Bypassing V1: a direct geniculate input to area MT
... of higher extrastriate cortical areas. Historically, these regions were defined as ‘higher’ because they were not thought to receive direct geniculate input. In humans, loss of V1 devastates eyesight by cutting off the flow of visual information from the LGN to extrastriate visual cortex. Curiously, ...
... of higher extrastriate cortical areas. Historically, these regions were defined as ‘higher’ because they were not thought to receive direct geniculate input. In humans, loss of V1 devastates eyesight by cutting off the flow of visual information from the LGN to extrastriate visual cortex. Curiously, ...
1 - Institut Jean Nicod
... The mode M of an experience determines that (if all goes well) a certain relation RM, determined by the mode, holds between the subject of the experience (S) and what the experience represents (its content p). The subject undergoing an experience M(p) is therefore entitled to proceed as if he or she ...
... The mode M of an experience determines that (if all goes well) a certain relation RM, determined by the mode, holds between the subject of the experience (S) and what the experience represents (its content p). The subject undergoing an experience M(p) is therefore entitled to proceed as if he or she ...
Visual Literacy + Composition Elements, Composition, Form
... Visual Literacy Donis A. Dondis Verbal Literacy capable of reading and writing clear understandable prose, correctly spelled + syntactically sound operative at many levels Visual Literacy capable of understanding what is workable, appropriate, effective? Visual Data 1) visual input ...
... Visual Literacy Donis A. Dondis Verbal Literacy capable of reading and writing clear understandable prose, correctly spelled + syntactically sound operative at many levels Visual Literacy capable of understanding what is workable, appropriate, effective? Visual Data 1) visual input ...
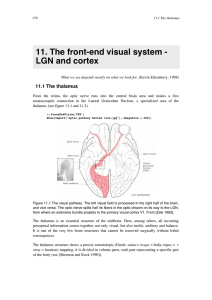
11. The front-end visual system - LGN and cortex
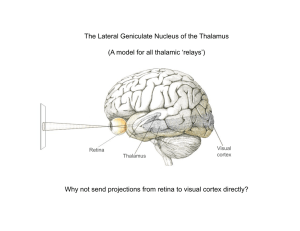
... From the retina, the optic nerve runs into the central brain area and makes a first monosynaptic connection in the Lateral Geniculate Nucleus, a specialized area of the thalamus (see figure 11.1 and 11.2). ...
... From the retina, the optic nerve runs into the central brain area and makes a first monosynaptic connection in the Lateral Geniculate Nucleus, a specialized area of the thalamus (see figure 11.1 and 11.2). ...
Layer 3
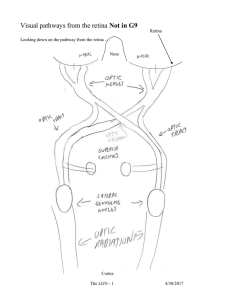
... contralateral hemisphere. RGC axons from temporal hemiretina enter the ipsilateral hemisphere. ...
... contralateral hemisphere. RGC axons from temporal hemiretina enter the ipsilateral hemisphere. ...
phys chapter 51 [3-20
... o For each orientation of line, specific neuronal cells stimulated (simple cells; found mainly in layer IV of primary visual cortex) As visual signal progresses farther away from layer IV, some neurons respond to lines oriented in same direction but not position specific (complex cells; stimulated ...
... o For each orientation of line, specific neuronal cells stimulated (simple cells; found mainly in layer IV of primary visual cortex) As visual signal progresses farther away from layer IV, some neurons respond to lines oriented in same direction but not position specific (complex cells; stimulated ...
Definitions of Visual Impairment
... development, and social interaction? Why is it important that teachers know about the types of visual impairments affecting children in their classroom? How do the educational goals and instructional methods for children with low vision differ from those for children who are ...
... development, and social interaction? Why is it important that teachers know about the types of visual impairments affecting children in their classroom? How do the educational goals and instructional methods for children with low vision differ from those for children who are ...
Visual Rhetoric - Purdue Online Writing Lab
... Color is the most basic and most critical choice you, as an author, can make: • Black text on white background shows high contrast and is the most common choice. ...
... Color is the most basic and most critical choice you, as an author, can make: • Black text on white background shows high contrast and is the most common choice. ...
Cones
... shortest distance by which 2 lines can be separated & still be perceived as 2 lines •Snellen letter charts designed so that the height of the letters in the smallest line a normal individual can read at 20 ft (6m) subtends a visual angle of 5 minutes •Jaeger’s cards test for near vision (reading) ...
... shortest distance by which 2 lines can be separated & still be perceived as 2 lines •Snellen letter charts designed so that the height of the letters in the smallest line a normal individual can read at 20 ft (6m) subtends a visual angle of 5 minutes •Jaeger’s cards test for near vision (reading) ...
Zum Thema Kategorisierung
... We can discriminate visual objects at multiple levels, from coarse categorization to individual identification. It is not known how the brain adapts to the varying levels of discrimination required in different behavioral contexts. In the present study, we investigated whether the stimulus selectivi ...
... We can discriminate visual objects at multiple levels, from coarse categorization to individual identification. It is not known how the brain adapts to the varying levels of discrimination required in different behavioral contexts. In the present study, we investigated whether the stimulus selectivi ...
Top 10 Bizarre Case Studies
... The perception of pain is highly paradoxical in nature. It’s tough to live ‘with’ and it’s tough to live ‘without’. It’s funny how an experience that seems in every respect to be so bad is, in fact, extremely important for our survival. Pain is needed because it warns us to stop engaging in potenti ...
... The perception of pain is highly paradoxical in nature. It’s tough to live ‘with’ and it’s tough to live ‘without’. It’s funny how an experience that seems in every respect to be so bad is, in fact, extremely important for our survival. Pain is needed because it warns us to stop engaging in potenti ...
What is Graphic Design?
... • “Personalities” of type – Formal and informal fonts – Consequences and font choices • Consider effect of font choice • Personality and appropriateness ...
... • “Personalities” of type – Formal and informal fonts – Consequences and font choices • Consider effect of font choice • Personality and appropriateness ...
CVI
... some days are better than others. Visual functioning can even change from hour to hour with some children. Visual field defects may also be associated with CVI due to specific neurological damage. Movement cues, especially in the peripheral fields can often stimulate a visual response. Visual in ...
... some days are better than others. Visual functioning can even change from hour to hour with some children. Visual field defects may also be associated with CVI due to specific neurological damage. Movement cues, especially in the peripheral fields can often stimulate a visual response. Visual in ...
Visual Field Defects - Northwestern Medical Review
... however, true of the visual system. Unilateral damage to the visual cortex is manifested by characteristic partial loss of vision in both eyes. Neither of the eyes is able to see the contralateral visual field with respect to the location of lesions. As we will see later this unique pattern also hol ...
... however, true of the visual system. Unilateral damage to the visual cortex is manifested by characteristic partial loss of vision in both eyes. Neither of the eyes is able to see the contralateral visual field with respect to the location of lesions. As we will see later this unique pattern also hol ...
LGN
... LGN interneurons make only local connections. There are more interneurons than relay neurons! LGN neurons get feedback connections from cortex. (The one-way connection from retina to rest of brain is unique in the visual system). LGN gets other inputs as well. For example: from brainstem and perigen ...
... LGN interneurons make only local connections. There are more interneurons than relay neurons! LGN neurons get feedback connections from cortex. (The one-way connection from retina to rest of brain is unique in the visual system). LGN gets other inputs as well. For example: from brainstem and perigen ...
Document
... Analysis of Visual Information: Role of the Association Cortex Two Streams of Visual Analysis • The outputs of the striate cortex (area V1) are sent to area V2, a region of the extrastriate cortex just adjacent to V1. As we saw in Figure 6.28, a dye for cytochrome oxidase reveals blobs in V1 and th ...
... Analysis of Visual Information: Role of the Association Cortex Two Streams of Visual Analysis • The outputs of the striate cortex (area V1) are sent to area V2, a region of the extrastriate cortex just adjacent to V1. As we saw in Figure 6.28, a dye for cytochrome oxidase reveals blobs in V1 and th ...
Perception - UBC Computer Science
... • Eye Movement • Visual Attention, Searching, and System Monitoring • Reading From the Iconic Buffer • Neural Processing, Graphemes and Tuned ...
... • Eye Movement • Visual Attention, Searching, and System Monitoring • Reading From the Iconic Buffer • Neural Processing, Graphemes and Tuned ...
single feature
... In the visual search task participants are asked to report the presence or absence of a target stimulus among various numbers of distracter stimuli. If the distracter stimuli differ by a single feature you usually find the “pop-out” effect: the RT to detect the target is independent of the numbe ...
... In the visual search task participants are asked to report the presence or absence of a target stimulus among various numbers of distracter stimuli. If the distracter stimuli differ by a single feature you usually find the “pop-out” effect: the RT to detect the target is independent of the numbe ...
Why light
... Note that layer 3 receives input from the left eye and layer 4 receives input from the right eye. Registration refers to the fact that the projections of activity in layers 3 and 4 are at the same place in their respective layers, even though the stimulation is from different eyes. That is, the acti ...
... Note that layer 3 receives input from the left eye and layer 4 receives input from the right eye. Registration refers to the fact that the projections of activity in layers 3 and 4 are at the same place in their respective layers, even though the stimulation is from different eyes. That is, the acti ...
Visual System Part 1 – Visual Perception
... • filters, decompresses and restructures the signals from the retina into a more distributed, temporally precise code • favours strong synchronous inputs, and often produces ...
... • filters, decompresses and restructures the signals from the retina into a more distributed, temporally precise code • favours strong synchronous inputs, and often produces ...
IDEA-Definition of Serious Emotional Disturbance (SED)
... • Cognition and language – Impaired or absent vision makes it difficult to see the connections between experiences ...
... • Cognition and language – Impaired or absent vision makes it difficult to see the connections between experiences ...
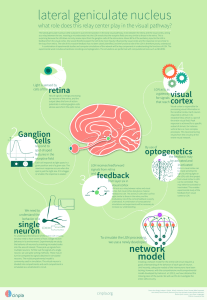
lgn - cinpla
... The lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) is placed in a prominent position in the early visual pathway. It sits between the retina and the visual cortex, acting as a relay between the two. Inserting a microelectrode into the LGN reveals that the receptive fields are very similar to those in the retina. ...
... The lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) is placed in a prominent position in the early visual pathway. It sits between the retina and the visual cortex, acting as a relay between the two. Inserting a microelectrode into the LGN reveals that the receptive fields are very similar to those in the retina. ...
From visual field to V1
... of the M and P layers. K cells are functionally and neurochemically distinct from M and P cells and provide a third channel to the visual cortex. ...
... of the M and P layers. K cells are functionally and neurochemically distinct from M and P cells and provide a third channel to the visual cortex. ...