Lecture notes
... proportion to log N • In effect, the classifier uses the nearest k feature vectors to “vote” on the class label for a new point y • for two-class problems, if we choose k to be odd (i.e., k=1, 3, 5,…) then there will never be any “ties” • Extensions: – weighted distances (if some of the features are ...
... proportion to log N • In effect, the classifier uses the nearest k feature vectors to “vote” on the class label for a new point y • for two-class problems, if we choose k to be odd (i.e., k=1, 3, 5,…) then there will never be any “ties” • Extensions: – weighted distances (if some of the features are ...
knn - MSU CSE
... • Consider N data points uniformly distributed in a pdimensional unit ball centered at origin. Consider the nn estimate at the original. The mean distance from the origin to the closest data point is: ...
... • Consider N data points uniformly distributed in a pdimensional unit ball centered at origin. Consider the nn estimate at the original. The mean distance from the origin to the closest data point is: ...
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
... • Numerous expert systems developed in 80s • Estimated $2 billion by 1988 • Japanese Fifth Generation project started in ...
... • Numerous expert systems developed in 80s • Estimated $2 billion by 1988 • Japanese Fifth Generation project started in ...
attachment=1477
... CS2032 DATA WAREHOUSING AND DATA MINING Note: 1.When u study the dwdm..study these topics and then move to some other topics wat u feel as important 2.most of the theory questions during the valuation they wil see correct definitions,key points,sub headings,presentation.... 3.Dont mugup all the poin ...
... CS2032 DATA WAREHOUSING AND DATA MINING Note: 1.When u study the dwdm..study these topics and then move to some other topics wat u feel as important 2.most of the theory questions during the valuation they wil see correct definitions,key points,sub headings,presentation.... 3.Dont mugup all the poin ...
AI-homework1-ensemble
... domain books. They use a Bayesian algorithm to statistically identify patterns in the translations. This creates a model, which can be used to create output to the user. The user may help to improve the model by submitting alternate translations. More information can be found at http://translate.goo ...
... domain books. They use a Bayesian algorithm to statistically identify patterns in the translations. This creates a model, which can be used to create output to the user. The user may help to improve the model by submitting alternate translations. More information can be found at http://translate.goo ...
MACHINE LEARNING
... • Some tasks cannot be defined well, except by examples (e.g., recognizing people). ...
... • Some tasks cannot be defined well, except by examples (e.g., recognizing people). ...
START of day 1
... instances into more general “statements” • Instead, the presented training data is simply stored and, when a new query instance is encountered, a set of similar, related instances is retrieved from memory and used to classify the new query instance • Hence, instance-based learners never form an expl ...
... instances into more general “statements” • Instead, the presented training data is simply stored and, when a new query instance is encountered, a set of similar, related instances is retrieved from memory and used to classify the new query instance • Hence, instance-based learners never form an expl ...
STAT 3610/5610 * Time Series Analysis
... Book Resources Appendix A: relevant math review Appendix B: relevant probability review Appendix C: relevant mathematical statistics review Appendices D and E: matrix algebra and linear regression in matrix form – These topics not covered in this course. Appendix F: answers to questions posed within ...
... Book Resources Appendix A: relevant math review Appendix B: relevant probability review Appendix C: relevant mathematical statistics review Appendices D and E: matrix algebra and linear regression in matrix form – These topics not covered in this course. Appendix F: answers to questions posed within ...
2013-11-18-CS10-L20-..
... You want to make a spam filter that can tell you if an email is spam or not. What might be some good features for your algorithm? ...
... You want to make a spam filter that can tell you if an email is spam or not. What might be some good features for your algorithm? ...
Applying Representation Learning for Educational Data Mining
... Other very interesting approach that won the third place [14] uses a model similar to traditional collaborative filtering, incorporating Matrix Factorization. The students are represented as users and the problems are represented as items, thus predicting if a student will resolve correctly a proble ...
... Other very interesting approach that won the third place [14] uses a model similar to traditional collaborative filtering, incorporating Matrix Factorization. The students are represented as users and the problems are represented as items, thus predicting if a student will resolve correctly a proble ...
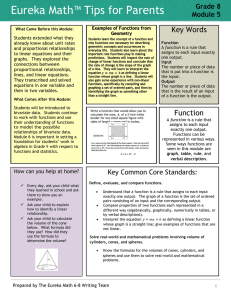
Additive Relationship
... What mathematical rule describes the relationship between the input and output values for this machine? Every input value is increased additively by five to produce the output value. The output value, y, ...
... What mathematical rule describes the relationship between the input and output values for this machine? Every input value is increased additively by five to produce the output value. The output value, y, ...
Application Identification in information
... What is the problem • How can I Identify the application class from a flow of packets? • Can I do this with sampled and summarised flow records(Netflow)? – Available in most routers – ISPs collect this as standard and often have been for many years – 25Gb per day for a 1st layer ISP (x000’s of rout ...
... What is the problem • How can I Identify the application class from a flow of packets? • Can I do this with sampled and summarised flow records(Netflow)? – Available in most routers – ISPs collect this as standard and often have been for many years – 25Gb per day for a 1st layer ISP (x000’s of rout ...