make catalysis unnecessary. C) their enzymes have high optimal temperatures. D) their enzymes are completely insensitive to temperature. E) they use molecules other than proteins or RNAs as their main catalysts. ...
Transferase-catalyses transfer of a group from one molecule to
... first. The phenomenon of one active site being activated by an event happening elsewhere in the enzyme is called allosteric activation. So enzymes subunits cooperate each other to cause the full activation of the enzyme. In order to start this activation process certain concentration of substrate i ...
... first. The phenomenon of one active site being activated by an event happening elsewhere in the enzyme is called allosteric activation. So enzymes subunits cooperate each other to cause the full activation of the enzyme. In order to start this activation process certain concentration of substrate i ...
universally valid preconditions of the biochemistry of living matter
... g) The three physical states also appear to be the minimum requirements for the ongoing biochemical reactions to run smoothly as series of reactions within BP. In practice biochemical reactions exists in one varying chemical reaction combination, with physical changes within the three existing/avail ...
... g) The three physical states also appear to be the minimum requirements for the ongoing biochemical reactions to run smoothly as series of reactions within BP. In practice biochemical reactions exists in one varying chemical reaction combination, with physical changes within the three existing/avail ...
Why Biomedical? Common Medical Issues Seen in Clinical Practice Treating Autism Conference
... Autism is a behaviorally defined neurodevelopmental disorder usually diagnosed in early childhood that is characterized by impairment in reciprocal communication and speech, speech, repetitive behaviors, and social withdrawal. Although both genetic and environmental factors are thought to be involve ...
... Autism is a behaviorally defined neurodevelopmental disorder usually diagnosed in early childhood that is characterized by impairment in reciprocal communication and speech, speech, repetitive behaviors, and social withdrawal. Although both genetic and environmental factors are thought to be involve ...
Click here
... Substrates need a lot of potential energy to reach a transition state, which then decays into products. The enzyme stabilizes the transition state, reducing the energy needed to form products. As all catalysts, enzymes do not alter the position of the chemical equilibrium of the reaction. Usually, i ...
... Substrates need a lot of potential energy to reach a transition state, which then decays into products. The enzyme stabilizes the transition state, reducing the energy needed to form products. As all catalysts, enzymes do not alter the position of the chemical equilibrium of the reaction. Usually, i ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI
... activity of hexosaminidase A. III. Complete the following: (5 x 1 = 5 marks) (11) Enzyme regulation by phosphorylation is known as ________ modification. (12) ________ is the number ber of moles of substrate converted to product per unit time. (13) ________ cloning is used to screen for microbial en ...
... activity of hexosaminidase A. III. Complete the following: (5 x 1 = 5 marks) (11) Enzyme regulation by phosphorylation is known as ________ modification. (12) ________ is the number ber of moles of substrate converted to product per unit time. (13) ________ cloning is used to screen for microbial en ...
+ Enzyme Inhibitors
... Lethal illness can be caused by the malfunction of just one type of enzyme out of the thousands of types present in our bodies. E.g., the disease phenylketonuria (PKU) results from a mutation of a single amino acid in the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase, which catalyzes the first step in the degrad ...
... Lethal illness can be caused by the malfunction of just one type of enzyme out of the thousands of types present in our bodies. E.g., the disease phenylketonuria (PKU) results from a mutation of a single amino acid in the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase, which catalyzes the first step in the degrad ...
Metabolic network modelling

Metabolic network reconstruction and simulation allows for an in-depth insight into the molecular mechanisms of a particular organism. In particular, these models correlate the genome with molecular physiology. A reconstruction breaks down metabolic pathways (such as glycolysis and the Citric acid cycle) into their respective reactions and enzymes, and analyzes them within the perspective of the entire network. In simplified terms, a reconstruction collects all of the relevant metabolic information of an organism and compiles it in a mathematical model. Validation and analysis of reconstructions can allow identification of key features of metabolism such as growth yield, resource distribution, network robustness, and gene essentiality. This knowledge can then be applied to create novel biotechnology.In general, the process to build a reconstruction is as follows: Draft a reconstruction Refine the model Convert model into a mathematical/computational representation Evaluate and debug model through experimentation↑